|
LOCAL
1) Media articles written by CKM member Tom Powell since the last newsletter. 01/03/2024 - Do we really need to fly? 29/03/2024 - Where does the plastic go? 27/04/2024 - We need to stick together. 25/05/2024 - Temporary rates rises? Don't count on it. 2) The big dry shuts off Wairau River water takes. This article from Maia Hart published in the Marlborough Express in March reported on discussion at the MDC March Environment and Planning Committee meeting. I attended the meeting and have put together some comments, which I've added here for those interested in the ongoing situation with the declining Wairau aquifer and the latest update from the Gravel Bed Rivers research team. Important points to note -
An update was also published by MDC on May 3rd. It is a good summary of the situation as it now stands. You can read the full statement on their website. 3) MDC Long Term Plan consultation - Consultation on the 2024-34 Long Term Plan closed on May 13th. CKM contributed a submission focusing on the big picture view as we see it, which you can download and read if interested. Here are a couple of extracts from our submission - INFRASTRUCTURE STRATEGY – We know the Plan is for the next ten year period but we note that in the Infrastructure Strategy you project expenditure for the next 30 years (page 54). Rather than attempting to project expenditure for 3 decades, which we believe is an impossible and pointless task, we propose the following –
AND We believe the overwhelming factors impacting the future of Marlborough and our planet as a whole will be environmental and climatic and it appears that the weighting of these factors in the graphs in the LTP document (pg 54) have been excluded or at the least minimalised. Why would we project infrastructure expenditure for 3 decades with the apparent assumption that life will continue as usual and that disasters such as the 2021 and 2022 extreme rainfall events were somehow unusual. It seems to us heroic or maybe wishful thinking to be projecting spending in the 2030’s to be trending downwards from the relative highs of the next five years. Likewise projecting five yearly expenditures from 2029 – 2054 as being less than the next 5 year period fascinates us. Is no one listening to the warnings of what we are to expect in the decades ahead? All those warnings tell us to expect more extreme events and that the time of living in a relatively benign climate has now passed. We do not comprehend how anyone can make financial projections about the next 10 years, let alone 30 years, without at least acknowledging the impacts of further disruptive events. 4) Marlborough to host first all-electric flights - The country’s first commercial electric plane will fly a Wellington-Marlborough cargo route for mail and parcels, Air New Zealand says. The cargo-only commercial demonstrator flights, carrying mail for NZ Post, will be up and running in 2026, using the Beta Alia plane ordered by Air New Zealand late last year. At the time they were ordered Air New Zealand hoped electric planes would be carrying passengers in the next decade. A key element of the deal to acquire smaller aircraft was to get Air New Zealand to the top of the list for more commercially viable passenger aircraft, where it was hoping to replace the 50-seater Q300 regional planes. You can check out the full article on Stuff and this media release on the MDC website. 5) The family that diverts 1000 tonnes of waste a year. Motueka couple Merv Hall and Ricarda Scherschel divert 1000 tonnes of waste a year from landfill, an impressive feat for a small business with only four full time equivalent employees. But they are not set at stopping there, and say with funding, they could help reduce Tasman’s waste by 10%. Hall and Scherschel took over Motueka’s Weka Peckers in 2020. The decision, Hall said, was “a bit of Covid thing”. The pair had been traveling back and forth between Scherschel’s native Germany, but with two young children, decided they needed a base. Passionate about environmental issues, when the business came up for sale, they grabbed it. Since then, it’s grown from a reuse shop to a larger focus on waste diversion areas - including the tricky pieces of recycling that kerbside bins won’t accept. Check out the full article in Stuff. NATIONAL 6) Recloaking Papatūānuku - Pure Advantage have made an impressive infographic available on their website outlining their vision for recloaking Papatūānuku. This is a very positive and uplifting initiative that aims to strategically reforest and restore two million hectares of indigenous forest in Aotearoa. The infographic is available to view and download from their website where they make the following statement. The Recloaking Papatūānuku infographic highlights the What, Why, How, When, Where and Who of the initiative. It shows that together, we have the tools to weave climate and ecological resilience into our whenua, and invest in the future economic and social prosperity of our country. Pure Advantage is built on a commitment to communicate professional climate and business aligned thought leadership, including support for the Ō Tātou Ngahere programme of work with Tāne’s Tree Trust and increasingly Recloaking Papatūānuku. With all the cuts and changes going on in the science community it is more important than ever for us to keep engaging with professional thought leaders and help to promote their views on the urgency and opportunities for New Zealand to respond to the challenges and opportunities we face with climate change and environment. 7) Fast-track bill could affect NZ's reputation - Transparency International. Transparency International which campaigns against corruption worldwide has expressed some valid concerns about the proposed "Fast Track" legislation. This article and short interview on the RNZ website gives more info. Resources Minister Shane Jones has reportedly asked officials for advice on whether oil and gas companies could be offered “bonds” as compensation if drilling rights offered by the present government were extinguished by any future administration. Such a move would have real implications under the government’s proposed Fast-track Approvals Bill, which is designed to “enable faster approval of infrastructure and other projects that have significant regional or national benefits”. Transparency International says the fast-tracking consent bill could taint New Zealand's international reputation. In March, the government unveiled a plan to fast-track infrastructure projects, giving just three ministers the power to greenlight significant projects. The bill, which is before a select committee, has been criticised for potentially exposing the ministers to corruption allegations. Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment Simon Upton said the role of ministers as decision-makers should be scrapped. And the auditor-general had urged that the bill included requirements for better managing conflicts of interest. Transparency International believed public perception around the fast-track bill might be improved by a sunset clause, "so that it doesn't just go on and on" and said the scope was currently "very broad", not just involving the Resource Management Act. "The bill seems to have exclusion clause for the OIA [Official Information Act] so it's not clear whether people will be able to seek information and gain it, and then there are the legal challenge rights which seem to be curtailed as well." There could be economic consequences if New Zealand's international reputation were to drop further, Haggie said. "The problem is we rely on our international reputation hugely in terms of our trading status... our mana internationally at trading tables, and generally as a good government citizen of the world... "That's really important for New Zealand to hold its head up high and be able to say its systems are clean, it's a good democracy, it's a safe place... it's running a good, fair system for doing business, and for its people in terms of participation." On the same theme this article from Jane Kelsey in The Conversation looks at the possible exposure of future NZ governments to expensive trade disputes. Last year, the UN Special Rapporteur on Human Rights and the Environment warned that governments could be liable to oil and gas corporations for US$340 billion in future disputes over fulfilling their commitments under the Paris Agreement on climate change. This is a major disincentive to ambitious climate action. States that once championed agreements containing ISDS are now withdrawing from them. This year, the European Commission proposed a coordinated EU withdrawal from the multilateral Energy Charter Treaty because energy companies are using ISDS to challenge new climate change laws and policies. The New Zealand parliament began to step back from ISDS in 2015, when NZ First MP Fletcher Tabuteau sponsored a private member’s bill “to protect New Zealand laws by prohibiting New Zealand from entering international agreements that include provision for investor-state dispute settlement”. And finally this article looks at potential impacts on NZ’s biodiversity. ....the proposed fast-tracking process leaves no time for thorough ecological surveys to assess a site’s biological diversity. It restricts consenting to just six months, which means expert panels would have to make their assessments based only on existing ecological information – known as a “desktop assessment”. None of the recent and proposed changes to environmental legislation are responsive to the dual biodiversity and climate crises. They are also inconsistent with the government’s own stated goal of evidence-based decision making. The fast-tracking agenda threatens to undermine New Zealand’s progress on biodiversity protection and other key environmental issues. It erodes rather than sustains the natural capital on which the economy depends. “These are not a replacement for on-the-ground surveys, particularly in New Zealand, where we have limited data on many species and for many parts of the country,” the authors write. 8) ELI has successfully overturned the granting of a nitrogen discharge consent to a major irrigation scheme. We all need to be thankful for the legal work that groups such as ELI (Environmental Law Initiative) do on behalf of Papatūānuku. This was an important legal challenge that may not have happened at all without ELI's efforts. The High Court has found that Environment Canterbury (ECan) unlawfully granted a resource consent for the discharge of nitrogen and other contaminants to Ashburton Lyndhurst Irrigation Ltd (ALIL). In a High Court judgment delivered on Wednesday 20 March, Justice Mander found that the decision to grant the discharge consent breached the statutory bar to consenting discharges likely to cause significant effects on aquatic life: "On the Commissioner's own findings, it appears indisputable there will likely be continuing significant adverse effects on aquatic life for the time being. I do not consider the grant of a discharge consent on the basis of the conditions imposed, albeit in anticipation that over time there will be a reduction in nitrogen leaching loads and some mitigation of the adverse effects that are likely to continue from the current activity, avoids breaching the s107(1) prohibition.” Based on this finding the judge found that the decision to grant the resource consent was based on a material error of law. ELI’s Director of Research and Legal, Matt Hall said: "This ruling is hugely significant for freshwater management, both in Canterbury and around Aotearoa New Zealand. The Court has upheld the clear prohibition on the granting of discharge consents that are likely to have significant adverse effects on aquatic life. The Court has also made it clear that where upstream discharges end up causing problems in the coastal environment, the relevant coastal policies apply." You can read more about the case on the ELI website and also access the full judgement if you are interested. 9) European court rules human rights violated by climate inaction. This appears to be a bit of landmark court case because "It comprehensively dismisses the argument that courts cannot rule on climate legal obligations because climate change is a global phenomenon or because action by one state is just a 'drop in the ocean'," This could have implications for the case taken by Mike Smith, which I included in the last newsletter. The court ruled that Switzerland had "failed to comply with its duties under the Convention concerning climate change" and that it had violated the right to respect for private and family life. It also found that "there had been critical gaps" in the country's policies to tackle climate change including failing to quantify reductions in greenhouse gases - those gases that warm Earth's atmosphere when we burn fossil fuels like oil, coal and gas. Check out the full article on the TVNZ website. This article on The Conversation website includes discussion about the possible implications of the Swiss case for the litigation that Mike Smith is taking here in NZ where he "....has sued the New Zealand government, claiming (among other things) that its inadequate emissions reductions framework breaches the rights to life and to practise culture under the Bill of Rights." 10) Ecosystems are deeply interconnected – environmental research, policy and management should be too. Below is an extract from an article in The Conversation authored by Rebecca Gladstone-Gallagher, Conrad Pilditch and Simon Francis Thrush. Why are we crossing ecological boundaries that affect Earth’s fundamental life-supporting capacity? Is it because we don’t have enough information about how ecosystems respond to change? Or are we unable, even unwilling, to use that information better? We have a lot to learn still, but as we show in our research, using current ecological knowledge more effectively could deliver substantial environmental gains. Our work focuses on improving links between research and ecosystem management to identify key trigger points for action in a framework that joins land, freshwater and sea ecosystems. Specifically, we investigate solutions to environmental and societal problems that stem from the disparities between scientific research, policy and management responses to environmental issues. We need managers and policy makers to consider ecological tipping points and how they can cascade though ecosystems from land into rivers and lakes and, ultimately, the ocean. Cyclones as a real-world example - As a result of massive soil erosion on the east coast of the North Island during Cyclone Bola in 1988, steep hillsides were retired from grazing and converted to pine plantations to help stabilise the land. Fast forward three decades and a large proportion of the forest reached harvest at the same time. The exposed soil associated with clear felling was left draped in woody debris to protect it from rain. However, Cyclone Gabrielle hit in February last year, with extreme rainfall washing both soil and woody debris into streams. This destroyed habitats, transported vast amounts of silt and wrecked lowland farms, orchards and critical infrastructure. The debris also clogged harbours and coastal beaches, smothered seafloor habitats, destroyed fisheries and affected cultural and recreational values. This real-world example demonstrates the severe consequences of lags in information flow and management responses. If land-use management decisions had considered the effects on other connected ecosystems and the potential for climate change to intensify those connections, the outcomes could have been different. We could have implemented more diverse strategies in land use and put emphasis on restoring native forest and coastal wetlands. INTERNATIONAL 11) Granting legal ‘personhood’ to nature is a growing movement – can it stem biodiversity loss? This article written by Viktoria Kahui and published in The Conversation highlights the importance of giving attention to legally defining who has liability in situations where natural objects are given legal personhood. Biodiversity is declining at rates unprecedented in human history. This suggests the ways we currently use to manage our natural environment are failing. One emerging concept focuses on giving legal rights to nature. Many Indigenous peoples have long emphasised the intrinsic value of nature. In 1972, the late University of Southern California law professor Christopher Stone proposed what then seemed like a whimsical idea: to vest legal rights in natural objects to allow a shift from an anthropocentric to an intrinsic worldview. Ecuador was the first country to enshrine rights of nature in its 2008 constitution. Since then, a growing number of countries have followed in awarding rights of nature. This includes Aotearoa New Zealand, where legal personhood was granted to the Whanganui River, the former national park Te Urewera and soon the Taranaki maunga. At its core, the rights-of-nature movement allows persons to take legal action on behalf of natural ecosystems, as opposed to on behalf of people affected by environmental degradation. Ecosystems can become separate entities with their own agency, in the same way other non-human entities such as charitable trusts and organisations can exist as separate entities in law. Liability matters - The recent overturning of two rights-of-nature decisions in particular puts the spot light on the importance of liability. In the US, farming operations challenged the Lake Erie Bill of Rights in 2020, which granted Lake Erie the right to “exist, flourish and naturally evolve”. Farmers argued the bill was too vague and would expose them to liability from fertiliser runoff. In India, the Ganges and Yamuna rivers were granted living-person status, where injury to rivers was to be treated equally to injury to human beings. The decision was challenged on the grounds of uncertainty about who the custodians are and who would be liable to pay damage to the families of those who drowned in the rivers. Both these were legally overturned, meaning these natural entities no longer have rights of nature. This suggests attention to legally defining who has liability for what may be an important building block for the movement to protect biodiversity in the future. Our recommendation is that future rights-of-nature frameworks need to have well-defined legal rights and include appointed guardians, established as separate legal entities with limited liability, as well as the support of representatives from interest groups. 12) Climate change from a wild animal's point of view: Adam Welz - I highly recommend this interview with Adam Welz, aired on RNZ on May 11th. In the interview Adam talks about his recent book titled "The End of Eden - Wild Nature in the Age of Climate Breakdown". Adam helps us to view our existence as a part of the greater miracle of life and emphasises how important it is to respect the right of all other lifeforms to coexist with us. I have tried hard to foster this in myself for many years against the constant pressure to consume more and to place our wants before the planet's needs. Are we able to change our mindset and behaviour and ensure we continue to play a part in this amazing cosmic play along with all the other lifeforms that have co-evolved with us? I live in hope that we can. 13) The Collapse Is Coming. Will Humanity Adapt? An evolutionary biologist and a science fiction writer walk into a bar... and mull over survival. Following on from the previous item here is a couple of extracts from a discussion between science fiction writer Peter Watts and evolutionary biologist Daniel Brooks. They discuss the book recently published by Daniel and his co-author Salvatore Agosta titled "A Darwinian Survival Guide - Hope for the Twenty First Century". You can read the full discussion on the MIT Press Reader website. It is fascinating and provides plenty of food for thought for those who, like me, might be "mulling over our survival". "....we should not be talking about sustainability, but about survival, in terms of humanity’s future. Sustainability has come to mean, what kind of technological fixes can we come up with that will allow us to continue to do business as usual without paying a penalty for it? As evolutionary biologists, we understand that all actions carry biological consequences. We know that relying on indefinite growth or uncontrolled growth is unsustainable in the long term, but that’s the behavior we’re seeing now. Stepping back a bit. Darwin told us in 1859 that what we had been doing for the last 10,000 or so years was not going to work. But people didn’t want to hear that message. So along came a sociologist who said, “It’s OK; I can fix Darwinism.” This guy’s name was Herbert Spencer, and he said, “I can fix Darwinism. We’ll just call it natural selection, but instead of survival of what’s-good-enough-to-survive-in-the-future, we’re going to call it survival of the fittest, and it’s whatever is best now.” Herbert Spencer was instrumental in convincing most biologists to change their perspective from “evolution is long-term survival” to “evolution is short-term adaptation.” And that was consistent with the notion of maximizing short term profits economically, maximizing your chances of being reelected, maximizing the collection plate every Sunday in the churches, and people were quite happy with this." AND "Everything that people did at any point in time seemed like a good idea at the time; it seemed to solve a problem. If it worked for a while, that was fine, and when it no longer worked, they tried to do something else. But now we seem to be at a point where our ability to survive in the short term is compromised, and what we’re saying is that our way to survive better in the short term, ironically, is now based on a better understanding of how to survive in the long run. We’re hoping that people will begin seriously thinking that our short-term well-being is best served by thinking about our long-term survival." 14) Post Carbon Institute. I've also recently come across the website of the "Post Carbon Institute", which has a view of our predicament with strong similarities to those espoused in the discussion in the previous item. So if you found the discussion between Peter and Daniel thought provoking then I recommend checking out the Post Carbon Institute website where they say -
Post Carbon Institute believes that the best way to confront this challenge is to build awareness of (a) the polycrisis, its drivers, and its trajectory, and (b) community resilience-building as an ideal response. Our specific areas of focus are:
15) Honey, I shrunk my life - Taking “degrowth” seriously. Finally on the topic of our future survival, here is a long read from Harry Flood for anyone who is wanting more on the theme of survival and the predicament in front of us. Here are a couple of extracts to give you some flavour - Of all the problems facing humanity, there’s arguably only one that really matters: how do we achieve carbon-neutrality quickly enough to save our bacon? People who haven’t just flat f...ing given up mostly count themselves as tech optimists; they believe we can science our way out of this mess – by pivoting to renewable energy, and tweaking our consumer behavior in the ways that matter most. But more and more people whose opinions count say such measures are doomed to fail. They amount to tapping the brakes, when there’s just not enough runway left for that. We need to slam on the emergency brake, as the Japanese philosopher Kohei Saito puts it – to avert environmental and social catastrophe. We’re talking about a major, really unprecedented paradigm shift. Which exposes the question under the question: Can it even be done? Is material growth inevitable? Or is it, as Wendell Berry once put it, “evitable”? AND The Franciscan monk Richard Rohr has some thoughts about a life well lived. You spend the first half of it acquiring things, and the second half giving them away. And the new space you have in the container, having got rid of your stuff, you fill with other people. If such an idea scales, we might come to think of the last century of escalating consumerism as the first half of life; it was all about acquiring power, consolidating our career, etc. And now we’re entering the second part ... a move from “I” to “we.” From building to sharing. From an ethic of power to an ethic of care. You have to take an idea like that seriously. Because the alternative is living with the dis-integration of our very souls. 16) Singing to protect nature's harmony! The Stop Ecocide team in Finland recently coordinated a 3 day program of press interviews and meetings with diplomats, politicians and eminent experts from various fields. This culminated with an amazing choral mega-concert. The "Choirs for Ecocide Law" concert was a wonderfully positive event. Lesley and I have listened to it and found it uplifting and inspiring. I love the idea of moving people's minds by moving their hearts. What a great initiative to support the cause of establishing Ecocide as a crime under international law. 3 packed days concluded with the extraordinary Choirs for Ecocide Law mega-concert on 27th April at the Helsinki Music Hall - 1000 singers and a completely sold-out auditorium! A recording of the entire glorious occasion, including the full concert and panel discussion is available on YouTube. Singing about something is a very powerful thing - especially with others. Research from the pilot Choirs for Ecocide Law project last year showed that 90% of those learning the songs said their worldview shifted… let's sing ecocide law into place! Choirs for Ecocide Law is an artistic choral project, whose main purpose is to spread awareness about the need to make large-scale environmental destruction (ecocide) an international crime. Choirs for Ecocide Law provides a sixty minute concert program, “Let us change the rules!”, ready to be rehearsed and performed by your choir – for free. The scores package includes music made by composers from different cultures, along with guidelines for an interactive rehearsal process, and with a script for bringing the concert storyline to stage. 17) Sail-powered cargo ship 'shows potential of wind' Retrofitting giant, rigid sails to a cargo ship has effectively cut its fuel use and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, shipping firm data shows. The Pyxis Ocean tested the British-designed WindWings for six months. Cargill says the data "underscores the potential" of wind to reduce the shipping industry's carbon footprint. Experts describe the results as "very encouraging", but say, at present, only a tiny volume of the international shipping fleet is using the technology. Sails have powered boats for millennia - but the type of sails trialled on the Pyxis Ocean are different to those normally seen on wind-powered vessels. Made of the same material as wind turbine blades, they are folded down in port then opened out to stand at 123ft (37.5m) on the open seas. Check out the full article on the BBC website. 18) Taxing big fossil fuel firms ‘could raise $900bn in climate finance by 2030’. A new tax on fossil fuel companies based in the world’s richest countries could raise hundreds of billions of dollars to help the most vulnerable nations cope with the escalating climate crisis, according to a report. The Climate Damages Tax report, published on April 29th, calculates that an additional tax on fossil fuel majors based in the wealthiest Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) countries could raise $720bn (£580bn) by the end of the decade. The authors say a new extraction levy could boost the loss and damage fund to help vulnerable countries cope with the worst effects of climate breakdown that was agreed at the Cop28 summit in Dubai – a hard-won victory by developing countries that they hope will signal a commitment by developed, polluting nations to provide financial support for some of the destruction already under way. Check out the full article in The Guardian. 19) Updates from James Hansen. For those who wish to keep up with the latest science observations from James and his team here are updates. Global Warming Acceleration: Hope vs Hopium Accumulating evidence supports the interpretation in our Pipeline paper: decreasing human-made aerosols increased Earth’s energy imbalance and accelerated global warming in the past decade. Climate sensitivity and aerosol forcing, physically independent quantities, were tied together by United Nations IPCC climate assessments that rely excessively on global climate models (GCMs) and fail to measure climate forcing by aerosols. IPCC’s best estimates for climate sensitivity and aerosol forcing both understate reality. Preservation of global shorelines and global climate patterns – the world humanity is adapted to – likely will require at least partly reversing global warming. Required actions and time scale are undefined. A bright future for today’s young people is still possible, but its attainment is hampered by precatory (wishful thinking) policies that do not realistically account for global energy needs and aspirations of nations with emerging economies. An alternative is needed to the GCM-dominated perspective on climate science. We will bear a heavy burden if we stand silent or meek as the world continues on its present course. Our paper, Global Warming in the Pipeline, was greeted by a few scientists, among the most active in communication with the public, with denial. Our friend Michael Mann, e.g., with a large public following, refused to concede that global warming is accelerating. We mention Mike because we know that he won’t take this notation personally. Accelerated global warming is the first significant change of global warming rate since 1970. It is important because it confirms the futility of “net zero” hopium that serves as present energy policy and because we are running short of time to avoid passing the point of no return. Check out the full March 29th update. Comments on Global Warming Acceleration, Sulfur Emissions, Observations. Global temperature (12-month mean) is still rising at 1.56°C relative to 1880-1920 in the GISS analysis through April (Fig. 1). [Robert Rohde reports that it is 1.65°C relative to 1850-1900 in the BerkeleyEarth analysis.] Global temperature is likely to continue to rise a bit for at least a month, peak this summer, and then decline as the El Nino fades toward La Nina. Acceleration of global warming is now hard to deny. The GISS 12-month temperature is now 0.36°C above the 0.18°C/decade trend line, which is 3.6 times the standard deviation (0.1°C). Confidence in global warming acceleration thus exceeds 99%, but we need to see how far temperature falls with the next La Nina before evaluating the post-2010 global warming rate. Present extreme planetary energy imbalance will limit La Nina-driven temperature decline. Thus, El Nino/La Nina average global temperature likely is about 1.5°C, suggesting that, for all practical purposes, global temperature has already reached that milestone. Temperature is temporarily well above the 50-100 percent increase that we projected (yellow region in Fig. 1) for the post-2010 warming rate. That projected increase is based on evidence that human-made aerosols and their cooling effect are in decline. In other words, we are beginning to realize the consequences of the Faustian bargain, in which humanity partly offset greenhouse gas warming with aerosol (particulate air pollution) cooling. Accurate evaluation of human-made aerosol forcing has double importance because of implications for climate sensitivity, as we have discussed elsewhere. If IPCC has underestimated aerosol forcing, they probably have also underestimated climate sensitivity. Check out the full May 16th update. 20) Russia reportedly finds vast oil and gas reserves in British Antarctic territory. Russia has reportedly found huge oil and gas reserves in British Antarctic territory, potentially leading to drilling in the protected region, according to the British publication The Telegraph and several online reports. The reserves uncovered are said to contain around 511 billion barrels worth of oil, equating to around 10 times the North Sea’s output over the last 50 years. The discovery, per Russian research ships, was revealed in evidence submitted to the British Commons Environment Audit Committee last week. The committee was assessing questions regarding oil and gas research on ships owned by the Kremlin’s Rosgeo, the largest geological exploration company in Russia. In particular, Rosgeo’s Alexander Karpinsky vessel is said to have conducted a number of surveys in the region. Check out the full article on the "Offshore" website. "Offshore" provides info to the offshore oil, gas and renewable energy industries. 21) Piloting underwater gliders into the heart of Earth's strongest current. RV Investigator set out from Hobart to investigate why the planet’s strongest current is leaking warm water into the polar seas. The Antarctic Circumpolar Current acts as a buffer between warm water to the north and the icy continent to the south. It helps keep Antarctica frozen. However, its whirling eddies and finer scale dynamics result in warm water seeping through this barrier towards Antarctica. The science team on board RV Investigator was led by the Australian Antarctic Program Partnership and CSIRO. Researchers wanted to paint a more detailed picture of these eddies and small-scale processes, to better understand the role they play in transporting heat across the current. The voyage sought to validate, for the first time, data of the Southern Ocean taken by the new Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite. SWOT is revolutionising how scientists observe Earth’s water elevation with 2 kilometres pixel, high-definition, topography. This is 10 times better than previously available. Check out the full article and excellent infographics on the CSIRO website. 22) Climate Change Is Likely to Slash Global Income. Here is more research highlighting that the cost of meeting disruptions arising from climate breakdown are far higher than the costs of making serious efforts to mitigate emissions now. It's logical of course, but unfortunately with the economic system we are addicted to, using money and resources today to improve the outcomes for our grandchildren tomorrow doesn't have a very high priority. Here's an extract from the article on the EOS website. EOS is published by AGU (Advancing Earth and Space Sciences), which is a global community supporting more than half a million advocates and professionals in the Earth and Space sciences. A new study estimates that climate change could cost $38 trillion per year, but emissions mitigation and adaptation strategies could limit future damages. Worldwide income may fall by 19% by 2049 because of changes in climate. That’s according to a new study published in Nature. Poorer countries in the tropics that have historically contributed the least to greenhouse gas emissions will experience the greatest economic burden, researchers said. The “huge” $38 trillion annual price tag of climate-related damages is 6 times greater than the cost of mitigating emissions to meet the targets in the Paris Agreement, said Anders Levermann, a climate scientist at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and one of the study’s authors. The treaty aims to limit global average temperatures to 1.5°C–2°C above preindustrial levels by 2100. 23) The Hydrogen Stream: Stadler finalizes longest hydrogen train test. Stadler says it has wrapped up a hydrogen train test, while Ballard has secured a long-term agreement to supply 1,000 hydrogen fuel cell engines through 2027. Stadler said that the FLIRT H2 has made it into the Guinness World Records database for the longest distance traveled by a pilot hydrogen fuel-cell, electric multiple-unit passenger train without refueling or recharging, covering 1,741.7 miles (2,803 kilometers). The Swiss company presented the train at InnoTrans 2022 in Berlin. “A significant number of detailed solutions were developed to integrate fuel cells and hydrogen storage systems into the modern FLIRT commuter train product line,” said Stadler. “These solutions have since been tested thoroughly, first in Switzerland and more recently on a dedicated test ring in Colorado in the United States.” Check out the full article on the PV Magazine website for other H2 developments, if you're interested. 24) Plastic-production emissions could triple to one-fifth of Earth’s carbon budget - Report. By the middle of the century, pollution from plastic industry could ‘undermine world’s effort’ to control climate crisis. The production of plastic, which is made from fossil fuels, is greenhouse gas-intensive. Coal, oil or gas must first be mined or extracted, and then those materials must be refined and processed in another emissions-heavy procedure. In some cases, other chemical compounds such as formaldehyde must also be produced, creating more pollution. Fully decarbonizing the power grid – a key focus of global climate plans – could limit this climate impact, yet would still leave the world on a perilous path. As much as 70% of the fossil fuel used in plastic creation comes from the raw materials used in production – not the electricity used in processing – the authors write. The report was released before the 4th Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC4) meeting for a global plastics treaty set to start next week in Ottawa, Canada. Neil Tangri, science and policy director at the environmental justice group Global Alliance for Incinerator Alternatives, who reviewed the report, said the findings made it clear that plastic production was a “wrecking ball for our climate” and that he hoped it would influence the forthcoming negotiations. “This report provides negotiators with the strongest scientific evidence to date on the need to stop and reverse the expansion of plastic production,” he said. Reading this article in the Guardian was a bit of an eye-opener, as I hadn't realised the GHG impacts of plastics production were quite so significant! 25) 77% of top Climate Scientists think 2.5°C of warming is coming – and they’re horrified. I know readers of this newsletter don't need reminding that we are facing a major crisis with climate breakdown and biodiversity loss, and that we don't have time to prevaricate. I've included this one article published on the Australian website "Pearls and Irritations." because I think the views expressed by a variety of climate scientists are worth sharing. Nearly 80% of top-level climate scientists expect that global temperatures will rise by at least 2.5°C by 2100, while only 6% thought the world would succeed in limiting global heating to 1.5°C above pre industrial levels, a survey published Wednesday by The Guardian revealed. Nearly three-quarters blamed world leaders’ insufficient action on a lack of political will, while 60% said that corporate interests such as fossil fuel companies were interfering with progress. “I expect a semi-dystopian future with substantial pain and suffering for the people of the Global South,” one South African scientist told The Guardian. “The world’s response to date is reprehensible—we live in an age of fools.” NASA climate scientist Peter Kalmus shared the article with a plea to “please start listening.” “Elected and corporate ‘leaders’ continue to prioritise their personal power and wealth at the cost of irreversible loss of essentially everything, even as this irreversible loss comes more and more into focus. I see this as literally a form of insanity,” Kalmus wrote, adding that “capitalism tends to elevate the worst among us into the seats of power.” However, he took issue with the idea that a future of unchecked climate change would be only “semi-dystopian.” “We’re also at risk of losing any gradual bending toward progress, and equity, and compassion, and love,” Kalmus said. “All social and cultural struggles must recognise this deep intersection with the climate struggle.”
1 Comment
LOCAL
1) Media article written by CKM member Tom Powell since the last newsletter. 03/02/2024 - Who are Climate Karanga Marlborough? Ian Allen at the Marlborough Express has invited us to contribute one article a month for their weekend edition so you will be seeing regular contributions from Tom in the future. Click on the link above to check out the first one published early in February. 2) Marlborough District Council Climate Change sub-committee. The CC sub-committee that was formed after the local body elections in 2022 finally met on January 30th. Two reports were presented at the meeting. Firstly the Emissions Inventory Report for 2022/23 which shows in detail the calculated emissions of activities that contribute to MDC’s direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions from its operations. You can read the staff report to the sub-committee and/or study the full Greenhouse Gas Inventory report from consultants WSP if interested. After the presentation of reports and some committee discussion CKM were invited to make a short presentation. I spoke to the committee and shared a couple of slides highlighting the latest report from the Stockholm Resilience Centre on the 9 identified Planetary boundaries, of which 6 have now been exceeded, and the 4 Laws of Ecology first expressed by Barry Commoner in the 1970's. Our contribution was well received and there was some useful informal discussion once the meeting was closed. You can check out my presentation if you're interested which has links to the material mentioned above. You can also read Penny Wardle’s article about the meeting published in the Express. I recommend "Earth beyond six of nine Planetary Boundaries" if you are interested in the details of the latest Planetary Boundaries report. 3) Climate Action Week - 2024. Catherine van der Muelen who is the driving force behind the Climate Action Marlborough group organised the second Climate Action Week from February 19 - 23. The program for the week covered the themes of Financing the Future for Post Growth and Impact, Transitioning to a low Carbon Emissions Economy, Energising Marlborough's Future, A bio-diverse Marlborough and Regenerative and Emerging economies. Hopefully you will have seen the comprehensive Weekend Express from February 17th which contains a "conversation about climate" between Kathryn Cannan and Marlborough Girls' College environmental prefect Alex Phelps plus a range of essays on climate and environment related topics. If you're interested in learning more about what happened over the week check out this summary put together by Tom who attended all 5 days. I managed to track down three of the essays published in the Weekend Express on the PressReader website -
4) Kelp Blue. One of the speakers on the first day of Climate Action Week was Daniel Hooft from Kelp Blue. They are a company that farms giant kelp in Namibia and are also starting farms in Akaroa Harbour and in Alaska. Daniel happened to be in Marlborough and was able to attend the first morning for a couple of hours. It was great to have the opportunity to hear about their achievements growing giant kelp and the potential it has for carbon sequestration. You can learn more about this venture from their website. "Kelp draws down more CO2 than terrestrial forests. By planting large scale Kelp Forests we can both restore the natural ocean wilderness, and capture carbon and throw away the key, keeping it locked away. As custodians of the planet we have a responsibility towards its preservation and protection. But excess human-made atmospheric CO2, the acidification of the oceans and the resulting destruction of marine ecosystems are just some of the areas where urgent action is needed to reverse the damage we have done. We believe cultivating kelp can be an important tool, together with carbon mitigation measures, to help restore planetary health. At Kelp Blue, we’re optimists and know action is possible. By planting large scale Kelp Forests we can both restore the natural ocean wilderness, and capture carbon and throw away the key, keeping it locked away forever. Kelp is one of the fastest growing organisms on the planet and can grow up to 60 cm in a day and reach lengths of up to 40 meters. To fuel this rapid growth, kelp performs photosynthesis. Through this process, carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and converted and stored (“sequestered”) into various parts of the organism (the stipe, the fronds, the bladders, the holdfast etc). Kelp continuously releases organic material, some of which is minuscule and dissolves in water, called Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC), and some larger material not able to dissolve in water. Any part of the kelp that breaks off and in size is larger than a pinhead is called Particulate Organic Carbon (POC). DOC released by the kelp is immediately consumed by microbes or is transported out to sea where it sinks to the bottom of the ocean floor. Because the bottom of the ocean is unlikely to be disturbed and has very little human contact, the risk of the carbon being released is effectively zero, it can therefore be considered “permanently sequestered” Here also is the website of a Kiwi organisation interested in seaweed farming called Blue Carbon. The "Climate Change" page on their website makes for some interesting reading. Tom Powell has also provided the following information learned during the Climate Action Week activities. One of the other benefits of kelp farming is that it raises the pH (lowers the acidity) of surrounding seawater by removing CO2 for photosynthesis. I’ve written the chemical reaction below. Remove CO2 on the right and it forces the reaction to the right, removing hydrogen ions, which constitute acid. HCO3- + H+ => H2CO3 => H2O + CO2 It may be in coming years that mussel farms will need to intercrop kelp just to allow the mussels to build healthy shells. 5) Government announce plan for Fast Track legislation. A letter was released to the public on January 31st by the Minister Responsible for RMA Reform Chris Bishop, announcing the governments intention to introduce Fast Track consenting legislation and make changes to the National Policy Statement on Freshwater. They also intend to progress changes to how the hierarchy of obligations contained in the Te Mana o te Wai provisions of the NPS-FM apply to consent applications and consent decisions. CKM are deeply concerned about the implications of these proposed changes for the environment in NZ. Don Quick wrote a response for CKM that was sent to the minister. If you are interested you might also like to read this hard-hitting response from Gary Taylor of the Environmental Defence Society. 6) Another missile launched in Government’s war on nature. This media statement released by the Environment Defense Society (EDS) is another hard-hitting statement from Gary questioning the priorities of this new government and showing what we can expect. I have to say it is alarming to see some of the quickfire decisions they are making, which appear to show a complete lack of understanding that it is the environment, good old Mother Nature, that we rely on 100% for our continued lifestyles. Taking for granted what she gives us every day is arrogant and self defeating. This latest decision is particularly applicable to us here in Marlborough where marine farming is such an important part of our local economy. Here is an extract. "The Government’s arrogant disregard for the natural world is again on display, this time threatening coastal waters and the ocean, as it plans to automatically extend the duration of all marine farm consents in the country. And it is giving stakeholders just one week to provide feedback. There are approximately 1200 marine farms in New Zealand and the proposal is to enable all of those, without exception, to continue operating for another 25 years (in addition to what they’re already consented for, which may be as long as 35 years). The extensions will be legislated for, without any substantive community input or assessment of environmental effects. “This is a preposterous proposal,” says EDS CEO Gary Taylor. “We know our seas are warming and acidifying and sites that may have been suitable for marine farming in the past will not necessarily be so in the future. We are already seeing the die-off of hundreds of salmon in the Marlborough Sounds during the warm summer months. “Aquaculture is a good way of feeding people, but it has the potential to cause significant adverse effects on marine ecosystems if located in the wrong place. In particular, farms located in shallow, low flow sites can significantly impact the water column and seabed habitats through the discharge of uneaten food, excrement and shell drop-off." 7) Marlborough Airport Ltd (MAL) public consultation - "A Sustainable Future." I reported in the last newsletter about my participation in one of several focus groups organised by MAL and MDC with the aim of trying to identify the "most important issues to foster a sustainable future, including environmental, social, economic and cultural issues." From these focus groups they identified 20 topics that they think are important to their operations now and in the future. The next step of the process was an invitation to interested people to participate in a survey which closed early in February. CKM made a group submission plus several members contributed individual submissions. These submissions challenged the dominant narrative that flying is something to be encouraged and put the idea to MAL that they should be actively discouraging unnecessary flying wherever possible if they are truly interested in a sustainable future. You can check out our group submission if you're interested to see more details. 8) Will water users from the Wairau Aquifer face their first ever cutoff this summer? CKM have had an ongoing interest in the situation with the long term decline in the Wairau Aquifer and the research trying to understand the causes of this and what might be the best ways to manage future water allocation. Here is an extract from my last report on this matter in August last year. Some limits were set when the draft Marlborough Environment Plan (pMEP) was first released in 2016 along with limits on all other rivers and aquifers in Marlborough. It is relatively simple to manage limits in rivers by measuring river flows and applying appropriate cut-offs to retain adequate flows in the rivers to meet environmental needs. As it is not possible to measure flows into the aquifer this method is not available. It can only be done by monitoring the fluctuating aquifer levels. With the Wairau aquifer being so dynamic, these fluctuations can be large in short time periods. The Wairau aquifer did have an annual maximum extraction limit set of 73,000,000 M3. The latest data on extraction indicates up to about half of that amount (about 35,000,000 M3) is currently being extracted annually depending on the season. Additional limits aiming to protect the springs were also set on three sub-zones adjacent to the springs where cut-offs apply once the aquifer drops to pre-set levels. As I’ve reported before, with the knowledge gained from the GBR research, it is now accepted that neither of these options are seen as being fair and equitable for users or adequate for optimum springs protection. In other words the hard cut-offs in the MEP are now seen as not viable. The water users in these sub-zones all objected but after discussions have agreed to accept the current limits as defined in the pMEP pending the completion of the process described in this paper. An annual allocation is also seen as too crude for managing seasonal variations. The three sub-zones referred to above are named Northern Springs, Central Springs and Urban Springs. They are all trending downwards at the moment due to the current extended dry period on top of the identified long term decline and are likely to reach the MEP limits in the next week or two without significant rain in the Wairau catchment. This would be the first time this has ever happened. If it does happens MDC have made the decision not to apply the limits this summer as the ongoing research and planning process aims to produce a new management regime before next year. There are only about 60 commercial users in the three sub-zones out of the total of about 1000 for the whole aquifer zone and placing limits on them would be unfair and not make a significant difference. As explained in my August report the new regime will likely treat all consent holders using water from the aquifer equally, but the final model has still to be decided. 9) GNS research on historic lower Wairau Plains sea levels. I reported in the November newsletter that Paul White and Martin Crundwell from GNS Science were giving a talk at the Marlborough Research Centre on December 11th. The topic was “Coastal Wairau Plain geological evolution in the last 10,000 years and what this could mean for the future.” Paul and Martin, through their research have identified where the coastline was during the Holocene about 8,000 years ago, when sea levels were roughly 1 to 1.5 metres higher than now. For anyone interested in this topic who didn't make it to the talk you can have a look at the powerpoint presentation. Slides 45 to 48 are of interest showing different historic coastlines. At 7700 years ago the coastline was roughly where SH1 currently runs between Blenheim and Tuamarina. The file is too large to include in this newsletter but if you email me I can send you a copy. 10) Earth Day 2024. The annual Earth Day will again be run by members of Envirohub with support from CKM. The date has been set for April 21st at Pollard Park on the usual site. Put it in your diary and watch out for more info about the activities being planned for the day. 11) Report says top of the south could be powered mostly by biomass. This article from Stuff is a follow up on items we've shared in the past looking at the potential for using wood as a major source of energy in Te Tauihu. 'Wood could be the next big thing powering the top of the south, a new report says. Published by the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority (EECA) on Friday, the Regional Energy Transition Accelerator (RETA) report said the forestry sector could play a key role in powering Nelson, Tasman and Marlborough in future years. The report showed that up to 72% of the top of the south’s energy needs could be met using biomass by 2037, pushing more fossil fuels out of the energy system and increasing the demand for wood residues. EECA group manager for business Nicki Sutherland said Te Tauihu was a forestry-rich area, and Nelson, Tasman and Marlborough were “well positioned” to use their resources to “bring in a clean and clever approach to industrial processing”.' NATIONAL 12) Closing Time: Why Aotearoa needs a just transition from fossil fuel production now. This Oxfam report shows that we urgently need a just transition to end production of oil, gas and coal in Aotearoa, as part of a full, fast, fair and funded global phase out of fossil fuels.
Our fossil fuel-dependent economy in Aotearoa New Zealand has been founded on the violent dispossession of tangata whenua and ongoing breaches of Te Tiriti o Waitangi. Moving beyond fossil fuels can be part of our journey to a just future from an unjust past. Oil and gas production in New Zealand is already declining at exactly the rate needed for an average share of the global phase out needed for 1.5 degrees. Doing our fair share would mean closing existing fields early. • Production from New Zealand’s currently developed oil and gas fields is projected to decline by 62% and 43% respectively by 2030. This represents a combined reduction of 48% in the annual emissions embodied in the produced fuels, which is the average global reduction in carbon dioxide emissions that the IPCC says is needed to keep global average temperature increases below 1.5 degrees. • As a developed economy, with historical responsibility for past carbon emissions and with a high capacity to transition, New Zealand needs to end fossil fuel production earlier than the global average. To contribute our fair share, New Zealand needs to close existing oil and gas fields early as part of a managed decline with a just transition. There is no way that exploring for new oil and gas fields can be consistent with the 1.5 degrees limit. The section headed "A just future from an unjust past" (page 15) talks about the "economies of mana" and gives some very good food for thought about ways we could change and adapt our economic system if we chose to. It states - "In economies of mana, people, land and resources are bound together by whakapapa, and this carries significant obligations. Manaakitanga drives escalating reciprocal exchanges of taonga and resources that create and maintain social obligations, determined and regulated by tikanga, and conducted within a web of whakapapa. In these exchanges, mana is attained by how much passes through one’s hands rather than how much accumulates in one’s hands. The focus on reciprocal exchange rather than accumulation in economies of mana makes a deep difference to how people interact with each other and with the natural world. Because economies of mana are not based on a drive for accumulation, there is not the same incentive to pursue growth at all costs. This means that economies of mana are more able to adapt when confronted with ecological and social limits. In an economy of mana, natural resources are not treated as property to be exploited, but are governed by tikanga that recognise the interconnected mana of people and nature. Similarly, rather than labour being an exploitative relationship controlled by those who have accumulated the most wealth, mahi has dignity and forms part of reciprocal relationships and collective efforts." 13) We could forecast floods better. Why don’t we? "Floods are New Zealand’s most frequent disaster, and one of the most costly. But regions have varying abilities to predict floods depending on local councils’ ability to buy weather data. And though that data is publicly funded, scientists who have created a national flood-forecasting system cannot put it into practice without free access to the same information. Should we prioritise profitability of our research institutes, or public safety?" This article in the NZ Geographic highlights another ridiculous outcome of the profit driven revolution in the 1980's and '90's that took perfectly well functioning public institutions that served the people of NZ and mandated that making a profit was their priority. Now we all pay the real price! I do wonder how some of the people who made these ideologically based decisions sleep at night? I recommend reading this article. 14) Mike Smith's court case against seven large NZ corporates. This extract from the Simpson Grierson website gives an outline of the case and the Supreme Court's decision. "After almost 18 months of deliberation, the Supreme Court has issued its landmark decision in Smith v Fonterra and has allowed all claims against a number of major corporates to proceed to trial. In finding that the Court of Appeal was wrong to strike out claims in tort against companies responsible for greenhouse gas emissions, the judgment will shape the future of climate change litigation in Aotearoa New Zealand. KEY TAKEAWAYS -
The article concludes with the statement - "Overall, the judgment will be met with enthusiasm and optimism by climate activists, not just in New Zealand but around the common law world. However, until the High Court hears full argument and evidence, the real significance of the decision, and its ramifications for corporate emitters, remains unknown. Given the number of parties and complexity of issues the High Court trial and subsequent judgment is likely to be some time away and, regardless of result, will almost certainly be the subject of appeals." You can read the full report on the Simpson Grierson website plus further info from RNZ and an article on the Stuff website. The RNZ item states - "An important feature of the case is the role of tikanga Māori, and how it determines Smith's relationship to coastal land and waters which are being flooded and damaged. The Supreme Court noted it was not ruling on whether the case had a good chance of succeeding, only that "Mr Smith now gets his day in court". Smith said he hoped the ruling would mean he would get a court date soon, but he did not know yet. "No we don't but it needs to be fast because the judgement spoke to the windown of opportunity closing fast., It's really good they picked up on that. So hopefully they'll hear the case soon on the strength of that." Smith was not seeking money, he just wanted a safer world. "It is our sacred duty to protect the future for our children and our grandchildren and the generations yet to be born. It doesn't matter what nationality they are or what ethnic culture or religion whatever, they're entitled to be on this Earth and to live safely." 15) Waitangi Tribunal to hold inquiry into climate change policy. The following statement was published earlier in February on the Voxy website. “The Crown will finally be held to account in front of the Waitangi Tribunal for its failure to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and being complicit in the destruction of our natural world and rising harm to communities across the country from climate chaos ” says Tuhi-Ao Bailey, claimant for WAI3262 on behalf of Climate Justice Taranaki. The Waitangi Tribunal has decided to hold a priority kaupapa inquiry into climate change policy. In its recent decision, the Waitangi Tribunal noted that “climate change is an existential threat not only to the claimants, but to Māori and the nation. All credible evidence points to climate change as a significant and potentially irreversible threat unless governments take urgent action. Māori have a unique and significant relationship with te taiao and the Tribunal can provide advice and guidance to the Crown as to interpretation of Treaty principles in this context.” This means that the climate change hearing will sit alongside other significant kaupapa inquiries such as the Mana Wāhine inquiry and the Constitutional kaupapa inquiry. “Together with the other claimants, we are ready to make our case in front of the Waitangi Tribunal to demonstrate how successive governments have generated inadequate climate change policy that has favoured polluting industries such as dirty dairying and oil, coal and gas mining over protecting communities and the planet. The Waitangi Tribunal noted our Toitū Taranaki 2030 plan which is a community powered strategy for a fast and just carbon neutral transition as an alternative approach to mitigation that aligns with Te Tiriti o Waitangi” says Tuhi-Ao Bailey. “With Mike Smith suing big polluters like Fonterra, Genesis Energy and Z Energy in the High Court for public nuisance and negligence for their contributions to climate change, we are now able to open another legal front in the quest to protect future generations from harm perpetuated by the crown and dirty companies. Across Aotearoa, hapū, iwi, community groups, students, workers unions and migrant organisations are mobilising and working together in the quest for climate justice. In 1854, our people in Taranaki collectively said ‘te tangata tōmua, te whenua tōmuri” – we will keep fighting to protect our land and our people. Collectively, we are upholding this legacy. Together, we rise for system change to ensure a just and peaceful future for all our tamariki and mokopuna” concludes Tuhi-Ao Bailey. 16) Five climate lessons from Māori communities (that are guaranteed not to depress you). This article from the Spinoff carries on with a focus on the role of Tikanga Māori and how it can help to guide us here in NZ, as we deal with the consequences of our actions. This extract gives plenty of food for thought. In environmental spaces, you’ll often hear the phrase “climate change is going to hit indigenous communities first and worst”. Invariably, it isn’t Māori saying it. That’s because the climate crisis isn’t imminent. Ever since the arrival of settlers and the signing of Te Tiriti o Waitangi, marae, hapū and iwi have been responding to catastrophic environmental changes caused by human activities. The only difference now is the consequences have become so widespread and severe, governments can no longer deny it is a crisis. The tendency to diagnose climate change solely by environmental symptoms – rising seas, extreme weather, drought, biodiversity loss – is a dangerous blind spot. Not only does it position the environment as the enemy, it shifts responsibility for global warming away from those who benefit from the hierarchies that privilege a few at the expense of every other living thing on the planet. These hierarchies are the same hierarchies that dispossessed Māori of their land, destroyed native forests, subjugated Māori knowledge, and created dependence where once there was sovereignty and self-sufficiency. To put it in plain language: climate change and colonisation share the same whakapapa. As Qiane Matata-Sipu, who works with Bishop and Newton in the Te Ahiwaru team, said: “We forget that the atua made us. We are the pōtiki. That’s the essence of the whakatauki ‘whatungarongaro te tangata, toitū te whenua’. We could all drop dead tomorrow and these things will thrive without us. We are the ones who need the whenua and the moana and the awa, not the other way around. That’s why it’s a bit egotistical to say we’re going to help the atua, because it’s us who need their awhi. We are the ones who need healing. Our mental wellbeing, every thread of our being, is tied into the health of te taiao.” 17) The ordinary rock we drive on holds a planet-saving secret. This is a follow up from an item I put in the January 2022 newsletter (item 20). Aspiring Materials have further developed their plan to use olivine rock, which is abundant in different places around the world including in the South Island to sequester carbon. They are making big claims about what they believe they can achieve. Below is an extract from an article on the Stuff website which gives a good outline of their work and you can also check out their website for more info. The scientists developing the process are clearly feeling very positive about the hugh potential they believe is there for sequestering large amounts of carbon. Here also is another article from the Scoop website "Olivine is found across the South Island and contains iron, silicon and magnesium – all sought-after materials. Typically, vast amounts of planet-heating carbon emissions are produced mining and refining these minerals around the globe. Now, Christchurch scientists Chris Oze and Megan Danczyk have a carbon-free way to pull them from olivine. The pair needs $10 million to build their first plant before their idea could “reverse” climate change, Oze said. But first, Oze and Danczyk will need to take the process from the lab to small-scale production. From next year, the proposed $10m pilot plant could transform one tonne of olivine per day into refined minerals – saving up to three tonnes of carbon pollution. Olivine – “the most abundant rock on Earth” – is combined with acidic liquid, and transformed into an elemental soup using renewable electricity, Danczyk said. The iron, silica and magnesium are separated and can be sold – replacing other mining operations. “People are making this stuff already… We’re just making them without carbon,” she said. “People are trying to condense carbon dioxide to have it react with the rock. We’ve done the exact opposite… we’re freeing up the magnesium to do its job naturally. It wants to react with the carbon dioxide.” A carbon-capture device could vacuum up emissions from a high-polluting factory before they leave the smokestack, or be used to bring down the amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere. The final product, magnesium carbonate – a “totally stable”, fire-retardant substance – could be used in the construction industry, Danczyk said, for example to make drywall.The team wants a zero-waste process. After the iron, silica and magnesium is removed, a “salty solution” remains, Oze said. That liquid can be split using electricity to make oxygen and hydrogen gas – two more desirable products, he added. “Everything gets recycled.” Putting everything to good use also makes the process cost-effective, he said. “If we sold all the other products – the hydrogen, the iron, the silica – … we can offer direct-air or industry carbon capture for free.” Oze and Danczyk, who both shifted from the US to Aotearoa to develop this technology, find optimism in their work’s ability to save emissions and the planet. Oze added: “The future is going to be amazing. We can’t lose sight of that.” INTERNATIONAL 18) “A Miracle Will Occur” Is Not Sensible Climate Policy. In our last newsletter I had an item about the "Warming in the pipeline" paper from James Hansen (Item 25). This info below is a follow up from James published in December. Here is the first paragraph of this paper titled “A Miracle Will Occur” Is Not Sensible Climate Policy". 'The COP28 Chairman and the United Nations Secretary General say that the goal to keep global warming below 1.5°C is alive, albeit barely, implying that the looser goal of the 2015 Paris Agreement (to keep warming well below 2°C) is still viable. We find that even the 2°C goal is dead if policy is limited to emission reductions and plausible CO2 removal. IPCC (the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, which advises the UN) has understated global warming in the pipeline and understated fossil fuel emissions in the pipeline via lack of realism in the Integrated Assessment Models that IPCC uses for climate projections. Wishful thinking as a policy approach must be replaced by transparent climate analysis, knowledge of the forcings that drive climate change, and realistic assessment of policy options. The next several years provide a narrow window of time to define actions that could still achieve a bright future for today’s young people. We owe young people the knowledge and the tools to continually assess the situation and devise and adjust the course of action.' In the blog James and his colleagues give a good outline of the science laid out in the "Warming in the pipeline" paper. As usual for his blogs it is technical but I believe very significant for those who wish to delve into the science. The most significant new information analysed in the paper is related to a decision made by the International Maritime Organization (IMO). "Separating cloud feedbacks from aerosol induced cloud changes might be a Sisyphean task, if not for the “experiment” initiated by the (IMO) when it placed a constraint on sulfur content of ship fuels beginning January 2015 and tightened it in January 2020. The IMO experiment and implications. The most informative diagnostic for interpretation of the IMO aerosol experiment is change of absorbed solar radiation. Earth radiation budget data are acquired by CERES 16 (Clouds and Earth’s Radiant Energy System) launched early this century. CERES measures solar radiation reflected by Earth and thermal (heat) radiation emitted by Earth. Reflected solar radiation declines coincident with imposition of the IMO sulfur rules. We graph the increase of absorbed solar radiation (Fig. 2); it reveals a decrease of Earth’ albedo (reflectivity) of 0.4% (1.37/340). This reduced albedo is a BFD (a big deal). It is equivalent to a sudden increase of atmospheric CO2 from 420 ppm to 525 ppm. This large change of Earth’s albedo accelerates global warming. We will infer that most of the increased absorption of solar energy following the IMO rule change is aerosol forcing. This added forcing also spurs “fast” feedbacks, which come into play not in immediate and direct response to the forcing, but in response to global temperature change, which lags the forcing." This further extract from his blog outlines what he believes is needed to address the serious nature of the position we are now in regarding the growing Earth Energy Imbalance (EEI). You will note it includes the controversial use of "modern nuclear power". This is a reflection of just how serious James sees the crisis we are faced with.
None of the three fundamental policy actions are presently occurring. Nor are they even on the agenda of the COP (UN Conference of the Parties) meetings. Our ex-student and research scientist, Surabi Menon, now a staff member of ClimateWorks on leave of absence to work six months for COP28, tried to get me on the agenda there. Unsurprisingly, given the Pipeline message that I would have been carrying, she did not succeed. On page 13 of the blog there is reference to significant differences between the general IPCC views, some climate scientists (Zeke Hausfather, Johan Rockstrom and Michael Mann) and James and his team. Those differences indicate that when James tried to speak to their paper at COP28 he was not accepted as a speaker. It is normal for most people to think the mainstream conclusions are more likely to be correct. My inclination is to go with the outlier views. History shows that they are often closer to the truth. Here is a comment from James in the blog to finish with. "Why am I optimistic about the possibility of a happy ending to the climate crisis? Mainly because of all the bright young people who can understand what is needed and are willing to work to make it happen. Young people can see and understand that the old geezers running the world are geoengineering the planet to destruction." This article from the Conversation about the difference in views between Mann and Hansen is worth a read if you're interested in their different perspectives. It is written by two scientists Robert Chris from The Open University and Hugh Hunt from University of Cambridge and they say - "We are scientists who study the feasibility and effectiveness of alternative responses to climate change, addressing both the engineering and political realities of enabling change at the scale and speed necessary. We find Mann’s rebuttal of Hansen’s claims unconvincing. Crucially, Mann does not engage directly with Hansen’s analysis of new data covering the last 65 million years. Hansen explains how the models used by IPCC scientists to assess future climate scenarios have significantly underestimated the warming effect of increased greenhouse gas emissions, the cooling effect of aerosols and how long the climate takes to respond to these changes. Besides greenhouse gases, humanity also emits aerosols. These are tiny particles comprising a wide range of chemicals. Some, such as the sulphur dioxide emitted when coal and oil are burned, offset the warming from greenhouse gases by reflecting sunlight back to space. Others, such as soot, have the opposite effect and add to warming. The cooling aerosols dominate by a large margin. Hansen projects that in coming months, lower levels of aerosol pollution from shipping will cause warming of as much as 0.5°C more than IPCC models have predicted. This will take global warming close to 2°C as early as next year, although it is likely then to fall slightly as the present El Niño wanes. Underpinning Hansen’s argument is his conviction that the climate is more sensitive to greenhouse gases than previously reported. The IPCC estimates that doubling atmospheric CO₂ raises Earth’s temperature by 3°C. Hansen calculates it to be 4.8°C. This, and the much longer climate response time that Hansen calculates from the historical record, would have a significant impact on climate model projections." James has published two more blogs in January both of which provide further concerning information. The first is titled "Groundhog Day. Another Gobsmackingly Bananas Month. What’s Up?" The abstract states - "December was the 7th consecutive month of record-shattering global temperature, driven by the combination of a moderately strong El Nino and a large decrease of Earth’s albedo. The El Nino will fade in the next few months, but we anticipate that the string of record monthly temperatures will continue to a total of 12 and possibly 13 months because of Earth’s unprecedented energy imbalance. By May the 12-month running-mean global temperature relative to 1880-1920 should be +1.6-1.7°C and not fall below +1.4 ± 0.1°C during the next La Nina minimum. Thus, given the planetary energy imbalance, it will be clear that the 1.5°C ceiling has been passed for all practical purposes." 19) Here’s a question Cop28 won’t address: why are billionaires blocking action to save the planet? This article in the Guardian by George Monbiot, was published before COP 28 and shines a light on the huge inequality on our planet with a very big proportion of the resources and finance being controlled by a very small number of people. The final paragraph in this extract is one I'm 100% in agreement with. I believe that until we can collectively face this extreme imbalance and rectify it we have no chance of seriously making the big changes that have to happen if we are to maintain a viable life-supporting biosphere. "But we cannot discount the possibility that some of these people really don’t care, even about their own children. There are two convergent forces here: first, many of those who rise to positions of great economic or political power have personality disorders, particularly narcissism or psychopathy. These disorders are often the driving forces behind their ambition, and the means by which they overcome obstacles to the acquisition of wealth and power – such as guilt about their treatment of others – which would deter other people from achieving such dominance. The second factor is that once great wealth has been acquired, it seems to reinforce these tendencies, inhibiting connection, affection and contrition. Money buys isolation. It allows people to wall themselves off from others, in their mansions, yachts and private jets, not just physically but also cognitively, stifling awareness of their social and environmental impacts, shutting out other people’s concerns and challenges. Great wealth encourages a sense of entitlement and egotism. It seems to suppress trust, empathy and generosity. Affluence also appears to diminish people’s interest in looking after their own children. If any other condition generated these symptoms, we would call it a mental illness. Perhaps this is how extreme wealth should be classified. So the fight against environmental breakdown is not and has never been just a fight against environmental breakdown. It is also a fight against the great maldistribution of wealth and power that blights every aspect of life on planet Earth. Billionaires – even the more enlightened ones – are bad for us. We cannot afford to keep them." 20) Richest 1% bag nearly twice as much wealth as the rest of the world put together over the past two years. This Oxfam media release from January contains some pretty astounding statistics, as a follow on from the previous item, and confirms the urgent needed to redress this unjustifiable imbalance for the sake of all life forms on our beautiful planet. It identifies how that imbalance grew even larger over the Covid period. "Billionaire fortunes are increasing by US$2.7 billion (NZ$4.2 billion) a day even as at least 1.7 billion workers now live in countries where inflation is outpacing wages. A tax of up to 5 percent on the world’s multi-millionaires and billionaires could raise US$1.7 trillion a year, enough to lift 2 billion people out of poverty. The richest 1 percent grabbed nearly two-thirds of all new wealth worth US$42 trillion created since 2020, almost twice as much money as the bottom 99 percent of the world’s population, reveals a new Oxfam report. During the past decade, the richest 1 percent had captured around half of all new wealth." 21) The new ‘scramble for Africa’: how a UAE sheikh quietly made carbon deals for forests bigger than UK. This is a very interesting article which raises some important questions around the use of carbon credits and their validity as a way of trying to reduce GHG emissions. I struggle with the whole idea of forests being used to offset carbon. We've destroyed so much forest over the centuries that used to be an important part of the natural planetary carbon cycle. How can we claim that existing and regenerating forests are offsetting fossil fuels emissions when millions of hectares of forests need to be regenerated just to replace what has been destroyed. To suggest we can offset the carbon emission from fossil fuels that is from forests that grew millions of years ago when we haven't even replaced what we've destroyed over the last few centuries is magical thinking in my opinion. For some time now I've also had this big question in my mind about countries claiming they will meet their Paris commitments by buying credits from other countries. NZ is a prime example. The thing that has bothered me is no one says who these other mythical countries are that are going to have so many excess credits above their own commitments, that they will be able to come to the rescue of rich countries like us. In this article I was interested to note that it appears some African countries will sell credits to get desperately needed funds and then not be able to meet their own Paris commitments. They will only succeed in pushing indigenous people off their traditional lands, which seems very much like another colonial land grab. Have a read of the article and decide for yourself if this seems like a fair way to address the whole emissions problem. This extract from the article highlights my concern. "David Obura, founding director of Cordio east Africa and head of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), said: “Carbon is one of the only contributions from nature to people that is easily monetised. So, it means that all those (contributions from nature) that are not monetised get excluded or forgotten about. There are such high risks of exclusivity and obtaining access and rights away from people.” 22) Greenhouse gas emissions soar – with China, US and India most at fault. Satellite tracking data shows many countries and firms do not provide accurate figures. I believe information like this is important for people to see and think about. The use of satellite data to identify real gains or losses with emissions is a great use of technology. It is perfectly understandable for people to want to believe that renewable energy, etc are turning the tide on GHG emissions but I personally believe that a lot of what passes as evidence for emissions reductions is too often due to creative accounting rather than actual emissions reductions. We have a very simple way of checking. The inexorable rise in CO2 levels in our atmosphere is the final evidence of which direction we are going in. The trajectory keeps increasing - until that trajectory starts flattening out I take announcements of emission reductions with a grain of salt. Basic maths tells me that if reductions are achieved in one area but cancelled out by some new development elsewhere then the CO2 curve will keep getting steeper with all the consequences that entails. 'Electricity generation in China and India, and oil and gas production in the US, have produced the biggest increases in global greenhouse gas emissions since 2015, when the Paris climate agreement was signed, new data has shown. Emissions of methane, a greenhouse gas 80 times more powerful than carbon dioxide, have also risen, despite more than 100 countries signing up to a pledge to reduce the gas, according to data published on Sunday by the Climate Trace project. The data shows that countries and companies are failing to report their emissions accurately, despite obligations to do so under the Paris agreement. At the core of the Cop28 UN climate summit in Dubai is a process known as the “global stocktake” – an assessment of progress towards meeting the emissions cuts needed to stay within the 1.5C limit. Many countries, however, have failed to make updates. Gavin McCormick, a co-founder of Climate Trace and executive director of environmental nonprofit WattTime, said: “By harnessing the power of AI and machine learning paired with the right data from satellites and beyond, our models are giving us a picture of the world we’ve never seen before. And it’s allowing us to make climate progress in a way some never believed possible.” There was also good news. Deforestation is dropping in key regions, with emissions from the degradation and destruction of forests in the Congo Basin dropping by up to 19% in 2022, compared with the previous year.' 23) Giant batteries drain economics of gas power plants. This article has something positive to say about the disruption to using gas-fired peaker power plants, that giant batteries are having in some parts of the world. It does bother me a little that there is no mention of the issues around supply of critical minerals required for large scale battery uptake, that I have included in previous newsletters. I'm wary when it appears people might be making assumptions that good old Mother Nature will be able keep supplying an endless amount of whatever we think we need. "Giant batteries that ensure stable power supply by offsetting intermittent renewable supplies are becoming cheap enough to make developers abandon scores of projects for gas-fired generation world-wide. The long-term economics of gas-fired plants, used in Europe and some parts of the United States primarily to compensate for the intermittent nature of wind and solar power, are changing quickly, according to Reuters' interviews with more than a dozen power plant developers, project finance bankers, analysts and consultants. They said some battery operators are already supplying back-up power to grids at a price competitive with gas power plants, meaning gas will be used less. Electric vehicles are a further disrupter as they can be charged when demand is weak and then power homes or send power back to the grid during peak demand periods. A typical EV sits parked 90% of the time with a battery capable of storing enough energy to power the average modern home for two days, energy software platform Kaluza said in a report published in December. In Europe, 40 million electric vehicles are expected by 2030, capable of displacing around one third of the region's gas power capacity, according to Kaluza. "There are lots of things the grid can look to when it starts to look away from conventional generation," Carlton's Clarke said." Summary -
24) Humanity declares war on its children. This article from the Pearls and Irritations website is hard-hitting and judging by the small number of signatures in support is not seen by many as an important issue. I signed it because it rings true for me. Here is an extract - "If climate were the world’s only problem, this would be bad enough. But there are nine other major risks to human civilisation. Together they add up to the greatest threat humans have ever faced in three million years of our existence. These threats cannot be separated, or dealt with singly. Some of them are even deadlier in impact than climate, though they receive much less publicity. And, in many cases, industry, wealth and governments now work hand-in-glove to make them worse. One answer, for all those who do not wish to be destroyed by this evil confederation, is an Earth System Treaty, a global legal agreement signed and ratified by all the decent people and countries left on Earth to save a habitable planet for our children. An agreement with the power to rein in the wreckers, state or corporate. The reasons for such a treaty are many – but one thing is clear: without global agreement to overcome our existential crisis, nothing can prevent it. The petrolobby and its puppets will see to that. Thanks to their continued sabotage of the last, best hope for humanity exemplified at COP27 and COP28 it is clear that the petrolobby is willing to sacrifice a habitable Earth and its young people to their ungoverned lust for short-term riches. Riches that will vanish as soon as the global economy collapses. Now is the time for all good citizens of Earth to stand together, speak out and act to prevent the ruin of our world. The people who are causing it must be brought to justice for crimes against humanity." You can check out the Earth System Treaty and watch a short youtube clip about it if interested - 25) Changing climate casts a shadow over the future of the Panama Canal – and global trade. Isn't it ironic that oil tankers are being held up from passing through the Panama Canal due to climate change induced reduced rainfall! To quote from this Guardian article - "The canal authority says it is “implementing operational and planning procedures, innovative technologies, and long-term investments to mitigate [the] impact and safeguard [the canal’s] operation”. It says that the current situation is unprecedented and it “could not have predicted exactly when the water shortage would occur to the degree that we are experiencing now”. But while the authority says it could not have predicted the crisis, others did. For years, experts have warned that the changing climate will have far-reaching effects on global supply chains and the systems that govern them. Structures like the Panama Canal are miracles of the modern world – solid totems of engineering wonder that were responsible for accelerating the economic boom of the 20th century, pulling up living standards across the globe and ushering in a revolution in technology, healthcare and consumer culture. The tacit implication was that the natural world had been tamed. But as the seas rise and temperatures soar, those assumptions are falling like dominoes." There is hope that things will improve when the wet season is due to start in the next month or two. I also note in a recent update that the Canal Authority was receiving increasing demand for transits through the waterway due to the crisis in the Red Sea, but they say changes to transit restrictions will depend on water availability which has restricted the canal from accommodating rerouted traffic. 26) "Where is everybody?": The Fermi Paradox, the Drake Equation, and climate change. This is a worthwhile read from the Climate Brink website which looks at the question "Where is everybody", asked by the famous scientist Enrico Fermi. This is in relation to the likelihood of other forms of intelligent life being out there somewhere. The conclusion the author reaches might well be close to the mark? "Thus, one plausible answer to Fermi’s question, “Where are they,” is that their own stupidity and greed killed them. It’s conceivable that climate change is a threat that most civilizations need to deal with. Advanced civilizations civilizations inherently require energy, which initially might be sourced from the combustion of carbon-based materials. That would lead to the emission of greenhouse gases, which would lead to climate change. So perhaps, in climate change, we’re facing the same test that most or all advanced civilizations need to pass. But climate change is just one challenge. We also need to deal with threats of nuclear war, pandemics, economists, and many potential disasters, all of which could knock humanity off its pedestal. If we fail any of those tests, then some future alien society might one day wonder where we are." 27) Genomic evidence for West Antarctic Ice Sheet collapse during the Last Interglacial. This study was a fascinating and innovative way to confirm the last major collapse of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. If their conclusions are correct this is more sobering confirmation of the difficult consequences our grandchildren and their grandchildren will be dealing with. "How the West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) responded to warmer climates in the geologic past has obvious relevance to our understanding of what its future could be as global temperatures rise due to human activities. Using genetic analyses of a type of circum-Antarctic octopus, Pareledone turqueti, Lau et al. showed that the WAIS collapsed completely during the last interglacial period, when global sea levels were 5 to 10 meters higher than today and global average temperatures were only about 1°C warmer. The implication of this finding is that major WAIS collapse and the consequent rise in sea level could be caused even by the minimal temperature rises projected for stringent climate change mitigation. —H. Jesse Smith Abstract The marine-based West Antarctic Ice Sheet (WAIS) is considered vulnerable to irreversible collapse under future climate trajectories, and its tipping point may lie within the mitigated warming scenarios of 1.5° to 2°C of the United Nations Paris Agreement. Knowledge of ice loss during similarly warm past climates could resolve this uncertainty, including the Last Interglacial when global sea levels were 5 to 10 meters higher than today and global average temperatures were 0.5° to 1.5°C warmer than preindustrial levels. Using a panel of genome-wide, single-nucleotide polymorphisms of a circum-Antarctic octopus, we show persistent, historic signals of gene flow only possible with complete WAIS collapse. Our results provide the first empirical evidence that the tipping point of WAIS loss could be reached even under stringent climate mitigation scenarios." These two articles from CBS News and from the Smithsonian Magazine provide more info. The scientific paper can also be purchased if you're interested. 28) Video shows research ship's "incredibly lucky" encounter with world's largest iceberg as it drifts out of Antarctica. Check out the drone video footage which is linked to the CBS article. It's an impressive iceberg! 29) Human Behavioural crisis at root of climate breakdown say scientists. This is a follow up to the final item in our last newsletter in November. The question of how irrational human behaviour is driving the climate and biodiversity crises and how we might change that human behaviour is an area of research that I personally find fascinating. That this work is being undertaken by the Merz Institute, which is a Kiwi company is encouraging and wonderful to see. I'm interested to note on their website that Mike Joy and Simon Michaux are two of the Institute's Trustees. Their Mission statement says - "Age Quod Necesse Est' literally translates to 'Do What Is Necessary'. Our broad mission ensures our continual relevance in a world where the only constant is change." Below is an extract from an article printed in the Guardian in January. The team calls for more interdisciplinary research into what they have dubbed the “human behavioural crisis” and concerted efforts to redefine our social norms and desires that are driving overconsumption. When asked about the ethics of such a campaign, Merz and Barnard point out that corporations fight for consumers’ attention every second of every day. “Is it ethical to exploit our psychology to benefit an economic system destroying the planet?” asks Barnard. “Creativity and innovation are driving overconsumption. The system is driving us to suicide. It’s conquest, entitlement, misogyny, arrogance and it comes in a fetid package driving us to the abyss.” The team is adamant that solutions that do not tackle the underlying drivers of our growth-based economies will only exacerbate the overshoot crisis. “Everything we know and love is at stake,” says Barnard. “A habitable planet and a peaceful civilisation both have value, and we need to be conscious about using tools in ethical and justice-based ways. This is not just about humanity. This is about every other species on this planet. This is about the future generations.” “I do get frustrated that people sit in paralysis thinking, what do I do? Or what must we do? There are moral hazards everywhere. We have to choose how to intervene to keep us working on a path forward as humanity, because everything right now is set up to strip us of our humanity.” 30) In memory of Barry Commoner. Barry Commoner was credited as being a founder of the modern environmental movement and was among the world’s best known ecologists in the 1960s, 70s and 80s. He was famous for his public campaigns against nuclear testing, chemical pollution and environmental decay. In 1970, Time featured Commoner on its cover, calling him “The Paul Revere of Ecology” (after the American revolutionary hero Paul Revere, who famously warned the rebel militia about approaching British forces before a decisive battle). Time said he had “probably done more than any other US scientist to speak out and awaken a sense of urgency about the declining quality of life”. The Australian "Green Left" website published an article when Barry died at 95 in 2012. In this extract from the article they give a nice clear description of his Four Laws of Ecology, which I thought it worthwhile revisiting 12 years later. "Commoner addressed the environmental crisis and humans and nature’s interaction on many different aspects: including population growth, consumer demand, politics, capitalism, greed, and other factors. He sums it up with this quote: In the book, he formulated the Four Laws of Ecology. The first of these informal laws, Everything is connected to everything else, indicates how ecosystems are complex and interconnected. This complexity and interconnectedness are not like that of the individual organism whose various organs have evolved and have been selected based on their contribution to the survival and fecundity of the whole. Nature is far more complex, variable, and considerably more resilient than the metaphor of the evolution of an individual organism suggests. An ecosystem can lose species and undergo significant transformations without collapsing. Yet, the interconnectedness of nature also means that ecological systems can experience sudden, startling catastrophes if placed under extreme stress. “The system,” Commoner writes, “is stabilized by its dynamic self-compensating properties; these same properties, if overstressed, can lead to a dramatic collapse.” Further, “the ecological system is an amplifier, so that a small perturbation in one place may have large, distant, long-delayed effects elsewhere.” The second law of ecology, Everything must go somewhere, restates a basic law of thermodynamics: in nature, there is no final waste, matter and energy are preserved, and the waste produced in one ecological process is recycled in another. For instance, a downed tree or log in an old-growth forest is a life source for numerous species and an essential part of the ecosystem. Likewise, animals excrete carbon dioxide into the air and organic compounds into the soil, which helps sustain plants upon which animals will feed. Nature knows best, the third informal law of ecology, Commoner writes, “holds that any major man-made change in a natural system is likely to be detrimental to that system.” During 5 billion years of evolution, living things developed an array of substances and reactions that together constitute the living biosphere. However, the modern petrochemical industry suddenly created thousands of new substances that did not exist in nature. Based on the same basic carbon chemistry patterns as natural compounds, these new substances enter readily into existing biochemical processes. But they do so in ways that are frequently destructive to life, leading to mutations, cancer, and many different forms of death and disease. “The absence of a particular substance from nature,” Commoner writes, “is often a sign that it is incompatible with the chemistry of life.” There is no such thing as a free lunch. The fourth informal law of ecology expresses that the exploitation of nature always carries an ecological cost. From a strict ecological standpoint, human beings are consumers more than they are producers. The second law of thermodynamics tells us that in the very process of using energy, human beings “use up” (but do not destroy) energy, in the sense that they transform it into unworkable forms. For example, in the case of an automobile, the high-grade chemical energy stored in the gasoline that fuels the car is available for useful work while the lower grade thermal energy in the automobile exhaust is not. In any transformation of energy, some of it is always degraded in this way. The ecological costs of production are, therefore, significant.  LOCAL 1) Media article written by CKM member Tom Powell since the last newsletter. 15/10/2023 - Opinion article: Technology to the Rescue 2) CKM submissions. Tom has continued putting together some excellent submissions that you can view if you are interested. Regional Hydrogen Transition submission. In this submission he said - "We have serious concerns with this program and request a change in direction. We support a subsidy for green hydrogen used in industrial processes and aviation & ship fuel but we do not support the use of green hydrogen for heavy transport. Considering its low efficiency, ready alternatives, lack of infrastructure, explosivity, limited industrial benefit and climate impact of leakage, green hydrogen for transport should not be given preferential price support." MBIE Interim Hydrogen Roadmap energy strategy submission. Review of the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme submission. A Redesigned NZ ETS Permanent Forest Category submission. MDC also recently publicised the second round of public consultation for the National Policy Statement on Freshwater Management (NPSFM). This was an opportunity to respond to the proposed values, visions and environmental outcomes as defined after the first round of consultation. Budyong put together a brief submission with an emphasis on our concern that the needs of Nature are given the highest priority when making decisions about our freshwater resource. You can check out the full submission below if interested. NPS-FM 2020 Community Engagement - round two submission. 3) Students letters to incoming Prime Minister. Climate activist group Climate Karanga Marlborough invited Marlborough school pupils to write a letter based on the theme of caring for Papatūānuku, the Earth Mother, to be sent to the incoming prime minister following the General Election. The aim was to give the citizens of tomorrow the opportunity to voice their ideas in regard to protecting the health and well-being of our environment. You can read the Stuff article about it and see two of the letters received. 4) Talk at Marlborough Research Centre (MRC). Paul White and Martin Crundwell from GNS Science are giving a talk at the Marlborough Research Centre on December 11th in the evening. The topic is “Coastal Wairau Plain geological evolution in the last 10,000 years and what this could mean for the future.” Here is an asbtract of the content of the talk. “Today’s Lower Wairau Plain (LWP) geology and geomorphology developed (mostly) during two climatic periods: the last glacial (cold) and the current interglacial (warm). This development will be described in a ‘virtual’ tour of today’s LWP geology and with new geological research that models past environments, approximately: 10,000 years ago, as sea level rose rapidly; 6,000 years ago when sea level was probably a little higher than today; and pre-European. LWP geology is a major control on numerous local resources (e.g., groundwater, soils, and rivers). The talk will conclude with geological perspectives on LWP resource futures to 2100.” When : Monday 11th December 2023, 6:30-8:00 pm Where : Marlborough Research Centre lecture theatre, Budge Street campus Blenheim Audience: Open to public – no need to register. Here also is a link to a powerpoint of some current work they are doing (some of this will be discussed in the above meeting.) In it they make a case that pre-historical (i.e., Holocene) geology is a proxy for climate-change-induced sea level rise to 2100. Lesley and I met with Paul, Martin and several of their colleagues in May after Paul had contributed to another talk at the MRC, along with James Renwick. Paul had asked to meet with CKM to talk about a project where they are planning to do some research in the Lower Wairau to do with climate change adaptation. Paul and Martin will be staying on in Marlborough for a few days after their talk and are keen to meet with us again to further discuss this research project. I’m looking for others who will be willing to participate in a meeting. Paul has suggested we could meet anytime on Thursday, Dec 14th or Friday morning, Dec 15th. He says “I’d like to discuss some research ideas that could possibly involve CKM members, if they wish.” If anyone is interested please let me know. 5) Letter to MDC Mayor regarding replacement Chief Executive. We put together a letter which we sent to the mayor. The letter was also supported by Marlborough Forest and Bird. In it we said - "We encourage you to spread your search for a new CEO wider than the places that local bodies might traditionally advertise. Marlborough needs a leader that is fully committed to supporting the transition and shift to a low carbon emissions economy where the needs of the environment are given top priority. He or she will need to inspire existing Marlborough residents and businesses and attract organisations and industry’s into our region that want to help create a thriving, diverse and most importantly, sustainable local economy. An effective CEO needs to lead by example, and show that the visions and values expressed for our region aren’t just lip-service but are core to all our local decision making." Check out our full letter if you're interested. In our letter we referred to the Headline Messages of the Dasgupta Report of 2021. Maia Hart also wrote a very good article for Stuff outlining the discussion around the Council table on this issue. Here is the response received from Nadine. Nadine also told me in conversation at the Environment and Planning Committee meeting recently that she had received a letter with a similar message from local Iwi. Tēnā korua Budyong and Helen, Thank you for writing to us and sharing your thoughts on the importance of weighting being given to environmental experience in the selection of our new Chief Executive. A view I very much agree with. As a Unitary Authority which covers the roles and responsibilities of a Regional Council as well as a Territorial Authority, our new Chief Executive will need to provide leadership across all Council functions and all areas of responsibility. To find such a CE we are undertaking a nationwide search, led by Mike Stenhouse of Shefield Consulting. Mike is currently drafting the new CE specification documents for Councillors to review, so I have forwarded your letter on to Mike for his reference. We are very aware the appointment of a new Chief Executive is not only a significant decision for Council, it is also significant for many individuals, organisations, groups and communities within Marlborough – it is a decision all Councillors will be focusing on with great care. Ngā mihi Nadine 6) Coastal Water Temperature Trends Report Card 2015 – 2023. In this report presented to the MDC Environment and Planning Committee on November 16th it states -
Check out the full report on the MDC website. It is item number 3 on the Nov 16th agenda. Here are some of my reflections after reading the sea temperature report -
Maia Hart also wrote an article published on the RNZ website about the report. This Guardian article from May 2023 provides a very good overview of the causes and implications of ocean heating. 7) Marlborough Airport (MAL) focus group. Budyong was invited to join a focus group to share his thoughts about Marlborough Airport and material issues relating to sustainability, now and into the future. The group he joined had two other local people with environmental perspectives, Bev Doole and Helen Ballinger, along with the organiser Stephanie Flores from MDC and resulted in a wide ranging discussion. If you're interested you can also read a paper Budyong submitted expressing some big picture views consistent with CKM's values. 8) Marlborough business CarbonScape is revolutionising how we produce graphite. "One Marlborough company is on the path to commercialise a sustainable graphite alternative that overseas companies can use to produce lithium-ion batteries and now a new investment will see them grow their team at home and overseas. CarbonScape is a business that uses timber and forestry industry by-products and waste to make biographite, a carbon-negative graphite product for EV and grid scale battery supply chains. They are the first to market this sustainable option and this week the company announced an US$18 million investment led by Stora Enso, a leading provider of renewable products around the world, and Amperex Technology Limited (ATL), a global lithium-ion battery producer and innovator." Check out the full article on Stuff. 9) Climate Positive grape growing. This article in the NZ Winegrower magazine looks at the efforts of the Holdaway Family, Lowlands Wines operation to grow climate positive grapes on their land in the Lower Wairau/Dillons Point area. 10) Climate Action Week 2024. Catherine van der Muelen is all fired up again organising the Climate Action Week activities for next year. It is scheduled to run from February 19 - 24. "Climate Action Week Marlborough has been designed to create awareness, develop our Marlborough business community's knowledge by embracing education, and take action towards creating a low carbon emissions, highly productive, and thriving community, no matter what stage of the journey you are at." You can check out the full week agenda and purchase tickets if you're interested. National 11) Emergency Weather. Emergency Weather is a new novel by Tim Jones and is available in bookstores nationwide. The book’s synopsis is: “Three people find themselves in Wellington as the climate crisis crashes into their lives. A giant storm is on its way – what will be left of the city when it’s over?” Tim is a member of CKM and a key person in the Coal Action Network Aotearoa. In this article in Newsroom Tim talks about his childhood in Mataura and two of the big floods he experienced there. He says "All my life, Mataura has been living in Nature’s shooting gallery. But as the climate warms and the weather gets more extreme – drier, hotter, wetter, wilder – more and more of us are in the firing line. The cyclone, fuelled by warming seas, that sweeps across your city. The forest slash that slides across the highway at just the wrong time. The exotic forest that, dry and windswept, ignites from a single spark. Beneath it all, the rising of the sea, starting slow and growing faster, raising the baseline of storms. Papatūānuku isn’t to blame. We’re in the world made by the fossil fuel companies, by industrial dairying, by the accumulation of capital at the expense of everything else. Will we act to save ourselves, like the people of Mataura acted, or will we shut our eyes and pretend the danger is not real? Emergency weather is now on every doorstep." 12) Updated forestry regulations increase council controls and require large slash removal. The outgoing government announced new regulations on October 3rd. I thought it was interesting to note that non-indigenous forests planted for carbon sequestration will now have to be managed in the same way as plantation forests. Hopefully this will survive under the new government. "Local councils will have more power to decide where new commercial forests – including carbon forests – are located, to reduce impacts on communities and the environment. New national standards give councils greater control over commercial forestry, including clear rules on harvesting practices and new requirements to remove slash from erosion-prone land." You can check out the full media release on the Beehive website. 13) Recloaking Papatūānuku: A nation-wide indigenous forest initiative. Once, New Zealand was cloaked in a rich array of indigenous forests, alive with the song of birds, and our rivers and streams ran clear. Yet, since settlement began 800 or so years ago, we have progressively removed 82% of the natural forest cover, destroying the habitat of many plant and animal species, and increasing the vulnerability of our landscapes at great cost to our economy, our biodiversity, and our future. At the same time we have introduced deliberately or by accident a multitude of invasive plant animal and fungal species that are further impacting our Indigenous biodiversity. And these impacts will only get worse with climate change. Today, we face a climate and biodiversity crisis. In 2020, Aotearoa’s Government declared a climate emergency, recognising climate change as “one of the greatest challenges of our time”. Since then, the risk of surpassing irreversible climate and ecological tipping points has continued to increase, and we are already witnessing the devastating effects of increasingly frequent and severe weather events, prompting the United Nations Secretary General to announce recently that “the era of global boiling has arrived”. Despite this alarming context, our current regulatory settings and incentives for mitigating climate change are failing to: (a) Drive urgent gross emissions reductions at source and at scale; (b) Secure enduring, biodiverse and resilient long-term carbon sinks for future generations; (c) Reverse the catastrophic decline of our indigenous flora and fauna; (d) Protect our freshwater and marine ecosystems; (e) Encourage land-use diversification over intensification; and (f) Harness opportunities to weave climate and ecosystem resilience into our landscapes and our communities. Check out the full proposal on the Pure Advantage website. 14) Methane myths come up against textbook science. I included an item (#14) in the last newsletter titled "A new paradigm shift, indeed." It was about an article published in the Rural News, which claimed that the climate impact of methane is so low as to be disregarded. The item included a rebuttal written by our own Tom Powell. We've now been informed by one of our members of another very thorough rebuttal published in the Farmers Weekly on November 6th. If you are interested in this discussion the article by Professor Dave Frame from Canterbury University is a must read. I have to say, to see Farmers Weekly publishing such a well written, informed and cogent article on this contentious topic and to know that farmers all over NZ receive this publication presenting them with such good science is encouraging. All those open minded farmers, of which I'm sure there are many, get the opportunity to make their own decisions about what is myth and what are clear well presented facts. 15) Huge insurance cost increases hit farmers. This item from the Farmers Weekly is a sobering look at one of the significant consequences of extreme weather events. What impact will this have on the viability of farming operations as we experience more of these major weather events? Insurance premiums for farmers are going up by as much as 30% after a number of very high-cost adverse weather events in the past year. FMG, which has a rural market share of about 55%, said Cyclone Gabrielle was the biggest single event in the company’s 118-year history. Dave Kibblewhite, FMG’s chief financial, investment and risk officer, said for Cyclone Gabrielle, reinsurers will be paying approximately 90% of the total claims cost of FMG clients. “Not only are these weather events from the last year the most significant in our history, but they also coincided with the hardest reinsurance market in over 40 years following a number of large global natural disaster events. “These factors have resulted in large price increases for reinsurance, in excess of 30%, and also global capacity has been reduced.” Farmers and orchardists can take small comfort in the knowledge that their premium cost increases are similar to those right across the insurance industry, and in towns and cities. Check out the full article. 16) IAG says it has paid out more than $1 billion in insurance claims for the North Island floods & Cyclone Gabrielle. New Zealand's biggest insurer is urging the incoming government to push on with natural hazard risk reduction, climate change adaptation and managed retreat work to help keep insurance available and affordable in the face of stark impacts, and rising costs, from extreme weather and natural hazards. The previous government last year released NZ's first national adaptation plan, which set out that the Ministry for the Environment and Treasury would lead a programme of work on how NZ meets the costs of climate change and invests in resilience. Banks have told a subsequent parliamentary inquiry into climate adaptation that insurance withdrawal would leave them with stark options. Check out the full article on the interest.co website. 17) Climate Action Tracker (CAT) NZ rating for climate action. I thought with a new government taking over the reins of power that it would be an appropriate time to review the current assessment for NZ on the Climate Action Tracker website. This assessment was released in March this year and a new one is due soon. As we can expect our climate policies to be watered down with the new government we can also expect our rating to get worse. Overall rating - The CAT rates New Zealand’s climate targets, policies and finance as “Highly insufficient”. The “Highly insufficient” rating indicates that New Zealand’s climate policies and commitments are not stringent enough to limit warming to 1.5°C and need substantial improvements. New Zealand’s NDC target is rated “Critically insufficient” when compared with its fair share contribution to climate action and “Insufficient” when compared to modelled domestic pathways. Its policies and action do not put it on track to meet this target and its climate finance is inadequate. New Zealand should increase both its emissions reduction target and climate policies, and provide additional, predictable, finance to others to meet its fair share contribution. Policies and action against modelled domestic pathways - New Zealand’s current policies are “Highly insufficient” when compared to modelled domestic pathways. The “Highly insufficient” rating indicates that New Zealand’s policies and action in 2030 are not at all consistent with limiting warming to 1.5°C. If all countries were to follow New Zealand’s approach, warming could reach over 3°C and up to 4°C. You can check out the full report on the CAT website. GLOBAL 18) COP-out: Why the petrostate-hosted climate talkfest will fail. "After a succession of record-breaking months of record heat including 1.8°C in September, global warming for 2023 as a whole will likely tip 1.5°C, with 2024 even hotter as the effect of the building El Nino is felt more fully. Already hundreds of thousands have died and millions displaced, primarily in countries least responsible for climate change. The annual economic cost globally is in the hundreds of billions. So what will the 28th meeting of the Conference of the Parties (COP28) of the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), starting 30 November in the United Arab Emirates (UAE), say about this? And in particular what will Sultan Al Jaber, the CEO of the UAE state oil company ADNOC, who will preside over the international negotiations, say? Probably nothing; instead there will be much blather about reaffirming the commitments at the Paris COP in 2015 “to hold the increase in global average temperature to well below 2°C, and to pursue efforts to limit the temperature increase to 1.5°C”. And lots of “net zero” posturing based on sham Integrated Assessment Models, and farcical assumptions about bodgy carbon offsets, carbon capture and storage (CCS), bioenergy with CCS, machines to draw carbon from the atmosphere, and the like. All given unwarranted credibility by the Sultan’s advisers, Mckinsey & Co. Many of the petrostates are highly dependent on fossil fuel revenue to fund their strategic ambitions, so there is every reason to believe they will pump all the oil and gas they can. So it is unsurprising that a new UN report says the world is heading towards 3°C and perhaps a good deal more, bringing down the curtains on contemporary civilisation. Eight years after Paris, the evidence is overwhelming that “net zero 2050” was always a bad target, that there is no carbon budget left, and that major system tipping points have already been passed, or are now within range in the short-term. COP28 will not produce a statement that says a word about any of this. If there is to be a modicum of truth-telling, front and centre of the COP outcome would be recognition that fossil fuel expansion is a death trap, that zero emissions fast is absolutely necessary, and that unprecedented interventions to mitigate 1.5°C climate overshoot are now required. That is the focus of another new report The Overshoot: Crossing the 1.5C threshold and finding our way back, from the Climate Crisis Advisory Group. The report again emphasises the need for a three-pronged strategy to reduce, remove and repair. In the Gulf, petrostates are now installing floodlights on beaches and encouraging night-time use because it is simply becoming too hot to use during the day. “In a city where weather that would constitute a deadly heat wave in Europe is just a typical summer day, official ‘night beaches’ have become a popular way to cool down”, reports the New York Times. Perhaps the COP delegates could adjourn for a midnight skinny dip, and experience first-hand what the future holds." Check out the full article from David Spratt and Ian Dunlop on the Pearls and Irritations website. 19) Inside the new climate assault on the oil majors. Climate litigation against American Oil Majors is being taken on by bigger legal firms in the US. Firms that have large war chests after winning cases against big pharmaceutical firms over their role in the US opioid abuse crisis. "The infernal heat that began killing people in the normally temperate north-west of the United States in June 2021 began with unusually heavy rain over China, which drove energy into the jet stream which crosses the Pacific and set off a cascading set of climatic events resulting in a heat dome that settled across parts of the US and Canada. In Multnomah County, Oregon, temperatures reached 42 degrees Celsius, 44.5 degrees and 46.6 degrees over successive days. Before that week began, the county’s record temperature was 41.6 degrees, and its average high temperature was just 21 degrees. By the time it subsided, the heat had killed 69 people. At the time an event like it was inconceivable. But due to rapid global warming, it is predicted similar heatwaves will strike the region once a decade or so. Climate litigation is increasing around the world, but the Multnomah case is attracting significant attention. How these cases will play out is not yet clear, but in April, some of the jurisdictions bringing them had a win when the US Supreme Court ruled that they should remain in state courts, where they are thought to have more chance of success than in federal courts. Kysar says the (oil) companies are drafting an “army” of lawyers to fight every case in every jurisdiction around the world because “every one of them feels like an existential threat” to the industry. In Ango-American political systems, governments are constrained from taking overarching action, he says. The trade-off is that when people are injured, courts can intervene. “That means when there’s some big social harm that’s not being addressed, people turn to the courts, and the courts have to give an answer. “You could call your MP 100 times a day and say ‘I’m worried about climate’, they might never call you back.” Cases like this one have the potential to have significant impacts on the major oil companies. Check out the full article on the Sydney Morning Herald website. 20) Ban private jets to address climate crisis, says Thomas Piketty. "Questions of social and economic class must be at the centre of our response to the climate crisis, to address the huge inequalities between the carbon footprints of the rich and poor and prevent a backlash against climate policies, the economist Thomas Piketty has said. Regulations will be needed to outlaw goods and services that have unnecessarily high greenhouse gas emissions, such as private jets, outsized vehicles, and flights over short distances, he said in an interview with the Guardian. Rich countries must also put in place progressive carbon taxes that take into account people’s incomes and how well they are able to reduce their emissions, as current policies usually fail to adjust for people’s real needs. “We have to put class and the studies of inequality between social classes right at the centre of our analyses of environmental challenges in general,” Piketty said. “If you don’t, you will just not be able to get a majority [of people in favour of strong action] and will not be able to make it.” Check out the full article. 21) EU to criminalise severe environmental harms "Comparable to Ecocide". "The EU has agreed to enshrine in law a new offence that aims to punish the most serious crimes against the environment. The final text emerged following several months of negotiation (“trilogues”) between the European Council, Commission and Parliament considering, inter alia, the establishment of a “qualified offence” aimed at preventing and punishing the gravest environmental harms including, as the accompanying recitals specify, “cases comparable to ecocide”. Check our the full report on the Ecocide website. 22) Hydrogen Leakage: A potential risk for the hydrogen economy. Here are three items to contribute to the ongoing material I've included in the last few newsletter regarding the pros and cons of hydrogen as a GHG free fuel. This first one highlights that hydrogen leaking into our atmosphere does have an indirect climate forcing. "Hydrogen is expected to play a key role in the decarbonization of the energy system. As of June 2022, more than 30 hydrogen strategies and roadmaps have been published by governments around the world. Hydrogen has been identified as a potential safety issue based on the fact that it is the smallest molecule that exists and can easily pass through materials. To date, however, very little attention has been paid to the potential contribution of hydrogen leakage to climate change, driven by hydrogen’s indirect global warming effect through mechanisms that extend the lifetime of methane and other greenhouse gases (GHG) in the atmosphere (Paulot et al. 2012; Derwent et al. 2020). A literature analysis turns up very little data on hydrogen leakage along the existing value chain, and that which does exist comes from theoretical assessments, simulation, or extrapolation rather than measures from operations. As the production methods and uses of hydrogen evolve over time, there is even less data available on what could represent key parts of the hydrogen economy going forward. In the future, leaked hydrogen will likely be concentrated in a few key processes (e.g., green hydrogen production, delivery, road transport, and chemical production). There is a risk of increased leakage rates in the future mostly because the leaking processes that will be key by 2050 do not exist at scale today. A high-risk scenario based on hydrogen demand from the International Energy Agency (IEA) net-zero scenario (528 million tons [Mt] by 2050) (IEA 2021) could potentially lead to a 5.6 percent economy-wide leakage rate, compared with an estimated 2.7 percent in 2020." Check out the full research paper for more info. 23) Plastic Waste Becomes Clean Hydrogen Goldmine. "A technique called flash joule heating at Rice University can convert plastic waste, even unsorted and unwashed, into clean hydrogen and valuable graphene. If sold at just 5% of its market value, the graphene produced could make the hydrogen essentially free, provided the process is powered by renewable energies. While green hydrogen offers significant potential for decarbonization, especially in high-heat industrial applications, its production requires vast amounts of clean energy, necessitating a balanced approach to its adoption." Tom's comments - Sounds interesting. I’ll wait to hear what the fishhooks are, though. I would imagine there would be lots of “interesting” waste products from such a process - gases and solids. Check out the full article if you want to learn more. 24) Solar energy storage breakthrough could make European households self-sufficient. "One of the biggest issues with solar energy is that it is inconsistent over days and over seasons. Many startups have focused on trying to smooth energy supply over the day — saving up energy during the day for use during the night-time or outside peak hours. But few have tackled interseasonal storage of solar energy. What if homes could save abundant solar energy created in sunny months to be used for heat and electricity in winter? So far, this vision has been impossible to achieve. Batteries are too expensive and have short lifespans, and high costs and poor efficiency have crossed hydrogen, which does not emit greenhouse gases when burned, off the list of solutions. Now, one startup from Norway — a country in a region that probably hopes it could save a little sunlight for cold winters — says it could bring a solution to market in the next couple of years, using solid hydrogen." Check out the full article on the Sifted website. 25) To Understand and Protect the Home Planet. This is the title of a blog published by James Hansen on October 27th. I have had a longtime respect for the perspectives presented by James and his willingness to present a contrary view from the IPCC reports is a reflection of his independent view. There are sure to be those who dispute the conclusions of him and his team. For readers of this newsletter who have studied reports from James Hansen before you will know that they are technical so it is just for nerds who want to get into the nitty gritty of the science. The new paper he is talking about is titled "Global Warming in the Pipeline". He says in the blog - "GLOBAL WARMING IN THE PIPELINE will be published in Oxford Open Climate Change of Oxford University Press next week. The paper describes an alternative perspective on global climate change – alternative to that of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), which provides scientific advice on climate change to the United Nations. Our paper may be read as being critical of IPCC. But we have no criticism of individual scientists, who include world-leading researchers volunteering their time to produce IPCC reports. Rather we are questioning whether the IPCC procedure and product yield the advice that the public, especially young people, need to understand and protect their home planet. Discussion of our paper will likely focus on differences between our conclusions and those of IPCC. I hope, however, that it may lead to consideration of some basic underlying matters." Here is the full blog for those interested. It is not long and gives you a good summary of the content of the paper. This YouTube video is a 43 minute discussion about the paper between James and Paul Beckwith, another climate scientist. If you are like me and really want to get down to some of the nitty gritty of why 2023 is now the hottest year in the last 100,000 years then this video is a must to listen and watch. For the real nerds the paper is available on the Oxford Open Climate Change website. Alternatively you can read a subsequent blog from James on November 10th titled "How We Know that Global Warming is Accelerating and that the Goal of the Paris Agreement is Dead", which gives a good overview of the science in the paper. 26) Hallucinatory world: Governments blind as multiple catastrophes besiege human civilisation.
The first two statements above are from two new scientific reports, issued this week – one from the United Nations and another from the same group of 15,000 scientists who gave us the world climate warning in 2020. Yet governments globally didn’t bat an eyelid. It was as if they do not occupy the same planet as the rest of us, but some hallucinatory world where everything is fine." You can read the full article on the Pearls and Irritations website. FUTURE OPTIONS? I have added an extra section to this newsletter. It is focussed on discussion about alternatives to the dominant Capitalist Growth economy. I think this quote from Donella Meadows, one of the original authors of the 1972 "Limits to Growth" report says it all really. 26) "Beyond Growth" Conference. I participated (online) in an excellent conference held in Wellington over the weekend of September 16/17. The topic was "Beyond Growth" and the people from the "Degrowth NZ" group who organised it put together some thoroughly interesting and stimulating sessions with some excellent speakers. All the sessions are available on their YouTube channel. I recommend the opening talk from Sahra Kress. The first session "Beyond Growth - what can we learn from the International Movement?" was good value, in particular the contributions from Mike Joy (session 1.3) and Timothee Parrique (1.2). Also the session with Prof Jonathon Boston (3.2). The afternoon session "How do we mainstream degrowth in NZ" is worth checking out. It was very interesting to hear the views of the three business people involved as it was clear they consider the current economic model is not sustainable. (sessions 4.1 - 4.5.) Others worthwhile sessions were the presentations by Nate Hagens (1.1) and Rick Williment (5.1). There is plenty of other good stuff to explore if you're interested in the topic. 27) Reconsidering our Economic System. Dr Catherine Knight also did a session (3.1) at the Beyond Growth conference. This RNZ interview with her is worth a listen. 28) Vaclav Smil: ‘Growth must end. Our economist friends don’t seem to realise that’. I recommend this interview between Jonathon Watts and the author Vaclav Smil about his latest book "Growth: From Microorganisms to Megacities." – an epic, multidisciplinary analysis of growth – and why humanity’s endless expansion must stop. Here is his first question - "You are the nerd’s nerd. There is perhaps no other academic who paints pictures with numbers like you. You dug up the astonishing statistic that China has poured more cement every three years since 2003 than the US managed in the entire 20th century. You calculated that in 2000, the dry mass of all the humans in the world was 125m metric tonnes compared with just 10m tonnes for all wild vertebrates. And now you explore patterns of growth, from the healthy development of forests and brains to the unhealthy increase in obesity and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. Before we get into those deeper issues, can I ask if you see yourself as a nerd?" Check out the full Guardian article. 29) Critics of ‘degrowth’ economics say it’s unworkable – but from an ecologist’s perspective, it’s inevitable. This article by Mike Joy with input by Jack Santa Barbara provides an excellent, well explained description of the state of overshoot humanity has created - "The climate crisis is seen as a problem requiring a solution rather than a symptom of overshoot. The problem is generally formulated as looking for a way to maintain current lifestyles in the wealthy world, rather than reducing overshoot. The ecological perspective accepts that we exceed biophysical boundaries and emphasises the importance of reducing energy and material consumption – regardless of how the energy is provided. The scope of human disruption of the biosphere is now global. This ecological perspective highlights the current magnitude and closeness of significant and unwelcome changes to Earth systems. The reduction of humanity’s demands on the biosphere is an overriding priority. Ecological economics, with its emphasis on a steady-state economy, is perhaps the most rigorous existing economic framework with specific proposals for determining priority actions. We urge scholars of all disciples to examine these." Check out the full article in the Conversation. 30) Richest 1% emit as much planet-heating pollution as two-thirds of humanity. This report released by Oxfam on November 20th highlights the theme of this extra section. Those of us in the developed world need to consume much less - some of us a lot more than others!
The richest 1 percent of the world’s population produced as much carbon pollution in 2019 than the five billion people who made up the poorest two-thirds of humanity, reveals a new Oxfam report. It comes ahead of the UN climate summit in Dubai, amid growing fears that the 1.5°C target for curtailing rising temperatures appears increasingly unachievable. These outsized emissions of the richest 1 percent will cause 1.3 million heat-related excess deaths, roughly equivalent to the population of Dublin, Ireland. Most of these deaths will occur between 2020 and 2030. “The super-rich are plundering and polluting the planet to the point of destruction, leaving humanity choking on extreme heat, floods and drought,” said Oxfam International interim Executive Director Amitabh Behar. “For years we’ve fought to end the era of fossil fuels to save millions of lives and our planet. It’s clearer than ever this will be impossible until we, too, end the era of extreme wealth,” said Behar. Check out the full article on the Oxfam website. 31) New Paper Identifies ‘Behavioural Crisis’ Driving Overshoot. Ground-breaking academic paper, led by a New Zealand conservationist, reveals the behavioural crisis driving anthropogenic ecological overshoot and immediate actions needed. A ground-breaking peer-reviewed paper has been published today (20/09/2023) by a collection of well-known scientists, academics and behavioural science practitioners led by New Zealand-based conservationist, Joseph Merz, of the Merz Institute. The paper, published by Sage on 20 September 2023, details how our modern human behaviour is causing us to consume our natural resources at rates faster than they can be replenished, while also creating waste in excess of what the Earth can assimilate. The authors name and frame this existential threat the “Human Behavioural Crisis” and propose that the crisis, which stems from maladaptive human behaviours, be recognised globally as a critical intervention point for tackling ecological overshoot (and its symptoms like climate change). The authors, led by Merz, demonstrate that our previously adaptive human impulses have been exploited for-profit to the point that the resultant behaviours have become extremely maladaptive, threatening complex life on Earth. You can read the full media release on the Merz Institute website. LOCAL
1) Media articles written by CKM member Tom Powell since the last newsletter. 17/05/2023 - Opinion article: The Newest thing - Tesla Bashing. 28/07/2023 - Opinion article: Taking out the Greenwash. 2) Assessing Marlborough’s landslide risk. A report was presented at the July MDC Environment and Planning Committee meeting. “Weather events in 2021 and 2022 caused major environmental and property damage as well as significant trauma to residents. A detailed report prepared by GNS Science presented to Council’s Environment and Planning Committee illustrated the number of landslides and looked at ways of improving landslide hazard management in future. Environmental Scientist Matt Oliver said the report had significant implications for how Council managed things going forward. Mr Oliver said work in the Marlborough Sounds following the storms had been challenging. “The level of damage to property as well as the human trauma sits heavily with me,” he said. “The rainfall from both storms caused significant property damage and disruption to people’s lives.” Following the storm events and landslide related reports received in past years, it seemed such phenomena were a common hazard in the Marlborough Sounds landscape, he said. With increased intensity and frequency of storms forecast under climate change, the GNS report recommended Council investigate landslides further as part of a natural hazards programme.” The full report can be seen on the MDC website - July 13th meeting - Item 3. Marlborough floods a year on; new report suggests human behavior a major cause - It is also worthwhile listening to Kathryn Ryan's interview on RNZ with Matt Oliver, environmental scientist at MDC and Kenepuru Heads farmer Emma Hopkinson. 3) Wairau Aquifer science & management update for Climate Karanga Marlborough. Dave, Don, Pete and Budyong had a two hour meeting at MDC offices on Wednesday, August 23rd. Peter Davidson, MDC Groundwater Scientist organised the meeting to give us a presentation bringing us up to date on the latest research about the aquifer and its decline and sharing some of their thinking about how they might better manage the water allocations being extracted from the aquifer. Other staff attending were Pere Hawes, Sarah Pearson and Clementine (Clem) Rankin. I have put together this report using the material from the presentation for anyone interested in this topic. 4) Friends of Nelson Haven and Tasman Bay Annual Report. This report has a range of interesting information relevant to Marlborough and in particular to the Marlborough Sounds for anyone interested. 5) Marlborough Biodiversity Forum. The theme for the forum meeting in May was "Dramatic weather events - Effects on biodiversity and mitigation measures." I wanted to highlight some important thoughts shared that day. "Resilience means more that stability. It's the ability of an ecosystem to return to its original state following a disturbance or other perturbation." Te Korowai - An Ecosystem approach.
NATIONAL 6) Inquiry into community-led retreat. The Minister for Climate Change has asked the Parliamentary Environment Committee to open an inquiry into community-led retreat and adaptation funding. You can download from the MfE website, the "Community-led retreat and adaptation funding issues and options" paper and the "Report of the Expert Working Group on managed retreat". In the media release from the Beehive the Minister for Climate Change James Shaw said “Severe weather events such as Cyclone Gabrielle cause immense damage. Climate change is likely to bring more frequent and more severe events in the future. Decisions we take now, about how to prepare and adapt, will have a lasting legacy. Community-led retreat is a carefully planned process, that can mean anything from relocating homes, to cultural sites, to playgrounds, out of harm’s way, before a severe event, like a flood, happens. I have asked the Environment Committee to hold an inquiry so we can hear a broad range of views on how to develop an enduring system. An inquiry would explore how community-led retreat, including communities choosing to relocate away from areas of high risk, could become part of our adaptation system, and how the costs could be met.” 7) The planet is on fire. Are the Chrises not listening? Will 'bread and butter' solutions or a Ministry of Hunting and Fishing help save our children's future? As global warming tips into global boiling, Dame Anne Salmond asks if our leaders are honest and long-sighted, or cynical and expedient. Check out the full article on the Newsroom website. 8) Pumped Hydro – It’s already built! The Sustainable Energy Forum Inc. (SEF) recently sent an Open Letter to the Minister of Energy and Resources the Hon Dr Megan Woods, the Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment Simon Upton, the Energy spokespersons of all parliamentary parties and copied to representatives of the media. In the letter they said - "The mission of SEF is to assist “Facilitating the use of energy for economic, environmental, and social sustainability”. As such, we feel compelled to contribute vital information to the currently unfocused and unproductive discussion around the New Zealand Battery Lake Onslow project, and the proper application of pumped hydro technology within a future-proof New Zealand electricity system. The consensus among SEF members, many of which have decades of electrical, structural, environmental or civil engineering expertise, is that pumped hydro energy storage is a highly valuable and important technology for a sustainable New Zealand energy future, but that the current NZ Battery Project proposal for Lake Onslow is woefully inadequate, ill-targeted, and above all - obsolete. The project should therefore be abandoned sooner rather than later, as it is unfitting and too expensive to provide electricity back-up for genera on shortfalls occurring on the decade scale. All other features expected from Lake Onslow, including buffer and back-up capacity for the integration of more intermittent renewable genera on and price peak modulation ability, can alternatively be provided from New Zealand’s already built, tested, but unused pump hydro scheme on the Pukaki-Tekapo canal. We trust that this SEF contribution will add value to the discussions and the decision making process around the future of pumped hydro energy storage in New Zealand." You can download a copy of the full letter from the Scoop website if interested. 9) NZ Battery Project update. The August newsletter from the NZ Battery Project states that the MBIE team is seriously looking at a “portfolio” option for back up electrical power during a “dry year”, when hydro-generation is not expected to meet power demand, along with the here-to-for favoured option of a $16 billion pumped hydro scheme at Lake Onslow in Central Otago. The portfolio option would include biomass and geothermal energy and possibly other sources that the energy market might provide. There is no mention of the above mentioned Pukaki/Tekapo option. Tom makes the following comments in that regard. "It apparently has a generation potential of only 90 MW. It could be part of a wider portfolio of energy projects, though. With National coming out against Lake Onslow, I think this is the direction the government is heading (toward the Portfolio option, rather than Lake Onslow). Even if it isn’t part of the NZ Battery Project, it has merit just stabilising prices on the wholesale electricity market, as the Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment (PCE) has pointed out. As the nation develops more intermittent renewables, there is going to be greater need for energy storage. And, given the huge difference in present wholesale electricity prices between peak usage in the mornings and evenings and overnight, there is an opportunity for companies to make money on pumped hydro storage alone." The newsletter also announced that energy storage in green hydrogen will not be progressed further for Crown investment. You can read more about the NZ Battery Project and a full copy of the MBIE August E-news can be downloaded on their website. 10) Closed loop pumped hydro. This news release for a journal article on closed loop pumped hydro, energy storage is from the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in the US. It is closed loop because it is separate from the traditional river dams. The article suggests that closed loop hydro has the least lifecycle emissions of four other large scale energy storage options they investigated. Three battery technologies and compressed air. Some type of energy storage is needed to make intermittent renewable power, such as wind, tidal and solar, viable and in New Zealand’s deregulated power market, it would help to stabilise peak power prices. Cheap night-time power could be used to pump water up hill and then be available for the morning and evening power usage peaks. There will be the usual environmental problems with building and flooding upper and lower reservoirs, however. 11) Te Waikoropupū Springs Water Conservation Order. I wanted to include this item because I see it as being an important legal precedent that the WCO supports the applicants submission that the Springs have a sacredness that is unique and spiritually renewing and hence outstanding. I have included a statement below from the "Save Our Springs" (SOS) group. "The recommended Water Conservation Order (WCO) for Te Waikoropupū Springs has just been finalised and sent by the Environment Court to the Government. This is a major step forward in the campaign to protect the Springs. The full Recommended Order is publicly available from the Environment Court website. It’s important to understand that the WCO process is not yet complete. There are fifteen working days in which a legal challenge to the draft can be made; i.e. by the 18th of August. Assuming it is not appealed, it usually goes to Parliamentary Counsel Office for checking; then the Minister for the Environment – assuming he agrees – will recommend to the Governor-General that it be adopted. One exciting part of the recommended draft is that the Court has officially accepted SOS’s spiritual evidence. Marion Sanson, from our Committee, and I brought evidence that Te Waikoropupū Springs have ‘Outstanding Spiritual Characteristics’ for Pākehā (non-Māori). Ngāti Tama had already proven that the Springs have ‘Outstanding Spiritual Characteristics’ for the Māori people. This means it has now been legally proven that Te Waikoropupū Springs have ‘Outstanding Spiritual Characteristics’ for all visitors. This strengthens the grounds for the ongoing protection of the Springs. During Save Our Springs' (SOS’s) final submissions, the group's lawyer Sally Gepp asked the Court to formally record their response to our evidence. They have done so. Here is their response (from paragraph 54): “We accept the evidence of Mr Moran and Ms Sanson on these matters. They explained how they find the Springs to have a sacredness that is unique and spiritually renewing and hence outstanding. In essence, their experience was that the subject waters are extraordinary in those terms. Those are of course personal experiences. Nevertheless, our site visits enabled us to appreciate how the special qualities of the Springs include the way people experience them as spiritually rejuvenating and renewing. It is associated with the vibrancy and purity of the waters in their peaceful setting. We adjudge that the Springs have outstanding spiritual values.” This is an epic moment for the campaign. It is the first time the Environment Court has accepted a waterway as having ‘Outstanding Spiritual Characteristics.’ It thus creates legal precedence. I’m especially happy for the Mohua (Golden Bay) community who can now say their local springs have been legally acknowledged as having ‘Outstanding Spiritual Characteristics;’ i.e. that they can be experienced as Sacred." Here is an extract from a further letter received from SOS on Augusty 22nd. Friday, the 18th of August, was the cut-off day to appeal the Te Waikoropupū Water Conservation Order (WCO). There can now be NO APPEAL to the High Court. No appeal is very, very good news! The WCO now needs to be checked by the Environment Ministry. When this is complete the Environment Minister, David Parker, will (hopefully) give it the thumbs up. It then goes to the Governor General to be signed into law. This process takes time. SOS’s priority is that the Te Waikoropupū Springs Water Conservation Order be passed into law before the election. The WCO ensures that the kaitiaki, Manawhenua Ki Mohua, will be working equitably alongside the Tasman District Council to protect the springs. The equal involvement of the kaitiaki is vital for the long-term protection of the springs. With this in mind, we are concerned a National/Act party coalition government could endanger the WCO. We want to make certain this does not happen. This week we will be contacting David Parker asking that passing the WCO into law before the election be given a high priority. We will also send an open letter to the Minister with media cc’d in. We will note that the Court, in the concluding paragraph of its report, asked the Minister to promulgate the WCO at the earliest possible opportunity. 12) Beyond Growth Aotearoa conference - Sep 16-17. This information comes from Degrowth Aotearoa. They say - "Following the successful European Beyond Growth 2023 Conference, we are ready to continue this kōrero in Aotearoa New Zealand. This interactive event will provide a forum to share the latest knowledge and insights related to ecological economics, resource scarcity and the planned response measures that could be taken to strengthen resilience and maximise future opportunities. Day 1 will cover opportunities and challenges at a systems level, Te Ao Māori perspectives, government policy and business strategies. Day 2 will explore practical action drawing on community, local government and ethical, circular business perspectives. There will be opportunities to network with experts, peers, and decision-makers faced with similar challenges." If you are interested to attend you can book tickets here. 13) F&B Room for Rivers national campaign. As a follow up to the item in the last newsletter about this topic you can also listen to a good informative interview on RNZ. The F&B Freshwater Advocate Tom Kay has been traveling around NZ giving presentations to local bodies and communities and was interviewed about this on the Saturday Morning show. 14) A new paradigm shift, indeed. Tom Powell wrote a rebuttal article to the Rural News publication, following a member’s alert to an article published on 1 August (Could the paradigm be shifting?) which claimed that the climate impact of methane is so low as to be disregarded. This would be welcome news to the farming community if it were true but an examination of the claim shows it not to be. The claim was made by an American physicist on a road tour of New Zealand, based upon a research paper by a pair of climate scientists in North America. The research paper in question was never peer-reviewed, which is standard procedure for scientific research, and so there is no way to verify its findings. In addition, the paper was published by an avowed climate sceptic organisation, making it more suspect. Beyond the science, Tom points out that the paradigm is changing but not how the author expects. Overseas markets are demanding that exporters reduce their greenhouse gas emissions, so reducing emissions is not just good for the environment, it is good for business too. You can read the full rebuttal article on our website. If you're interested in more detailed information check out this document with the initial research done by Tom. 15) New emissions reduction plan will future-proof NZ’s largest export sector. This is the headline from the recent media release from the Agriculture Minister Damien O'Connor. It's a big claim and I personally think it will need a lot more than this to future proof our largest export sector, but after much talking and consulting a step has been taken towards trying to address this very difficult issue. We will have to wait until after the election to know if it has any meaning. The Hipkin’s government with this announcement of their agriculture emissions reduction plan are moving ahead with He Waka Eke Noa but have delayed it to the last quarter of 2024 (for reporting) and 2025 (for levys) rather than the 1 January, 2024 dates in the Climate Change Response Act (CCRA.) According to Tom, our CKM expert on the ETS, it is a good outcome that on farm sequestration will go through the ETS, rather than be a discount on the methane levy. He says the fact the government are selling this partly based upon the emissions reduction requirements of overseas buyers is a paradigm shift, indeed. Check out the full media release for more info. 16) A Redesigned NZ ETS Permanent Forest Category. In this consultation, the Ministry for the Environment (MfE) asked how to define “permanent forests” and what tree types should qualify for permanent forests. Permanent forests are those planned to last more than 50 years and never be clear cut. The MfE consulted on this topic last year but realised that the issue was more complex than anticipated and the responses from submitters didn’t give them a clear way forward. In this consultation they ask for definitions and rules for permanent forests, as well as how to manage “transition forests”, which are forests planted in fast growing exotic trees (such as radiata pine) in order to earn carbon credits quickly and then, as the exotic trees age and reach maturity, replace them with indigenous and more long lived trees. CKM’s submission stressed the importance of indigenous forest as habitat for wildlife and protection against erosion. We also stressed the importance of drought, disease and wildfire resistance and non-wilding tree types. We argued against wilding and fire prone species like radiata. We supported mechanisms that would incentivise indigenous forests in the early years after planting, so as to offset the incentive to plant exotics and attempt to transition these forests to indigenous forests later. On the other hand, we supported the imposition of strict management regimes and accountability for transition forests. Our full submission is available on our website. 17) Review of the New Zealand Emissions Trading Scheme. In this consultation, the MfE asked how forestry should be “disincentivised” in the Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) so that the abatement of gross greenhouse gas emissions (i.e., those from the burning of fossil fuel) are prioritised in the coming decade. Right now in the ETS, gross emissions can be offset one-for-one by credits for carbon sequestered in forests. The Climate Change Commission has pointed out that the existing high price of carbon credits has incentivised the planting of new forests and within a decade a surplus in forestry credits will drive the price of carbon credits too low to incentivise continued reduction in gross emissions by industry. In other words, there will be so many forestry carbon credits around, that the carbon credit price on the ETS will drop and industries will simply buy cheap credits rather than upgrade their processes to emit less greenhouse gas. The MfE gave 4 options for reforming the ETS with respect to forestry credits. CKM’s submission supported the option to remove forestry credits entirely from the ETS and set a separate price for those credits. This option aligns with the Climate Change Commission’s advice and will give government better control over its acclaimed goal of “right tree, right place”. This option also allows for different prices for different types of forests – i.e., a premium could be paid for indigenous forests and enhanced protection of biodiversity, over exotic forests. Our full submission is available on our website. 18) Government partners with more industrial users to lower emissions. Below is an extract from a recent media release from the Beehive - "Minister of Energy and Resources, Dr Megan Woods, has today announced support for 17 industrial energy users to help them stop using fossil fuels faster through the Government Investment in Decarbonising Industry (GIDI) Fund. “We are seeing some of the country’s largest food processors and manufacturers, like Alliance and Open Country Dairy, make further commitments on multiple, large decarbonisation projects at the same time. There is real momentum building in pushing fossil fuels out of the energy system and lowering emissions through renewables and energy efficiency. We’ve come a long way in the last three years GIDI has been operating. Aside from our large partnership agreements with NZ Steel and Fonterra, this is the largest allocation of GIDI: Industrial funding to date. Businesses from one end of New Zealand to the other are stepping up to the challenge of lowering their emissions. The projects announced today will reduce carbon emissions by 67,300 tonnes each year, which is equal to taking approximately 25,000 cars off the road. That’s a great result for the environment and helping us meet our climate goals,” Megan Woods said. “New Zealanders and export markets want lower-carbon products and services, and GIDI support is helping them switch sooner to low emission options, proving again that businesses don’t have to deindustrialise, to decarbonise." Round 5 of GIDI commits $33.3 million in government investment and leverages private funding of over $62 million. 19) Transition HQ. In 2018, Grant Symons and Fiona van Petegem were introduced by Professor Susan Krumdieck at the University of Canterbury. She was developing a branch of engineering called transition engineering, an emerging interdisciplinary methodology of large-scale systems change that would facilitate a future state of reduced emissions, materials and energy use. Grant and Fiona saw how essential Susan’s research was and understood that it urgently needed to be shared with the public in an accessible way. Drawing on Grant’s background in strategy, project and change management and organisational capability development, and Fiona’s background in engineering, manufacturing and process engineering, they created Transition-HQ. It became a registered company in New Zealand in 2019 and has been steadily growing ever since. While there is much debate about what New Zealand’s future could and should be, what is still missing from the larger conversation is how we do the work of innovating, engineering, and enabling the real transition. You can learn more about Transition HZ on their website. I was interested to read an item titled Magic Blue Droplet from their recent newsletter written by Grant. He puts into context and gives us all a timely reminder of the life giving role water plays on our planet and how critical it is for us to protect that water. GLOBAL 20) Global fight to end fossil fuels. Here is some info about a global action happening in September. On September 15 to 17, millions of people around the world will take to the streets to demand a rapid, just, and equitable end to fossil fuels. This wave of global mobilisations will include the March to #EndFossilFuels fast, fast, forever in New York City on September 17, as world leaders attend the United Nations Secretary General’s Climate Ambition Summit. This is a call to solidarity with Indigenous and First Nations across the world who have been fighting the deadly fossil fuel industry and its enablers for decades. We need all hands on deck to keep building a fossil fuel-free world: youth activists, civil society organisations, social movements, feminist and migrant rights groups, trade unions, faith institutions, academic centres, health institutions, families and peoples of all genders and backgrounds, everywhere, all voices matter! 21) Global Workshops organised by Climate Action Network. This information has come through from the Climate Action Network office in Kenya. These workshops could be worthwhile for anyone interested in these two topics. The eastern time works best for us here in NZ, as we are 12 hours later than the notified time (i.e., 6:00 am UTC on 28 August is 6:00pm NZ time 28 August). Zoom links are provided, so there appears to be no need to register. We are pleased to invite you to two consultative workshops on Green Hydrogen and Critical Minerals on Monday 28th and Tuesday 29th August 2023. Eastern and Western times are available for both. These workshops are aimed to facilitate network-wide discussions on these two key and timely subjects, ahead of consultations and further progress on a comprehensive energy package of asks/demands, particularly at COP28. Please find below the schedule of the workshops: Green Hydrogen Workshops Eastern Time: Monday 28th August 2023 at 06.00am to 07.30am UTC (Zoom link) Western Time: Tuesday 29th August 2023 at 12.00pm to 13.30pm UTC (Zoom link) Critical Minerals Workshops Eastern Time: Monday 28th August at 07.30am to 09.00am UTC (Zoom link) Western Time: Tuesday 29th August 2023 at 15.00pm to 16.30pm UTC (Zoom link) 22) UN advises against offsets for carbon removal technologies. Billions of dollars are pouring into tech-based solutions to suck carbon dioxide from the atmosphere but the UNFCCC says they are unproven and pose unknown risks. The United Nations climate body has cast doubt over technologies that aim to suck carbon pollution from the atmosphere, calling them “unproven” and potentially risky. In a briefing note, unnamed authors from the UN’s climate body (UNFCCC) said these removal activities are “technologically and economically unproven, especially at scale, and pose unknown environmental and social risks”. It concludes they are therefore not suitable for offsetting carbon emissions under the upcoming UN’s global scheme. The UN assessment has angered the growing industry, which is seeing billions of dollars of investment from governments and corporations. The UN document does not spell out why these carbon removal technologies do not contribute to sustainable development and the industry disputed this. “We would be pleased to connect you with carbon removal leaders advancing projects in Kenya, Kiribati, India, Brazil and other locations around the world where Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) is contributing directly to local regional economic development”, their letter said. The Center for International Environmental Law called carbon removal “a dangerous distraction”. The NGO argued that relying on removal technology, “both delays the immediate reduction of emissions and presents independent risks to human rights and the environment, some of which remain poorly understood”. Check out the full article for more info. 23) Batteries are the environmental Achilles heel of electric vehicles – unless we repair, reuse and recycle them. In other words, the answer to the question of “Are electric vehicles really eco-friendly?” largely depends on how we manage the downsides associated with their batteries. Changes in how we design, produce, use and recycle electric car batteries are urgently needed. These changes can ensure that, in solving the problem of fossil fuel emissions, we also minimise other environmental harms. The long list of benefits of giving electric vehicle batteries a second life, then recycling their materials, is enticing. Given the scale of the potential economic and environmental gains, along with the countless jobs such work can create, batteries could be more generous in their afterlife than in their first incarnation in electric vehicles. This is an area I am particularly interested in. As EV use grows let's hope there are adequate incentives to ensure the precious resources used in the batteries are reused and then fully recycled. Check out the full article which details ways we can significantly reduce demand and hence the emissions associated with EV battery production, simply by fully utilising the batteries before recycling. 24) Young Montana residents bring climate change case to court. This court case was filed in March 2020 in the US and is the first constitutional climate trial in that country. This article gives some background information about the trial. “We’re asking the government and the courts to do their job and protect us, along with the rest of Montana’s citizens and our incredible home state; this case is one big opportunity for the state to become a leader in preserving a safe, beautiful and prosperous future for Montana,” Grace Gibson-Snyder, a 19-year-old plaintiff, said. Advocates hope the trial could set precedent for similar cases to move forward and that it could inspire legal action in other states. The state’s constitution has since 1972 guaranteed that the “state and each person shall maintain and improve a clean and healthful environment in Montana for present and future generations”. By propping up fossil fuels, the plaintiffs argue, the state has failed to uphold this responsibility. The case closed on June 20th and Judge Seeley who presided over the case recently issued her 103 page order in favour of the complainants. This article calls the decision a "Gamechanger". Hopefully it provides some impetus for further similar cases. Among the policies the challengers targeted was a provision in the Montana Environmental Policy Act (MEPA) barring the state from considering how its energy economy impacts climate change. This year, state lawmakers amended the provision to specifically ban the state from considering greenhouse gas emissions in environmental reviews for new energy projects. That provision is unconstitutional, Seeley ruled. “By prohibiting consideration of climate change, [greenhouse gas] emissions, and how additional GHG emissions will contribute to climate change or be consistent with the Montana constitution, the MEPA limitation violates plaintiffs’ right to a clean and healthful environment,” Seeley wrote. This YouTube video from Democracy Now also has info about the case and this Guardian article looks at some implications of this case. 25) Fungi Lock Away Over One-Third of Annual Global Fossil Fuel Emissions In the Soil, Study Finds. This is some very interesting research giving preliminary information about the role of underground fungi in carbon sequestration. More research is needed to confirm how accurate their calculations are but this initial work indicates we need to gain more understanding of the processes involved and do whatever is necessary to avoid harming these fungal networks. Fungi stores a third of carbon from fossil fuel emissions and could be essential to reaching net zero, new study reveals.
Professor Katie Field, Professor of Plant-Soil Processes at the University of Sheffield and co-author of the study, said: “Mycorrhizal fungi represent a blind spot in carbon modelling, conservation, and restoration - the numbers we’ve uncovered are jaw-dropping, and when we’re thinking about solutions for climate we should also be thinking about what we can harness that exists already. Soil ecosystems are being destroyed at an alarming rate through agriculture, development and other industry, but the wider impacts of disruption of soil communities are poorly understood. When we disrupt the ancient life support systems in the soil, we sabotage our efforts to limit global heating and undermine the ecosystems on which we depend. More needs to be done to protect these underground networks - we already knew that they were essential for biodiversity, and now we have even more evidence that they are crucial to the health of our planet.” Check out the full article for more information. 26) The Spanish Government favours promotion of initiatives to make Ecocide an international crime. Jojo Mehta, Stop Ecocide International’s Co-founder and Executive Director, says: “This is a very encouraging response from the Spanish government and shows it is now unequivocally time for ecocide law to be progressed at national as well as regional and international levels. It responds to the growing global awareness of how downright dangerous it is to destroy the ecosystems upon which we entirely depend - for lives and livelihoods, for sustaining crucial and threatened biodiversity, and for regulating climate on our shared planet. There is no stopping this direction of travel - it is now only a matter of time before legal recognition of ecocide becomes the norm around the world.” For more info go to the Stop Ecocide website. 27) Degrowth: Is There Any Alternative? This article from the Truthdig website offers a thought provoking critique of an essay published in May in the New York Times. I appreciate critical analysis of big claims made in the main stream media that paint a rosy picture of our predicament when in fact the reality is much more complicated. The expectation that we can get ourselves out of the mess we have created on our planet without making major changes to our lifestyles and economic systems is a pipe dream in my opinion, so I have a lot of sympathy for the view expressed in the Truthdig article and recommend reading it in full. Here is an extract - To slow climate change and rescue key ecosystems from the brink, a new economic paradigm is needed. In a May 30 essay for the New York Times titled “The New Climate Law Is Working. Clean Energy Investments Are Soaring,” one of the architects of last year’s Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), Brian Deese, wrote, “Nine months since that law was passed in Congress, the private sector has mobilized well beyond our initial expectations to generate clean energy, build battery factories and develop other technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.” There’s just one problem. Those technologies aren’t going to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The only way to reduce emissions fast enough to prevent climate catastrophe is to phase out the burning of oil, gas, and coal by law, directly and deliberately. If, against all odds, the United States does that, we certainly will need wind- and solar-power installations, batteries, and new technologies to compensate for the decline of energy from fossil fuels. There is no reason, however, to expect that the process would work in reverse; a “clean-energy” mobilization alone won’t cause a steep reduction in use of fossil fuels. I think top leaders in Washington are using green-energy pipe dreams to distract us from the reality that they have given up altogether on reducing US fossil fuel use. Societies must decide: do we want a growing GDP or a livable future? We can’t have both. 28) Nate Hagens - Reality Roundtable series. These are roughly 90 minute long forums with Nate and usually 3 other participants. The three topics so far have been "Electric Vehicles," "Deep(er) Ecology" and "Unlearning Economics." Highly recommended if you are wanting to think about the bigger issues around how we got into this crisis and about the challenges that are emerging, as we attempt to deal with it. We found the Deep(er) Ecology session very interesting. The Unlearning Economics session is pretty technical in places but still worth the effort if you're interested in understanding the deep seated obstacles to change embedded in our current economic system. If interested you can check out the full series on YouTube. 29) Why science needs art according to Professor Tim Jackson. Sustainable economics expert Professor Tim Jackson is from the University of Surrey in England. In this RNZ interview he says we need less growth to put less demand on the planet's resources and slow down climate change, but we need more art, more plays and works of fiction to bring both sides of that argument to life. More is not always better. He's the Director of the Centre for the Understanding of Sustainable Prosperity at the University of Surrey and the man to bring these two worlds together as a scientist, playwright and philosopher. 30) Earth cries! We are the gods that must step up to the biggest crisis in history. Ben Okri is a Booker prize-winning author and poet. His book Tiger Work, a collection of stories, essays and poems about the climate crisis, is published by Head of Zeus. His poem "Earth Cries" was published recently in the Guardian. In it Ben calls for bold action in this era of wildfires, overheated oceans and shrinking biodiversity. My suggestion is that you take the time to read it our aloud to anyone who is willing to listen or just to yourself. 31) Why ideas of ‘planetary boundaries’ must uphold environmental justice. How many biophysical boundaries does our planet have? What are the limits of, say, carbon dioxide emissions, ocean acidification, chemicals and air pollution beyond which existence becomes unsafe for Earth and its inhabitants? Back in 2009, a team of researchers led by environmental scientist Johan Rockström grappled with these questions in an article published in Nature . In the researchers’ view, planet-altering human activities could be assembled into nine groups. Thresholds were calculated for most of them, beyond which the result could spell danger for the planet and its people. The scientists concluded that humanity has crossed three of these nine ‘planetary boundaries’, and that the remaining six would also be crossed unless remedial action was taken. A gap in the original concept was that it lacked environmental justice and equity — it needed to take into account the fact that everyone, especially the most vulnerable, has an absolute right to water, food, energy and health, alongside the right to a clean environment. Rockström, together with sustainability scientist Steven Lade and a team of researchers, have modified their original concept to incorporate justice alongside the biophysical boundaries. The resulting findings, which build on a study published in March in Nature Sustainability, show that seven out of eight thresholds have been crossed: the eight are climate, natural ecosystem area, ecosystem functional integrity, surface water, groundwater, nitrogen, phosphorus and aerosols. Check out the full article in "Nature". 32) Global temperature rises in steps – here's why we can expect a steep climb this year and next. This article from the Conversation, written by Kevin Trenberth, climate scientist at Auckland University, is the one item in this newsletter highlighting how truly unprecedented (overused word now isn't it) several climate parameters are this year. The global sea surface temperature (measured between 60 degrees north and 60 degrees south), the global 2M air temperature and the Antarctic sea ice extent graphs are all showing large anomalies, so much so that scientists are struggling to understand why. In the article there are two of those graphs for early July but if you wish to monitor them for yourselves and see their ongoing trajectory you can do so on the Climate Analyzer website. Click on the "Climate Data" tab at the top to access the different graphs. The explanation Kevin provides for the step nature of global temperature rises is worth reading. Here's an extract from the article - Now, in 2023, all kinds of records are being broken. The highest daily temperatures ever recorded globally occurred in early July, alongside the largest sea surface temperature anomaly ever. June had its highest global mean surface temperature, according to preliminary analysis. The extent of Antarctica’s sea ice has been at a record low. Meanwhile, atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations continue to increase at rates that show no sign of slowing. Evident consequences include torrential downpours in some parts of the world which contrast with excessive heatwaves and wildfires in other locations, notably recently in Canada. But global mean surface temperature does not continue relentlessly upwards. The biggest increases, and warmest years, tend to happen in the latter stages of an El Niño event. Human-induced climate change is relentless and largely predictable. But at any time, and especially locally, it can be masked by weather events and natural variability on interannual (El Niño) or decadal time scales. The combination of decadal variability and the warming trend from rising greenhouse gas emissions makes the temperature record look more like a rising staircase, rather than a steady climb. 33) Uh-Oh. Now What? Are We Acquiring the Data to Understand the Situation? The recent blog posting from James Hansen is worth a look if you're interested in the latest science regarding the unprecedented global heating happening this year and referred to in the previous item. I appreciate James' postings. They are technical but he is always blunt and direct in his assessment of the latest data. At the end of the blog post he says - "A new climate frontier. The leap of global temperature in the past two months is no ordinary fluctuation. It is fueled by the present extraordinarily large Earth’s energy imbalance (EEI). EEI is the proximate cause of global warming. The large imbalance suggests that each month for the rest of the year may be a new record for that month. We are entering a new climate frontier. When the first author gave a TED talk 10 years ago, EEI was about 0.6 W/m2, averaged over six years (that may not sound like much, but it equals the energy in 400,000 Hiroshima atomic bombs per day, every day). Now EEI has approximately doubled. Most of that energy is going into the ocean. If Southern Hemisphere sea ice cover remains low, much of that excess energy will be poured into the Southern Ocean, which is one of the last places we would want it to go. That does not mean that the problem is unsolvable. It is possible to restore Earth’s energy balance. Perhaps, if the public finds the taste of the new climate frontier to be sufficiently disagreeable, we can begin to consider the actions needed to restore a propitious climate." You can download a pdf of the full post from his website. 34) Beware ‘blue carbon’ bold, but uncertain claims. This article from Newsroom advocates asking the hard questions and undertaking sound scrutiny when it comes to some of the claims made to entice investors. Forests of seaweed grow much faster than forests of trees and so absorb carbon dioxide far more rapidly. That is leading to some bold claims for the potential for seaweed to solve climate change. And it’s being matched with bold actions – Microsoft, Shopify and Stripe are already buying seaweed-based carbon removals. Is this boldness justified? The biggest challenges do not always bring out the best in people, companies, or nations. There is an inevitable temptation to make bold claims based on little evidence, especially when disproving those claims is hard. This temptation keeps being realised for claims about emissions and emissions reductions. The best solution, as always, is solid science that reveals the truth of those claims. That science takes time. That creates a gap between claims and truth that allows for hogwash to proliferate. New Zealand’s current climate strategy is broken – we’ve under-invested in clean technologies, we’re planting permanent forest as fast as we can, and we plan for two-thirds of our emissions reductions to come from overseas forestry credits but we don’t know where or when, or how much they will cost, or whether those credits will be real. Given those uncertainties and the fact of New Zealand’s long coastline and huge Exclusive Economic Zone, blue carbon projects look like a life raft we can grasp onto. Certainly they have the potential to play a much larger role in our emissions reductions than for other nations. However, we don’t yet know if those projects will turn out to be a life-saver or a straw. The science is always improving, with remote observation offering promising insights. The message here is caution. Investments and policy should not outpace science. We need to avoid falling into the trap of making and believing audacious claims without solid evidence, especially when those claims purport to serve our national interest. It’s too easy to find credulous customers and investors for emissions reduction projects that lack credibility, additionality, or permanence. For blue carbon, investors should be asking the hard questions and scrutinising the science before opening their wallets. 35) Contributions from CKM members. Here are links to some articles sent in by CKM members with topics that may be of interest. The first is an article titled "I’m a climate scientist. Here’s how I’m handling climate grief". "For me, healing comes in the form of spending my time outside work enjoying the world around me, rewilding hard-to-access land, writing letters to congresspeople and protecting migrating birds. I’ve spoken to many others who have planted gardens for native pollinators, eaten from local farms and advocated for change with local policymakers. Although small actions might not solve the climate crisis, they remind us that we are intrinsic parts of the world and its ecosystems." The second is an article titled "Collapse is not a dirty word" by NZer Catherine Knight and published in Newsroom. "To assume our continued destruction of the planet’s life-supporting systems could lead to any other outcome than collapse is irrational. But, as writes Catherine Knight, the prospect of a 'great unravelling' does present an opportunity." and "Above all, the prospect of collapse is an opportunity. Just like a life-threatening illness, it should stop us in our tracks, to fundamentally re-evaluate what really matters in our lives. For most of us, it will be sustenance, warmth, connection with those we love, and the ability to find joy and laughter in everyday things. We can have all this with much simpler lives which don’t cost the earth." The third is an article titled "Despair is a luxury we can’t afford": This is from Canadian David Suzuki, on fighting for action on the climate crisis. "Amid the gloom, Suzuki sees cause to keep fighting. He traces humanity’s plight back to the Renaissance, when he says we lost the idea that we are embedded as a strand of nature dependent on everything around us – plants, animals, air, water, soil and sunlight – and instead placed ourselves at the top of a pyramid with everything else beneath us. He says this idea has only strengthened since the Industrial Revolution, but can be reversed." LOCAL 1) Media article written by CKM member Tom Powell since the last newsletter. 12/03/2023 - Opinion article: Electric rail should be the future of domestic transport 2) Earth Day Essays. CKM ran an Earth Day Essay challenge in 2020. Finally many of the entries have been published in a small booklet called "Earth Day Essays - A Child's Perspective". The theme for students was "It is important to have Earth Day because...." and many of the resulting entries were thought provoking, thoughtful and delightful. The winner of the competition was Sophie Kole who is now a Year 11 student at Marlborough Girls College (MGC). She has written a small piece for a recent MGC newsletter about her entry which you can read if interested. If anyone wants to purchase a copy for $15 please contact us and we can organise to get it to you. We are running another Essay challenge for students this year which will be publicised in June. The challenge this time is to write a letter to the Prime Minister of NZ saying - "What I'd like you to do for Papatuanuku is...." 3) MDC Environment and Planning Committee meeting – March 9th. You can download the full agenda if interested - March 9th agenda. A) ESMG report. There was a comprehensive report from the Environmental Science and Monitoring Group (ESMG) about their functions, key areas of responsibility and challenges. “The core activities of the ESMG focus on state of the environment monitoring, reporting, investigations and collection of environmental data. In addition, the ESMG delivers several environmental programmes that provide for both economic, and social wellbeing of the community and help protect and restore our natural environment. The collection of high-quality environmental data managed over the long term is a prerequisite to sound decision making for policy development, hazard management and achieving a range of community outcomes including resource consent requirements.” An important focus for them is consolidating the resilience of their data network and this is currently being reviewed. They recently lost access to some of their monitoring network for about 6 days due to a lightning strike on the repeater on Mt Riley. B) Wairau Plain Land-Use Intensification Modelling. Peter Davidson gave a presentation on the Wairau Plain Land-Use Intensification Modelling work they have been doing. The aim was to design a Wairau Plain nitrate-nitrogen predictor tool and provide forecasts of nitrate-nitrogen concentrations leached to groundwater for potential future crop types. Executive Summary
There are currently 14,000 Ha of vineyards growing over the Wairau Aquifer. They have determined the leaching rates in this area from the lysimeter data which feeds into their model. This shows that nitrate-nitrogen levels are around 1.2ppm which is very good compared to many other agricultural areas in NZ. It does tend to increase as you move from the river up towards New Renwick Rd. The model shows that nitrate-nitrogen levels north of Rapaura Rd would be about 3ppm for dairying. This would increase to about 7ppm at New Renwick Rd due to reduced flushing of the aquifer. C) Submission on Natural and Built Environment Bill and Spatial Planning Bill. For anyone interested here is a copy of the full submission. In the introduction they provide the following summary. MDC’s submission focusses on key areas of importance to Marlborough.
It is also interesting to note - “MDC supports the concept of combining plans at a regional level. It promotes efficiencies and enhances useability for the public. The Randerson Report identified a lack of vertical integration between the hierarchy of regional and district planning documents as one of the key drivers for recommending combined plans. The Proposed Marlborough Environment Plan’s (PMEP) structure is the very model the Randerson Report recommended. It is a combined regional policy statement, a regional coastal plan, a regional plan, and district plan, with the one planning document containing all regional and district provisions in an integrated way. This structure, authorised by s 80 of the Resource Management Act 1991 (RMA), is unique in the country.” D) Regional Sea Level Rise Modelling. The National Institute of Water and Atmosphere (NIWA) has been engaged to undertake ‘first pass’ Sea Level Rise (SLR) inundation modelling for the region. The SLR modelling will use the latest national sea level rise projections, vertical land movement data, and recently updated national SLR guidance material (MfE, August 2022). The project is a specific action within the MDC Climate Change Action Plan 2020 (action 2.(b)). This ‘first pass’ will help to identify which stakeholders should be involved in the next level of investigation, and provide the basis for community engagement, while helping Council decision makers to get resources, support, and future commitment. It’s important to highlight to the committee that this ‘project’ integrates with Climate Change policies, objectives, and methods that have already been actively developed with the community as part of the proposed Marlborough Environment Plan (PMEP) All appeals on the ‘Climate Change’ Topic, Issues, Objectives, Policy, and Methods have now been resolved. This is an important factor as having the MEP framework beyond challenge means that we have a strong connection to several strategic elements of the MfE DAPP process and the 10-step decision making cycle. While this is giving effect to the MEP implementation it also sets up the need for a future ‘Coastal Hazard’ longer-term strategic response. Once MDC has the information on SLR and coastal hazard assessments we can begin a process of linking work streams together, creating community awareness of the MfE DAPP process and next steps for Council, creating greater clarity around the SLR work, and efforts underway in the climate change topic. The calls for action for this focus area include.
Finally this Stuff article by Maia Hart on the SLR report provides a good analysis - 4) Slow Water: how to combat floods and droughts. This 25 minute interview on Radio NZ in March deals with a matter that has risen a lot in people's consciousness over the last few months with the multiple extreme rainfall and flood events we have experienced in Aotearoa. "Treating water management as an engineering problem ignores the complex systems in which it operates, a US author says. Just as floods and droughts are the first obvious sign of climate change, we are making things much worse by the way we manage or mismanage water, award-winning independent journalist and author Erica Gies says. In her book Water Always Wins: Thriving in an Age of Drought and Deluge, she travels the world, examining ‘slow water’ systems where wetlands, floodplains, high altitude grasslands and forests soften flood peaks, store water for droughts, and keep natural systems healthy." Tom Kay from Forest and Bird also gave an excellent presentation recently on the topic of giving "Room for Rivers" at Blenheim school. I have highlighted this info before but for anyone interested here is the link again to the F&B "Room for Rivers" campaign. 5) Why I strike: A student's plea for action. This hard hitting opinion piece written by Petra Graney from Nelson Girls College and published in Stuff is well worth a read. "Earth is not at any risk from damage caused by humans. It’s been around for 4.5 billion years, witnessing thousands of versions of creation, existence, and life. It will be around for billions more, no matter what we do - or do not do. Planet Earth will be fine. What I’m worried about is everything on it, that we know and rely on and love. Oceans, forests, biodiversity, culture, cities and people. All these things are so heavily integrated into everything we do that we can't even imagine existence without it, like a subconscious denial. And if we can’t have the foresight to see the version of Earth that we are hurtling towards, how can we take action to stop it? " 6) Climate Adaptation calendar from Nelson Tasman Climate Forum. The Nelson Tasman Climate Forum people have produced a Climate Adaptation calendar to help build community resilience. You can download a copy on their website. NATIONAL 7) Rod Carr talk at EDS annual conference. This video recording is of a talk given by Rod Carr, the Chair of the Climate Commission at the recent annual conference of the Environmental Defense Society (EDS). To be honest I'm a little in awe of Rod's ability to share critical information in such a coherent and succinct way and highly recommend listening to this talk titled "Jointly addressing Aotearoa's Climate and Biodiversity Crises." Here is an example from his talk when Rod was highlighting the delusional reality of planning to meet our Paris commitments by buying carbon credits offshore. "....It is not surprising that we believe in global markets and the efficiencies that can be derived through specialisation. We also therefore extrapolate that if somewhere in the world there is somebody we assume can abate their emissions at lower cost than us, why would we suffer the cost for local abatement rather than pay others to do it more cheaply? The theory appears sound. The practice however is highly problematic. For offshoring to work, that is paying another country to do more than it would have done, so that it is truly additional, truly permanent, truly measurable, and here's the kicker, truly enforceable reductions, is a mechanism yet to be determined. And yet by the end of this decade we're assuming we will be able to acquire 100 million tonnes equivalent of carbon dioxide emissions from someone yet to be identified, at a price yet to be determined, that is truely enforceable. Good luck!" 8) Health checks on the carbon in New Zealand's native forests were halved despite warnings over the risks. "Roughly every five years, conservation workers go deep into the forests of Aotearoa to count animal droppings, birds and carbon. This data is a health check for our native forests. But government funding for the task has quietly been halved, meaning the checks are happening less thoroughly. Stuff's Climate Change Editor Eloise Gibson set out to find out why." You can listen to a 12 minute podcast from Radio NZ and/or read this Stuff article for more info. 9) We planted pine in response to Cyclone Bola – with devastating consequences. It is now time to invest in natives. This article written by David Norton, Emeritus Professor at Canterbury University. In it he writes - With more than 40 years experience researching forest ecology and sustainable land management in Aotearoa, I believe there are four key areas where we need to urgently act to address these issues. i) As a country we need to rapidly reduce greenhouse gas emissions and rapidly increase the draw-down of CO2 out of the atmosphere. These are national issues and not confined to Tairāwhiti but as a nation we seem to be sleepwalking in our response to the climate emergency. ii) We need a comprehensive catchment-by-catchment assessment across all of Tairāwhiti (and likely other areas of Aotearoa) to identify those plantations that are located in the wrong place in terms of potential harvesting impacts. There should be no further harvesting in Tairāwhiti plantations until this exercise has been completed. We also need to identify those areas that currently lack plantations but should never be planted in exotic tree crops (for any purpose). iii) The government then needs to buy out the current owners of these plantations and embark on a programme of careful conversion to native forest. This will come at a cost, but it needs to be done. We already have models for this in Tairāwhiti where the Gisborne District Council has started converting pine forests in its water supply catchment to native forests. iv) Finally, we need to establish substantially more native forests throughout all Tairāwhiti, and Aotearoa more generally, to help build resilience in our landscapes. Here are some further items of interest on this topic now that the hard hitting Ministerial Inquiry looking into slash damage in Tairāwhiti/East Coast has been released. The press release from the Beehive with a link to the "Outrage to Optimism" Report. From Aaron Smale of Newsroom - Scathing slash report takes aim at multiple parties. From RNZ - Forestry report urges immediate halt on wide-scale felling. Iwi call on government to commit to forestry report recommendations. The Detail also has a 24 minute podcast available titled "Forestry's uncertain future on the East Coast" for anyone interested in a more in-depth analysis. 10) The new climate denial: adaptation over mitigation. Cindy Baxter from Coal Action Network wrote an article on this topic available on the CAN website. She lives in Piha so witnessed plenty of devastation during the Auckland floods. She says "What’s also lurking behind my tears is the fact that I’ve been working to stop climate change for 30 years and the same old arguments keep coming up: that it’s too expensive to act on. For years we’ve been pushing the government to do the work to understand the costs of climate impacts, to weigh them up against the costs of action, of cutting emissions and moving to a low-carbon economy. Because if the only numbers you have are the costs of action, it bolsters all those who object to taking the strong action we need. The Climate Change Commission didn’t have the numbers either. The work on the cost of climate impacts just hasn’t been done. Perhaps we should start with the bill from Gabrielle. And now we’re hearing a new kind of climate denial – most ridiculous claims from people like Chris Trotter, and Matthew Hooton, arguing that it’s now too late to act on climate change, now we just have to get on with adapting to it. Act’s Brooke Van Velden joined the fray on TVNZ Breakfast. Hooton has spent decades trying to (incorrectly) spin New Zealand’s lack of real climate action in favour of planting pine trees as somehow being world-leading. It isn’t and has never been the case. The question they haven’t looked at is how much you can adapt to: and when it simply becomes what the UNFCCC views as “loss and damage.” 11) ‘Slipping through our fingers’: New Zealand scientists distraught at scale of glacier loss. There is a grief in watching the ice melt. Some of these scientists have been monitoring these glaciers for decades, returning every year to take their pictures. They know each by name, and have their personal favourites. Some of the glaciers they used to record have vanished over the last decade. Mackintosh and Lorrey occasionally lean over their grey vinyl seats to exchange observations, gazing out the shuddering windows. “She looks like shit,” one of them says. “It’s interesting as a scientist, and a bit challenging as a human being to see that change,” Mackintosh says. “There’s a kind of conflict: of fascination in how the system can change so rapidly, combined with the emotional response of seeing the loss of ice that’s such an important part of the landscape, and so beautiful and so culturally important.” Checkout the full article. 12) Are New Zealand's marine heatwaves a warning to the world? "As seas around Aotearoa heat at an unparalleled rate, scientists are starting to understand what it might mean for marine ecosystems. New figures provided to the Guardian by scientists studying ocean temperature shifts show that on average, over the year to April 2023, New Zealand’s coastal waters sat stewing in marine heatwave conditions for 208 days. Some southern regions experienced marine heatwave conditions for more than 270 days during the period. In the north island’s Bay of Plenty, the waters remained in heatwave for an entire year. With little respite for species to recover between the waves of heat, scientists warn that some ecosystems are reaching tipping points under the surface, with effects that will be felt years into the future. No one yet knows what it will mean for the fish, seabirds, whales, dolphins, and New Zealand’s multi-billion dollar fishing industry. As scientists and communities begin to reckon with the impact, the conditions hitting Aotearoa provide a preview of the future of the world’s oceans under climate change: waters around the world are projected to rise by about 4C on average by 2100, if the world maintains its course on global heating. Heatwaves around New Zealand are already seeing spikes that high, giving a glimpse of what it can do to species under the surface. In Marlborough’s fish farms last year, the fish had died in their thousands, unable to survive the rising temperatures around them. In warmer areas, about 42% of total fish stock died. The country’s largest salmon producer, NZ King Salmon, announced it would have to shut down some of its farms as the climate heated waters around the sounds. “When I joined this company, I never heard of the term ‘marine heatwave’,” said CEO Grant Rosewarne, as the company reckoned with the losses. “Recently, there’s been three of them. “We thought we had more time,” he said. “Climate change is a slow process. But faster than many people think.” Check out the full article which includes some excellent graphics showing the increase in marine heatwave conditions over the last few decades. 13) Dealing to Climate Change - Professor Jonathon Boston and Climate Minister James Shaw. The Fabians hosted a public meeting recently where Jonathon Boston and James Shaw had a session about managed retreat. There was some very interesting discussion and questions from a large audience. Worth a listen if you want to understand more about some of the current thinking regarding the dynamics, obstacles and options for managed retreat in NZ. 14) A Case for a United Parliament to manage NZ's response to Global Warming and Climate Change. This paper written by Robert Simpson, an old friend of Lesley and mine from our time living on the West Coast in the 1970's and '80's, is an excellent, well thought out proposal stating what so many of us know is essential if we are to collectively and constructively manage the challenges arising from the climate and biodiversity emergency. In the paper Robert says - "This paper proposes a new, effective, encompassing concept for addressing the Global Warming catastrophe. It will not be actioned today. But it opens and brings to consciousness an idea that may gather momentum and influence because it makes sense. Hopefully before it is too late." Robert also shared a poem he wrote to express his deep seated sorrow for the predicament we find ourselves in. EARTH’S RESPONSE Sorrow. There’s nothing I can do. I raised you on my bosom but what you’ve set in motion I cannot heal. It’s only you. My golden tribe in whom I had such hope wrenched the divine from the earth without imagining what would come to pass. INTERNATIONAL 15) New study helps solve a 30-year-old puzzle: how is climate change affecting El Niño and La Niña? The Conversation recently printed an article highlighting this new study. It's very topical after the flooding events in Australia and NZ over the last three La Nina years. "Human-caused greenhouse gas emissions mean strong El Niño and La Niña events are occurring more often, according to our new research, which provides important new evidence of the human fingerprint on Earth’s climate. For more than 30 years, climate researchers have puzzled over the link between human-caused climate change and El Niño and La Niña events. We set out to bridge this knowledge gap. Climate scientists have long observed a correlation between climate change impacts on our oceans and atmosphere, and the increase in greenhouse gas emissions from human activity. Our research examined when this activity may have started to make El Niño and La Niña events more extreme. Our deep analysis found a relationship between human-caused greenhouse gas activity and changes to El Niño and La Niña. Our findings were five years in the making. They help us understand how El Niño and La Niña will change as the world warms in the future." 16) ‘Everyone should be concerned’: Antarctic sea ice reaches lowest levels ever recorded. This Guardian article published on March 4th said - "For 44 years, satellites have helped scientists track how much ice is floating on the ocean around Antarctica’s 18,000km coastline. The continent’s fringing waters witness a massive shift each year, with sea ice peaking at about 18m sq km each September before dropping to just above 2m sq km by February. But across those four decades of satellite observations, there has never been less ice around the continent than there was last week. “By the end of January we could tell it was only a matter of time. It wasn’t even a close run thing,” says Dr Will Hobbs, an Antarctic sea ice expert at the University of Tasmania with the Australian Antarctic Program Partnership. “We are seeing less ice everywhere. It’s a circumpolar event.” In the southern hemisphere summer of 2022, the amount of sea ice dropped to 1.92m sq km on 25 February – an all-time low based on satellite observations that started in 1979. But by 12 February this year, the 2022 record had already been broken. The ice kept melting, reaching a new record low of 1.79m sq km on 25 February and beating the previous record by 136,000 sq km – an area double the size of Tasmania." 17) ‘Headed off the charts’: world’s ocean surface temperature hits record high. The temperature data referred to in these articles is the world average sea surface temperature between the latitudes of 60 degrees N and 60 degrees S, measured by satellite and ocean buoys. "The temperature of the world’s ocean surface has hit an all-time high since satellite records began, leading to marine heatwaves around the globe, according to US government data. Climate scientists said preliminary data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (Noaa) showed the average temperature at the ocean’s surface has been at 21.1C since the start of April – beating the previous high of 21C set in 2016. “The current trajectory looks like it’s headed off the charts, smashing previous records,” said Prof Matthew England, a climate scientist at the University of New South Wales. A study last year said the amount of heat accumulating in the ocean was accelerating and penetrating deeper, providing fuel for extreme weather. England, a co-author of that study, said: “What we are seeing now [with the record sea surface temperatures] is the emergence of a warming signal that more clearly reveals the footprint of our increased interference with the climate system.” Check out the full article. This second article published about 3 weeks later said - "Temperatures in the world’s oceans have broken fresh records, testing new highs for more than a month in an “unprecedented” run that has led to scientists stating the Earth has reached “uncharted territory” in the climate crisis. The rapid acceleration of ocean temperatures in the last month is an anomaly that scientists have yet to explain. Data collated by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), known as the Optimum Interpolation Sea Surface Temperature (OISST) series, gathered by satellites and buoys, has shown temperatures higher than in any previous year, in a series stretching back to 1981, continuously over the past 42 days." Check out the full article. For anyone interested you can see the ongoing trend updated every 2 days on the Climate Reanalyzer website. As of May 29th it was slowly descending but still well above any previous records. 18) Antarctic alarm bells: observations reveal deep ocean currents are slowing earlier than predicted. "Antarctica sets the stage for the world’s greatest waterfall. The action takes place beneath the surface of the ocean. Here, trillions of tonnes of cold, dense, oxygen-rich water cascade off the continental shelf and sink to great depths. This Antarctic “bottom water” then spreads north along the sea floor in deep ocean currents, before slowly rising, thousands of kilometres away. In this way, Antarctica drives a global network of ocean currents called the “overturning circulation” that redistributes heat, carbon and nutrients around the globe. The overturning is crucial to keeping Earth’s climate stable. It’s also the main way oxygen reaches the deep ocean. But there are signs this circulation is slowing down and it’s happening decades earlier than predicted. This slowdown has the potential to disrupt the connection between the Antarctic coasts and the deep ocean, with profound consequences for Earth’s climate, sea level and marine life. Our new research, published today in the journal Nature Climate Change, uses real-world observations to decipher how and why the deep ocean around Antarctica has changed over the past three decades. Our measurements show the overturning circulation has slowed by almost a third (30%) and deep ocean oxygen levels are declining. This is happening even earlier than climate models predicted." Check out the full article. 19) The Current Mass Extinction Is Already Far More Dire Than We Realized. "Ambitious targets intended to slam the brakes on our current mass extinction may already be slipping out of reach barely a year after they were established, new research suggests. Data on birds and mammals reveal there's a huge time lag between environmental change and its impact on animal populations, of up to 45 years depending on the species and the drivers of change. This means the historic 'peace pact with nature' pledged at the United Nation's Biodiversity Conference (COP 15) in December last year may already be out of date, as the extent of this lag was not taken into account in projections of future losses. "There is wide recognition that time is short for the integrated, ambitious actions needed to stop biodiversity loss by 2050," write Natural History Museum zoologist Richard Cornford and colleagues. "This work shows that time is even shorter than had been thought." The good news is that active management of protected areas does mitigate the threats from direct use of wildlife like hunting, which is important for the livelihoods of many people. This can continue if sustainable limits are maintained like hunting quotas. What's more, taking the effort to manage and restore habitats has direct benefits for human health too, as healthy, functioning ecosystems are less likely to spill diseases into human populations. Conserving biodiversity is a massive win-win for ourselves, the wider ecosystems we live within, and for climate change mitigation. Our actions had better be fast and meaningful if we're serious about saving what remains." Check out the full article. 20) The coming EV batteries will sweep away fossil fuel transport, with or without net zero. This looks like the real deal! Maybe finally we have a breakthrough in new battery technology that is sustainable and can help drive down transport emissions? The good news is that it is a solid state battery that needs no cobalt and can potentially be made with sodium instead of lithium. Sodium is a plentiful resource. This should be good news for renewable energy and bad news for hydrogen proponents. "The Argonne National Laboratory in the US has essentially cracked the battery technology for electric vehicles, discovering a way to raise the future driving range of standard EVs to a thousand miles or more. It promises to do so cheaply without exhausting the global supply of critical minerals in the process. The joint project with the Illinois Institute of Technology (IIT) has achieved a radical jump in the energy density of battery cells. The typical lithium-ion battery used in the car industry today stores about 200 watt-hours per kilo (Wh/kg). Their lab experiment has already reached 675 Wh/kg with a lithium-air variant. Prof Curtiss said the current prototype is based on lithium but does not have to be. The same type of battery could be developed with sodium. It will take more time, but can be done,” he said. Switching to sodium would halve the driving range but it would still be double today’s generation of batteries. Sodium is ubiquitous. There are deposits in Dorset, Cheshire, or Ulster. The US and Canada have vast salt lakes. Sodium can be produced cheaply from seawater in hot regions via evaporation. There is no supply constraint. This knocks out another myth: that the EV revolution is impossible on a planetary scale because there either is not enough lithium, or not enough at viable cost under free market conditions in states aligned with the Western democracies. (The copper shortage is more serious, but there may be solutions for that as well using graphene with aluminium)."The study is peer-reviewed and has just appeared in the research journal Science. Their solid-state battery has achieved the highest energy density yet seen anywhere in the world. Check out the full article for more info. 21) Revisiting The Limits to Growth. There was a reference in the preamble of the August newsletter last year to the report prepared by KPMG Director Advisory Gaya Herrington in which she analysed the original Club of Rome "Limits to Growth" report from 1972. Here's a quote from Gaya - "Given the unappealing prospect of collapse, I was curious to see which scenarios were aligning most closely with empirical data today. After all, the book that featured this world model was a bestseller in the 70s, and by now we’d have several decades of empirical data which would make a comparison meaningful. But to my surprise I could not find recent attempts for this. So I decided to do it myself." The full report can be downloaded on the KPMG website for anyone interested. I recently came across a blog by Andrew Curry on the resilience.org website. Andrew works for the the School of International Futures in London and has done a useful brief critique of Gaya's paper. He says - "In her paper, Gaya Herrington has taken four of those scenarios to find out how they are playing out against actual data, and what that means for likely outcomes over the next couple of decades. The four scenarios she chose are, Business As Usual (BAU); Business as Usual 2 (BAU2), which is a revised later version of BAU; Comprehensive Technology (CT); and Stabilized World (SW). Both BAU and BAU2 are catastrophic; global industrial decline in the near future followed by population decline. And when you look at the slowing growth rates and declining productivity rates that keep perplexing economists, it’s maybe a sign that we are already on the runway for this outcome. Comprehensive Technology has an industrial decline, while population stabilises. In Stabilized World, industrial output and population both stabilise. In comparing outcomes with the Limits projections, Herrington finds that BAU2, and CT track the actual outcomes closely: BAU quite a lot; SW not so much." Andrew concludes by stating - "There’s one more point here that’s relevant. Economists such as Branko Milanovic argue that flattening out growth—whether that’s “post-growth” or “de-growth”—is not going to be possible because people won’t accept it. But that’s not the choice. The choice is that either we end up with unmanaged decline, which would be catastrophic, or a managed levelling out of our economies, shaped by a shift in social values and expectations. We need some politicians who are willing to be honest about this." On a positive note (because I worry about too much doom and gloom) you may also be interested to know that the Club of Rome published a book last year titled "Earth for All – A Survival Guide for Humanity". On their website they say "Earth For All is both an antidote to despair and a road map to a better future." The Canberra Times also printed a review of the book if you want to check it out. 22) Post-growth Europe: 400+ experts call for wellbeing economy. "There is no empirical basis indicating that it is possible to globally and sufficiently decouple economic growth from environmental pressures. The pursuit of endless economic growth by high income nations is a problem as it either reduces or cancels the outcomes of environmental policies. The current climate chaos and unraveling web of life on which our society depends is an existential threat to peace, water and food security, and democracy. Advancing to a post-growth economy is not only to survive, but also to thrive. This calls for a democratically planned and equitable downscaling of production and consumption, sometimes referred to as ‘degrowth’, in those countries that overshoot their ecological resources." For those who are interested you can read the full Open Letter. 23) Time to pay the piper: Fossil fuel companies’ reparations for climate damages. I personally see some variation of this type of redistribution of wealth as being essential if we are to find a way to a world with a lot less conflict and a lot more co-operation and compassion. "The calls for climate reparations are rapidly growing in the scientific literature, among climate movements, and in the policy debate. This article proposes morally based reparations for oil, gas, and coal producers, presents a methodological approach for their implementation, and quantifies reparations for the top twenty-one fossil fuel companies. Human-caused climate change has long been acknowledged as essentially an ethical issue that threatens humanity and ravages the planet. While the Global North’s historical carbon emissions have exceeded their fair share of the planetary boundary by an estimated 92%, the impacts of climate breakdown fall disproportionally on the Global South, which is responsible for a trivial share — Africa, Asia, and Latin America contribute only 8%—of excess emissions. At the same time, the world’s richest 1% of the population contributed 15% of emissions between 1990 and 2015, more than twice as much as the poorest 50%, who contributed just 7% but who suffer the brunt of climate harm. This inequity is exacerbated by poorer societies’ lack of resources to adapt to climate impacts and by the persistent reluctance of the Global North to provide them with the necessary funding and assistance as required by the principle of common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities (CBDR-RC) of article 3 of the UNFCCC. Considering fossil fuel companies as moral agents of the global climate system and attributing them financial reparations help balance the distribution of burdens and benefits. The proposed framework for quantifying and attributing reparations to major carbon fuel producers will inform future efforts to direct payments to harmed parties. While this will not indemnify them from current or prospective climate litigation, it may, for companies that pay reparations and show strong progress on reducing operational and product emissions, defer or even avoid being named as defendants in future lawsuits. The focus on the fossil fuel industry, despite persistent market distortions, governance, and policy failures common in the fossil fuel world, will help bridge the divide between “the rich” and “the poor” worlds that still hampers climate progress. It would also lead to a fairer distribution of the burden of fighting climate change among the various responsible agents, while at the same time providing necessary funding to mitigate emissions, fund adaptation, and compensate subjects more vulnerable to climate harm such as climate migrants and refugees, Indigenous peoples, racial and ethnic minority communities, people with disabilities, and people who are socially and economically disadvantaged." Check out the full article on the One Earth website and more info from this Guardian article. 24) Global fresh water demand will outstrip supply by 40% by 2030, say experts. "The world is facing an imminent water crisis, with demand expected to outstrip the supply of fresh water by 40% by the end of this decade, experts have said on the eve of a crucial UN water summit. Governments must urgently stop subsidising the extraction and overuse of water through misdirected agricultural subsidies, and industries from mining to manufacturing must be made to overhaul their wasteful practices, according to a landmark report on the economics of water. Nations must start to manage water as a global common good, because most countries are highly dependent on their neighbours for water supplies, and overuse, pollution and the climate crisis threaten water supplies globally, the report’s authors say. Johan Rockstrom, the director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and co-chair of the Global Commission on the Economics of Water, and a lead author of the report, told the Guardian the world’s neglect of water resources was leading to disaster. “The scientific evidence is that we have a water crisis. We are misusing water, polluting water, and changing the whole global hydrological cycle, through what we are doing to the climate. It’s a triple crisis.” Check out the article which has a link to the full report. 25) Joelle Gergis - Humanity's Moment - A Climate Scientist's Case for Hope. Here is a positive experience for those needing a boost and to foster some hope. This webinar from March with Dr Joelle Gergis dives into the subject of climate reality, emotion, self care and hope. It was organised by the Psychology for a Safe Climate group and at 1 hour 22 minutes is a long session but both Lesley and found it very worthwhile putting aside the time to listen to it. The Psychology for a Safe Climate group aims to support people emotionally in facing the climate reality and they state that their purpose is to contribute psychological understanding and support within the community, helping people face the difficult climate reality. 26) Top lawyers defy bar to declare they will not prosecute peaceful climate protesters. This is an interesting development in the UK and highlights the tension between the state trying to maintain an illusion of being in control and members of the public trying to raise the alarm about the emergency that is right in front of us. "Leading barristers have defied bar rules by signing a declaration saying they will not prosecute peaceful climate protesters or act for companies pursuing fossil fuel projects. They are among more than 120 mostly English lawyers who have signed a declaration vowing to “withhold [their] services in respect of supporting new fossil fuel projects and action against climate protesters exercising their right of peaceful protest”. Noting that climate breakdown represents “a serious risk to the rule of law”, the so-called “declaration of conscience” calls on legal professionals “to act urgently to do whatever they can to address the causes and consequences of the climate and ecological crises and to advance a just transition. Tim Crosland, the director of the environmental law pressure group Plan B, which together with Maugham’s Good Law Project coordinated the declaration, said “behind every new oil and gas deal sits a lawyer getting rich. Meanwhile, it’s the ordinary people of this country, taking a stand against this greed and destruction that the British legal system prosecutes and imprisons, jailing them just for talking about the climate crisis and fuel poverty. The rule of law has been turned on its head. Lawyers are responsible. It’s time to take a stand.” Check out the full article if you're interested. 27) The Carbon Brief Interview: ‘Loss-and-damage’ finance pioneer Robert Van Lierop. As countries negotiated the world’s first climate change treaty in 1991, the Pacific island state of Vanuatu made a momentous proposal. It called for “industrialised” nations to pay for the “loss and damage” that islands expected to face as rising sea levels engulfed their lands. The idea was immediately rejected. Yet 31 years later, at the COP27 summit in Egypt, developing countries finally secured agreement on a new fund to deal with loss and damage. The man behind that 1991 proposal was Robert Van Lierop, a US civil rights lawyer who had been enlisted, a decade earlier, to represent the newly-independent Vanuatu at the UN. Here is a question from the interview with Robert. Q. As for the loss and damage fund itself, we have this agreement where the funds will be set up, but should there be concerns given developed countries have missed climate finance targets in the past? A. RVL: Absolutely. That’s always the problem with the developed countries…They are very prone to make all kinds of promises. It doesn’t matter if it’s to Indigenous populations, small-island countries or former colonies…They make grandiose promises, but then there are always excuses why they can’t deliver. They like to trot out the political pressures that they face at home, as if the developing countries don’t also have political pressures at home – political pressures to get results, and to get justice. The fight for justice is barely beginning, globally. Check out the full interview. 28) CEO of biggest carbon credit certifier to resign after claims offsets worthless. "David Antonioli to step down from Verra, which was accused of approving millions of worthless offsets used by major companies. The head of the world’s leading carbon credit certifier has announced he will step down as CEO next month. It comes amid concerns that Verra, a Washington-based nonprofit, approved tens of millions of worthless offsets that are used by major companies for climate and biodiversity commitments, according to a joint Guardian investigation earlier this year." Check out the full article. 29) The Rising Chorus of Renewable Energy Skeptics. This thought provoking and challenging item is a follow up to one I put in the March newsletter looking into the issue of availability of minerals required to supply the renewable energy transformation of our energy infrastructure. “It’s doubling down on the wrong thing: propping up and accelerating the machine that’s eating the planet alive. Barrelling forward on renewable energy is the last thing Earth’s critters would vote for, and would be considered one of the more disruptive decisions we could make. Our quest for a more ecological growth model has resulted in intensified mining of the Earth’s crust to extract the core ingredient — rare metals — with an environmental impact that could prove far more severe than that of oil extraction. Our quest for a more ecological growth model has resulted in intensified mining of the Earth’s crust to extract the core ingredient — rare metals — with an environmental impact that could prove far more severe than that of oil extraction.” Unfortunately this item begs the question - Are we just exchanging the devastating impacts on our climate from burning fossil fuels for the devastating impacts on our environment and biodiversity from mining rare metals? I believe it is critical that we face these questions openly so we can collectively make the best decisions for the future of all lifeforms on our wonderful planet. 30) Enzyme found that turns air into electricity. "New Zealand and Australian scientists have made a fairly startling discovery - an enzyme that turns air into electricity. After studying bacteria in soil that can oxidise hydrogen, scientists discovered the enzyme that could offer a new clean source of energy, the only by-product of which is water. Otago University's distinguished professor Greg Cook is part of the team studying this enzyme." Check out this 5 minute podcast interview with Professor Greg Cook from Otago University if you want to know more about this fascinating new development. This article on the SciTech Daily website has more details about this discovery. In the article they say "Australian researchers have uncovered an enzyme capable of transforming air into energy. The study, which was recently published in the prestigious journal Nature, shows that the enzyme utilizes small amounts of hydrogen in the air to generate an electrical current. This breakthrough paves the way for the development of devices that can literally generate energy from thin air. In this Nature paper, the researchers extracted the enzyme responsible for using atmospheric hydrogen from a bacterium called Mycobacterium smegmatis. They showed that this enzyme, called Huc, turns hydrogen gas into an electrical current. Huc is a “natural battery” that produces a sustained electrical current from air or added hydrogen. While this research is at an early stage, the discovery of Huc has considerable potential to develop small air-powered devices, for example as an alternative to solar-powered devices." I'd like to finish this newsletter by continuing our previous investigation into the pros and cons of hydrogen as an energy source. 31) Opinion: Green hydrogen is 'escapey, explodey expanded polystyrene'. These last three items are a continuation of our previous investigation into the pros and cons of hydrogen as an energy source. This article printed in Stuff was written by Tom Powell and Tim Jones of Coal Action Network. Yes, that's the same Tom Powell who is also co-chair of CKM. "Green hydrogen – “Escapey, explodey expanded polystyrene”. This is how technology advisor Michael Liebreich recently described hydrogen in Threadreader. In some renewable energy circles, green hydrogen is all the rage. It can be made from ordinary water and electricity. It can be burnt like fossil gas but without the greenhouse gas emissions. And, it can be used in fuel cells to make electricity again. What is there not to like? Quite a lot, it turns out. The usual argument against using green hydrogen for energy is the abysmally poor efficiency of turning electricity into hydrogen and then turning it back into useful energy. Presently, a hydrogen fuel cell vehicle gets back only about 30% of the electrical energy used to make the green hydrogen in powering the vehicle. A typical battery electric vehicle gets back around 80% of the electrical energy used to charge its batteries." Check out the full article. 32) Is hydrogen really a clean enough fuel to tackle the climate crisis? Here's a couple of items on the ongoing topic of the pros and cons of using hydrogen as an alternative fuel. The first is a Guardian article attempting to separate the hype from the facts. It's conclusion is that there is a role for hydrogen but it is a limited one. It says - "But for most forms of transport (cars, bikes, buses and trains) and heating there are already safer, cleaner and cheaper technologies such as battery-run electric vehicles and heat pumps, so there’s little or no merit in investing time or money with hydrogen. Howarth said: “Renewable electricity is a scarce resource. Direct electrification and batteries offer so much more, and much more quickly. It’s a huge distraction and waste of resources to even be talking about heating homes and passenger vehicles with hydrogen.” 33) The link between hydrogen leaking into our atmosphere and methane accumulation. This final item is concerning. It looks at new research highlighting the importance of hydroxyl ions in breaking down atmospheric methane and the role fugitive hydrogen plays in this cycle. It looks at a recent study claiming that "Potent clean fuel hydrogen could lead to methane accumulation" and "New Hydrogen Research Reminds Us Humanity Just Can't Win With Fuel Alternatives". In the study they say - "Hydrogen's potency as a clean fuel could be limited by a chemical reaction, potentially leading to accumulation of methane in the lower atmosphere, according to new research. This is because hydrogen gas easily reacts in the atmosphere with the same molecule primarily responsible for breaking down methane, a potent greenhouse gas. If hydrogen emissions exceed a certain threshold, that shared reaction will likely lead to methane accumulation in the atmosphere - with decades-long climate consequences, the research from Princton University, US and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association said." I recommend reading these articles as they contain some critical new information that needs to be further investigated before we humans rush into a new technology thinking it might help save us from our self-inflicted predicament. Nga mihi, Budyong. March 2023 CKM Newsletter
Welcome to the first newsletter for 2023. As usual there are a range of items for people to browse and choose anything they find of interest. The major disruptive weather events that NZ has experienced this year are on the top of my mind as they no doubt are for most people. It is an unfortunate reality with human beings that we seem to have extreme difficulty making the big decisions when consequences of our actions seem far away in the future. It was inevitable that the time would come when we would be face to face with what global warming means in our daily lives. My heart hurts for those caught in the midst of these disruptive events and for the loss and suffering they are experiencing. Knowing that as a species we have prevaricated for so long largely due to politics and economics only amplifies that pain. The simple physics of it is that for every degree warmer the atmosphere gets it can hold 7% more water. All the warnings that climate scientists and activists have been giving for decades now have not resulted in us making any really significant changes to the upwards global trajectory of GHG emissions. Our Finance Minister and now Cyclone Recovery Minister says we will be hearing two words much more often now - Managed Retreat. I highly recommend listening to this interview by Kim Hill on February 25th titled "How to manage managed retreat", if you have not heard it yet. She talks with Jonathan Boston, Emeritus Professor of Public Policy at Te Herenga Waka Victoria University, Boston and a contributor to the recently released working paper focussed on developing recommendations for the government's proposed Climate Adaptation Act. He is blunt in his assessment of the challenges we all face. I have also taken a particular focus this time looking at the "Future of Food and Agriculture in a low emissions world," as this is a topic that has been recently discussed amongst some CKM members. This discussion also feeds into two of the other topics - Limits to Growth and Degrowth that are currently getting considerable attention in some circles. LOCAL 1) Media articles written by CKM member Tom Powell since the last newsletter. 09/12/2022 - Opinion article: “Our Broken Electricity Market” 17/12/2022 - Opinion article: “What Does It Mean, Anthropocene?” 26/01/2023 - Opinion article: “High Noon in Aotearoa” 2) Climate Action Week - Marlborough Climate Action week was organised by Catherine van der Meulen and the Action Week organising committee. It was held from February 13th -17th and "designed to create awareness, develop our Marlborough business community's knowledge by embracing education, and take action towards creating a low carbon emissions, highly productive, and thriving community, no matter what stage of the journey you are at." Check out this document for further information about the week's activities and future planned activities. Marlborough Express also published a series of Opinion pieces as a part of the Climate Action Week activities with a wide representation of views shared by a members of the Marlborough community. Here are links to the different contributions if you haven't caught up with them yet. Catherine van der Meulen - "Knowledge plus passion inspires collaborative movement " Don Quick, CKM member - "Climate is central to Marlborough's rivers, forests and Sounds" Kathryn Cannan, CKM member - "Enforceable policy needed for a green growth future" Tom Powell, CKM member - "Will humanity's hubris cause permanent damage?" James Wilson, CKM member - "Former farmer's 'trifecta' of reasons for a plant-based diet" Ruihana Lewis, Te Hoiere Project Te Pou Hapai Taiao for Ngati Kuia - "Restoring the mauri to our special places" Edwin Massey, New Zealand Winegrowers sustainability manager - "Wine centre keeps industry ahead of global trends" Glen Proffit from Southern Water Engineering - "Preparing ourselves to weather the storm" Amber McNamara, a business management consultant - "Collaboration is key for primary industry transition" Tanya Pouwhare, NZ Ethical Employers chief executive - "Climate change is a human rights issue" Jo Griggs, chair of the Cawthron Marlborough Environment Awards - "Good environmental care is good business" Michael Wentworth, manager of sustainability and strategic projects at Yealands Wine Group - "Ambitious plans at Yealands Wine Group" Matt Sutherland, Dog Point general manager - "The organic, biodiverse, native planted vineyards at Dog Point" Edwin Massey from NZ Winegrowers - "Making sure future generations can still be winemakers" Heather Donachie from Export Logistics - "Exporters urged to consider more sustainable ways" Heather Keynton Turnbull from Awatere Valley Trust - "Healthy soils grow healthy food and people" Sean Weaver from Ekos - "Imagine if the economy actually protected the planet" Lee Watkins from MyNoke - "What worms can do for your company's waste" Ailie Suzuli from Environhub Marlborough - "Nurturing nature is action against climate change" Ben Leggett from Elemental Distillers - "Distiller shares his unique practices" Alistair Schorn from Marlborough Chamber of Commerce - "What businesses need to know about emissions regulations" Alec McNeil, MDC Solid Waste Manager - "Why should consumers pay for waste when producers could?" Tracey Goss from Kaituna Sawmill - "Sawmill team seeks sustainability, finds opportunity" Ruihana Lewis, Te Hoiere Project Te Pou Hapai Taiao for Ngati Kuia - "Restoring the mauri to our special places" 3) CKM submission to Natural and Built Environment Bill and Spatial Planning Bill. If interested you can check out a copy of our full submission put together by Tom Powell. These two new bills are part of an important revision of the existing Resource Management Act (RMA). 4) CKM submission to MDC - National Policy Statement of Freshwater Management. (NPSFM) In our submission we start with the following words - "We have an interest in how continuing climate and biodiversity degradation might impact the Marlborough community and how we can best prepare for the changing environment we all live in. The NPSFM has identified the four compulsory values, which are required to apply to freshwater management in Marlborough; ecosystem health, human contact, threatened species and mahinga kai. We agree with these values. Our main concern and focus is on and around “vision and values”. For us this relates primarily to ecosystem health, as we perceive the three other values to be secondary and totally reliant on the prioritising of that ecosystem health. Human contact and mahinga kai gathering need to be subservient so that the magnitude of these activities is governed by the needs of the ecosystem as a whole. Threatened species clearly have their threats reduced in a healthy ecosystem." You can read our full submission if interested. 5) Firm that makes fence posts from soft plastics to build Blenheim factory. "A New Zealand company that makes fence posts out of soft plastic will soon be manufacturing its products in the South Island. That means collection points for the Soft Plastics Recycling Scheme are expected to be re-established across Nelson and Marlborough. Future Post managing director Jerome Wenzlick said the company started making fence posts nearly five years ago in Auckland, using soft plastic waste. "We've built all our own machinery and figured out how to use all the different types of waste plastic that no one else can use and get our production up so we can make a post that's the same or better than wood, which is what we're up against." It is now experiencing strong demand for its products across the country, particularly from wineries in the top of the South Island." Check out the full article on the RNZ website. You can also learn more about Future Post on their website. NATIONAL 6) Huntley power station transition from coal to biomass. Genesis Energy have just completed trials to demonstrate the technical viability for using 100% biomass as a renewable fuel option for the existing three Rankine units. The trial has been done using 1000 tonne of black torrefied wood pellets imported from Canada. Black pellets (often referred to as biocoal) have been chosen because they are essentially a drop-in replacement for coal. The biomass must be ground to a consistency like talcum powder so needs to be hard. The fuel also must be able to be left uncovered in the rain without degrading. Black pellets are both hard and non-hydroscopic so large fuel storage sheds don’t have to be built. The pellets for the trial are not currently available in New Zealand but hopefully the success of these trials will encourage investment in a New Zealand based black pellet manufacturing facility. If black pellet fuel is available, the transition to biomass fuel will allow Huntley Power Station to remain in the electricity supply market providing a hydro firming insurance role which will allow greater sourcing of electricity from wind and solar resources. Scott Westbury from Genesis Energy is running a webinar on March 2nd at 2pm. This webinar will outline the opportunities for investment in processing wood residues from forest harvest and wood processing, into a high value biocoal. Fonterra has joined with Genesis Energy to investigate production of black pellets from local wood residues. Additionally, there is interest from steel makers who wish to replace their coal use, and other power station operators in Asia who are also seeking sources of biocoal. If you are interested you can learn more and register for the webinar here. 7) Environmental Law Initiative. The Environmental Law Initiative (ELI) are a registered charitable trust whose mission is to ensure the effective protection of New Zealand’s natural resources. They are advised by a small team of experts in environmental law, policy, science, ecology and management. I have been getting their newsletter and have been impressed with the successes they are having in the legal field. I am a strong supporter of using the legal system to challenge the powerful and the vested interests who too often put the needs of the environment low on their priorities list instead of at the very top where it must be if we are to retain a liveable planet. Check out their website and subscribe to their newsletter if you're interested. 8) Forest & Bird "Room for Rivers" campaign. Forest and Bird have recently launched their "Room for Rivers" campaign. If you're interested you can download a pdf file with info about the campaign. With increasing risk of extreme rainfall events associated with climate change it must be time to look seriously at this option being highlighted by Forest and Bird with a national campaign titled "Room for Rivers". Countries such as The Netherlands have successfully reduced flooding risks by taking this sort of action and giving their waterways more room to move during high rainfall events. Following consultation with flood management experts and practitioners, Forest & Bird proposes the Government adopt three steps to kickstart improved river management in Aotearoa and better protect communities and wildlife:
9) IAG seeks three step plan for natural hazard prone New Zealand homes – commits to being part of the solution. This initiative from IAG was launched back in August last year. With the recent devastating flood and storm events in Auckland and from Cyclone Gabrielle this topic will be getting a lot more attention now! IAG is calling for three practical, collaborative steps to be taken which will lead to a real reduction in the flood risk faced by some of New Zealand’s most exposed communities. IAG New Zealand CEO Amanda Whiting says: “Climate change is a critical issue for our country and it’s already having serious impacts on the lives of New Zealanders through more frequent and intense storms, floods, droughts, wildfires and, in time, rising sea levels. “The most important thing we can do is ensure people are not placed in harm’s way and do not suffer the loss and disruption caused by a flood event. Avoiding the impact on lives and people’s wellbeing must be the priority." The three steps are:
Check out the full article. 10) Government baulks at raising carbon price as cost of living bites. Cabinet has rejected a move that would have raised petrol and electricity costs. But now big polluters can keep gaming the carbon system and banking cheap credits – potentially putting New Zealand’s climate goals in jeopardy. Under the Emissions Trading Scheme, big carbon emitters have to pay for every tonne of emissions – one of the Government’s major tools for doing its bit on global heating. Cabinet papers show the Government has gone against the advice of both the independent Climate Change Commission and Climate Change Minister James Shaw. Shaw recommended following the commission’s advice and letting the price of carbon rise – and stopping pumping extra credits into the market so frequently. That would have given big polluters more incentive to rein in planet-heating emissions, as heat waves, floods and droughts keep worsening. Instead, Cabinet has chosen to allow only small, inflation-linked price rises. Check out the full Stuff article. 11) The power of eDNA. This article from Forest and Bird is about the son of a CKM founding member Pete Wilkinson. It is written by Jazmine Ropner and titled "Meet the man determined to change the face of conservation in Aotearoa one genetic "barcode" at a time." "Hidden away among the beige warehouses where movies are made on Wellington’s Miramar Peninsula, Wilderlab scientists are testing an environmental DNA sample sent in from college students who sampled water from two streams in Fiordland National Park. The results are exciting – the Fiordland College students have discovered a previously unknown population of a rare native fish – the Gollum galaxias! This information will help local efforts to protect and restore the population’s habitat (see right). Environmental DNA is genetic material shed from living things into water, air, or soil. Samples can be taken from a local river, beach, or reserve and sent to a lab for analysis. Over the past three years, eDNA has been quietly sparking a change in conservation – and Wilderlab has been at the forefront of making the technology more accessible to New Zealanders. The company’s easy-to-use eDNA sampling kits and lab-testing service are allowing more New Zealanders to discover the full range of species living in their backyards. At the helm of the operation is founder and principal scientist Shaun Wilkinson. He started his working career as a chef in Palmerston North before moving to Wellington and discovering a passion for biology while studying marine science at University of Victoria." Check out the full article on the F&B website and more information on the Wilderlab website. 12) Environment Select Committee submission on the Sustainable Biofuels Obligation Bill. This is a follow up to an item I put in the August newsletter last year. This submission from the group "Low Carbon Kapiti" gives an good analysis of the serious issues associated with introducing a Biofuels Obligation in NZ. It looks at issues that have already arisen in jurisdictions overseas where Biofuels have been mandated and raises very important questions about how realistic it is for NZ to be attempting to introduce a regime that appears to have failed in the US, the EU and Brazil. Here is one example they highlight - Biofuels obligations create subsidy-dependent industries that then lobby against reform, change or government U-turns on those obligations. There is no market for liquid biofuels without government mandates, and these mandates do not make biofuels more affordable in the long run – their price is locked to global commodity prices for the crops they are made from. So once fuel suppliers invest in infrastructure for biofuels (e.g. tanks and pipes), they expect a return on their investment, and the only way to get that is if governments keep the legal mandates in place. The EU, Brazil and the USA are locked into this trap. This makes avoiding establishing biofuels obligations or mandates, rather than trying to reform them once they are in place, critical. Please note that the incoming Prime Minister Chris Hipkins announced that this policy was being canned for the time being giving the cost of living crisis as the main reason. Probably a good outcome even if for the wrong reason! 13) Food production in Aotearoa in a perilous state. You may find this short interview from RNZ interesting if you didn't hear it back in late November. Among striking points - Southland has a collosal dairy factory yet all of Southlands milk is trucked from Christchurch! .... a bit of extra profit trumps the multifarious emissions associated with the overuse of trucks. 14) Heat and eat - The climate impact of food. "The food system is responsible for up to one-third of global greenhouse gas emissions. It won’t show up on a supermarket docket, but the production, transport, packaging, refrigeration and distribution of food all add to the climate bill before it even makes it to our mouths. Some foods are much more emissions-intensive to produce than others, though, and that can change depending on where in the world you live and the production techniques used. Research devoted to working out the ‘cradle-to-grave’ emissions cost of all sorts of different foods is growing every day. Here in Aotearoa, researchers at Otago University published a New Zealand-specific food emissions database in 2020, that shows the huge differences between certain groups of food, and even items within those groups." This article from Stuff is presented in a visual format with easy to read graphs showing the emissions intensity of the different foods we eat. The data comes from an Otago University research project. 15) Degrowth. This is a topic getting plenty of attention is some circles at the moment. Here are three items from two NZ authors and below a link to an Al Jazeera site. Jack Santa Barbara from the "Our Climate Declaration" group has written a good article titled "Give progress a chance: Embrace degrowth." "Continuing to prioritise economic growth is not a recipe for being a good ancestor. Nor is it a recipe for human progress. A large and growing number of scholars from many disciplines, are advocating for a reorientation of our social and political priorities by abandoning economic growth as our overriding priority. Even some progressive economists are making these arguments. This degrowth movement argues for prioritising genuine progress in terms of both human wellbeing and ecological sustainability. Indeed, these scholars argue that abandoning economic growth is essential for achieving these more important objectives. While recognising the need for social and economic change, others, mostly economists and business leaders, argue that economic growth is essential to achieve human wellbeing and ecological sustainability. They cite examples of green growth with clean technologies as pointing the way forward. Obviously, both groups cannot be right; their views are mutually exclusive. Green growth and degrowth cannot both provide a guiding framework for a just and sustainable future. Which is most likely to be helpful?" Dr Catherine Knight has written an article in The Spinoff titled "Why combatting climate change means embracing degrowth" and another published on the Newsroom website titled "A pathway out of environmental collapse". Here is an extract: "The burning of fossil fuels and destruction of ecosystems through the extraction of resources has led to the precipice of a catastrophe. How do we step away from the precipice? Catherine Knight examines what 'degrowth' would look like in a New Zealand context. Many of us are aware by now that we are facing multiple crises: climate change being just one – warming and acidifying oceans, depleted soils, global habitat and biodiversity loss are among the others in this ‘polycrisis’. The Auckland floods have made us acutely aware of how vulnerable our cities are to the ravages of extreme weather, events predicted to become more extreme and frequent as the effects of climate change bed in. We know that this is not going to get better any time soon. There will be more floods, droughts and other weather events that will cause destruction, economic loss and human distress on a scale that we cannot yet imagine. Even the issues that affect us day to day, such as the cost of living, have at their root the unsustainability of our current economic system." The XR viewpoint is that "As 2022 comes to a close, it’s time to face some hard truths. 1.5°C is over, and intolerable suffering is on its way. COP has been co-opted by greenwashers and oil lobbyists, and cannot deliver the policies needed to minimise that suffering. Nothing less than total economic transformation is necessary now, meaning a move beyond the infinite growth model of capitalism to the sustainable model of degrowth. It is up to us, as part of a movement of movements, to normalise this idea, rather than the competing fantasy that technology and geoengineering will eventually save the day. Every day we wait, the suffering increases. We don’t have time for fairytales." XR have provided a link to the Al Jazeera YouTube site "All Hail the Planet" which is a series delving into the social, economic and political forces undermining meaningful global action on climate change - In this clip Ali Rae speaks with economic anthropologist Jason Hickel, economic sociologist Juliet Schor, and development economist Ndongo Samba Sylla about the concept of Degrowth. Jason Hickel concludes by saying - "Until we are able to break free from these growth imperatives, then we're going to be in a situation where we watch continued failure over the coming decades, even as climate breakdown worsens before our very eyes. And so it's important that we understand that this failure to address the problem is not some kind of mistake. There's a structural reason for it. And until we start talking about the underlying economic system then we're going to continue making that fundamental error." 16) More info in the hydrogen debate. Green Hydrogen: Why NZ's in the box seat. This item may be of interest to some on the ongoing topic of hydrogen and especially in the NZ context. The inaugural New Zealand Hydrogen Symposium (NZHS-1) took place recently. You can read about the event on the Otago University website and this report on the "Hereon" website after the event. It was a multidisciplinary forum for the latest research on hydrogen, and involved local and international experts, iwi, universities, government research agencies, policy and industrial partners. In this interview Kathryn Ryan from RNZ speaks with one of the symposium's convenors, Professor in the Department of Chemistry at the University of Otago, Sally Brooker, who says New Zealand should take advantage of making green hydrogen to produce chemicals, provide energy, and reduce emissions, and German engineer and professor at Hamburg University of Technology, Professor Martin Kaltschmitt. Heat pumps ‘up to three times cheaper’ than green hydrogen in Europe, study finds. “Green” hydrogen, made by splitting water with low-carbon electricity, is unlikely to emerge as a cheap replacement for gas boilers in homes across Europe, according to a new study. The research, published in the journal Energy Conversion and Management, concludes that a green hydrogen heating system would be roughly “two to three times more expensive” than one relying on electric heat pumps in the EU and UK. Decarbonising heat is a key goal for governments seeking to hit their climate targets and end their reliance on expensive gas, amid a global energy crisis. Heat pumps have been widely accepted by experts as the primary option for cutting the sector’s emissions. However, gas-industry lobbyists and conservative politicians in the EU and UK have continued to make the case for hydrogen. The new study explores a range of scenarios for cutting emissions from Europe’s heating systems. It concludes that a low-carbon transition that keeps costs down without causing excessive environmental damage is “only possible through electrification via heat pumps”. It found that “blue” hydrogen, which is made using gas with carbon dioxide (CO2) captured, would have been a cost-effective option for a small proportion of properties, based on gas prices at their pre-crisis levels. However, the high gas prices driving the global energy crisis would likely make heating buildings with “blue” hydrogen “less cost-competitive”, one of the study’s authors tells Carbon Brief. Check out the full article on the Carbon Brief website. 17) Why restoring long-distance passenger rail makes sense in New Zealand – for people and the climate. "The government has committed the country to decarbonisation targets that require significant cuts to transport-related emissions. But decarbonising long-distance travel is not part of the plan – the national rail operator KiwiRail remains focused on freight. For those living in larger urban centres with good public transport and biking infrastructure or in 15-minute neighbourhoods, there is far less need to own a car. To make the necessary cuts to transport emissions in our larger cities, we need to re-imagine car ownership as an option rather than a necessity. It might be a lot to lay on the humble train, but civilisation is in a tight spot. We need to collectively halve emissions by 2030, while also laying the groundwork for a truly sustainable future. This means wise use of resources – long-lasting, economical infrastructure based on proven technology, combined with renewable electricity. Trains do that." Check out the full article in The Conversation. INTERNATIONAL 18) Could hemp be a key tool in fight against climate change? In all the debates on how to curb climate change, hemp is hardly mentioned. Better known as cannabis, modern varieties of hemp are too weak to use as narcotics, but they are extremely efficient at absorbing and locking up carbon. Hemp is one of the fastest-growing plants in the world and can grow 4 metres high in 100 days. Research suggests hemp is twice as effective as trees at absorbing and locking up carbon, with 1 hectare (2.5 acres) of hemp reckoned to absorb 8 to 22 tonnes of CO2 a year, more than any woodland. The CO2 is also permanently fixed in the hemp fibres, which can go on to be used for many commodities including textiles, medicines, insulation for buildings and concrete; BMW is even using it to replace plastics in various car parts. Check out the full article. This associated research Paper is on "Carbon storage potential in natural fiber composites." The results in this study show that use of natural fibers in thermoplastics have great potential to act as sustainable ‘sink’ for atmospheric carbon dioxide and at the same time saving non-renewable resources. The importance and urgency to expedite research activities in this area can be further augmented by the fact that consumption of different kinds of composites is growing very rapidly in various applications. 19) COP15: Everything you need to know about the biodiversity negotiations in Montreal. For anyone wanting to learn more about the COP15 Biodiversity Conference, which was held in Montreal last December I found this website very informative for gaining some background understanding. The organisation is called "Edie" and their website says they are a trusted and integral part of the workflow of more than 100,000 sustainability, energy and environmental professionals. The website delivers daily news and commentary, exclusive interviews and research, industry reports and business guides, videos, webinars and podcasts. I was particularly interested in the proposal "to mandate nature-related disclosures for all large businesses this decade." The opportunities for "greenwashing" will of course be there but the intention seems good. In their report they say - "Global collaborative initiative Business for Nature has convened more than 330 businesses and financial institutions from 52 countries to engage with policymakers on matters relating to the private sector’s impacts on biodiversity. It wants to see a strong mission statement for a nature-positive world. Ahead of COP15, it is specifically campaigning for a strong agreement for the treaty to require nations to mandate nature-related disclosures for all large businesses this decade. This call to action is being made through the ‘make it mandatory’ campaign, whose supporters include Ikea, Nestle, Unilever and H&M Group. The mandate, the group argues, should cover all large businesses and financial institutions and should be coupled with a target for these actors to at least halve negative impacts. ‘Make it mandatory’ is part of a broader set of recommendations from Business for Nature, which can be seen in full here. edie recently interviewed Business for Nature’s executive director Eva Zabey to find out more about these recommendations, including why there is such strong business support and what the final treaty would look like in an ideal situation." The United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) website provides a summary of the outcomes of the Conference. Here is an extract: The Global Biodiversity Framework (GBF) consists of four overarching global goals to protect nature, including: halting human-induced extinction of threatened species and reducing the rate of extinction of all species tenfold by 2050; sustainable use and management of biodiversity to ensure that nature’s contributions to people are valued, maintained and enhanced; fair sharing of the benefits from the utilization of genetic resources, and digital sequence information on genetic resources; and that adequate means of implementing the GBF be accessible to all Parties, particularly Least Developed Countries and Small Island Developing States. United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) Executive Director, Inger Andersen, emphasized that implementation is now key: “Success will be measured by our rapid and consistent progress in implementing what we have agreed to. The entire UN system is geared to support its implementation so we can truly make peace with nature.” The GBF also features 23 targets to achieve by 2030, including:
20) Addressing Climate Change Will Not “Save the Planet”. A group of conservationists took up the question of climate and extinctions last year in the journal "Conservation Letters", warning that “threats to biodiversity are increasingly seen through the single myopic lens of climate change.” The authors, who titled their article “An inconvenient misconception: Climate change is not the principal driver of biodiversity loss,” included Joel Berger, a wildlife biologist at Colorado State University; evolutionary biologist Andrew Dobson, who teaches at Princeton; and Tim Caro, an evolutionary ecologist at the University of California, Davis. “There is an assumption,” they observed, “that climate change is now the most important ‘horseman of the biodiversity apocalypse’” — despite this being “at best premature.” When it comes to effects on wildlife, climate change is more like a mule, slow and plodding. Yes, a warmed atmosphere is projected to be a significant factor in the extinction crisis in future decades, but what’s destroying species today is habitat fragmentation and loss, overhunting and overexploitation, agricultural expansion, pollution, and industrial development. It isn’t climate change that caused a 69 percent loss in total wildlife populations between 1970 and 2018, according to a World Wildlife Fund study published this year. The cause is too many people demanding too much from ecosystems, or human overshoot of the biophysical carrying capacity of the Earth. Overshoot is a product of both excessive numbers and rising affluence. Access to the things that create what we call quality of life, like indoor lighting and temperature controls, especially air conditioning; more diverse dietary choices, especially meat; and greater access to transportation, especially air travel — all signs of rising affluence, all delightful if you are a human, yet all demand more energy and material inputs that involve scouring and denuding more wildlands and animal habitat to feed, clothe, house, and energize burgeoning humanity. According to the co-authors of the Conservation Letters piece, we are “dangerously ignoring” this reality and instead doubling down on the “distortion” that climate mitigation is all that matters to protecting wildlife. Over the last 30 years, the proportion of scientific papers closely tying climate change and global warming to changes in patterns of biodiversity has “steadily increased,” according to their analysis. Media coverage of climate change in relation to biodiversity has followed suit, repeating and compounding the error. The net result of this “misguided focus on climate change” has been the undermining of conservation science “as an evidence-based scientific discipline.” As Dobson put it to me, “If conservation biologists don’t take a balanced look at the evidence, they can’t claim to be evidence-based.” The crux of the problem is that mainstream environmentalists have siloed climate change as a phenomenon apart from the broad human ecological footprint, separate from deforestation, overgrazing of livestock, megafauna kill-off, collapsing fisheries, desertification, depleted freshwater, soil degradation, oceanic garbage gyres, toxification of rainfall with microplastics, and on and on — the myriad biospheric effects of breakneck growth. Climate change is “but one symptom of an environmentally dysfunctional system of constant growth of economies and populations,” ecologist William Rees, professor emeritus at the University of British Columbia, told me. “The meta-problem that we need to keep our eyes on,” Rees said, is ecological overshoot. Modern techno-industrial culture, he writes, “is systematically — even enthusiastically — consuming the biophysical basis of its own existence.” Rees describes this as a malignant process, humanity as cancer. Check out the full article on The Intercept website. 21) The Future of Food and Agriculture in a low emissions world. This is a topic with a wide range of views. I wanted to do my best to provide any interested readers with a range of information from different sources. Agriculture, especially animal farming is a significant contributor to global emissions and we have to face up this fact if we seriously wish to achieve living in a carbon zero world by 2050. The first report is one published by Rethinkx. I have included material from this organisation in a previous newsletter and this report from 2019 is titled "Rethinking Food and Agriculture 2020-2030 - The Second Domestication of Plants and Animals, the Disruption of the Cow, and the Collapse of Industrial Livestock Farming." It presents a convincing case for the disruptive potential of Precision Fermentation (PF) for producing food protein and in particular animal protein both meat and dairy. I have also come across a counter perspective that provides an equally convincing case arguing that the Rethinkx report has misrepresented the energy and input costs of producing protein in this way. For those who are interested in the growing interest in this technology and the big claims being made by some I recommend reading further. You will have to make up your own mind about the different claims being made. Here is an extract from the Executive Summary of the Rethinkx report: We are on the cusp of the deepest, fastest, most consequential disruption in food and agricultural production since the first domestication of plants and animals ten thousand years ago. This is primarily a protein disruption driven by economics. The cost of proteins will be five times cheaper by 2030 and 10 times cheaper by 2035 than existing animal proteins, before ultimately approaching the cost of sugar. They will also be superior in every key attribute – more nutritious, healthier, better tasting, and more convenient, with almost unimaginable variety. This means that, by 2030, modern food products will be higher quality and cost less than half as much to produce as the animal-derived products they replace. The impact of this disruption on industrial animal farming will be profound. By 2030, the number of cows in the U.S. will have fallen by 50% and the cattle farming industry will be all but bankrupt. All other livestock industries will suffer a similar fate, while the knock- on effects for crop farmers and businesses throughout the value chain will be severe. This is the result of rapid advances in precision biology that have allowed us to make huge strides in precision fermentation, a process that allows us to program micro- organisms to produce almost any complex organic molecule. These advances are now being combined with an entirely new model of production we call Food-as-Software, in which individual molecules engineered by scientists are uploaded to databases – molecular cookbooks that food engineers anywhere in the world can use to design products in the same Food&Agriculture way that software developers design apps. This model ensures constant iteration so that products improve rapidly, with each version superior and cheaper than the last. It also ensures a production system that is completely decentralized and much more stable and resilient than industrial animal agriculture, with fermentation farms located in or close to towns and cities. This rapid improvement is in stark contrast to the industrial livestock production model, which has all but reached its limits in terms of scale, reach, and efficiency. As the most inefficient and economically vulnerable part of this system, cow products will be the first to feel the full force of modern food’s disruptive power. Modern alternatives will be up to 100 times more land efficient, 10-25 times more feedstock efficient, 20 times more time efficient, and 10 times more water efficient. They will also produce an order of magnitude less waste. Modern foods have already started disrupting the ground meat market, but once cost parity is reached, we believe in 2021-23, adoption will tip and accelerate exponentially. The disruption will play out in a number of ways and does not rely solely on the direct, one-for-one substitution of end products. In some markets, only a small percentage of the ingredients need to be replaced for an entire product to be disrupted. The whole of the cow milk industry, for example, will start to collapse once modern food technologies have replaced the proteins in a bottle of milk – just 3.3% of its content. The industry, which is already balancing on a knife edge, will thus be all but bankrupt by 2030. This is not, therefore, one disruption but many in parallel, with each overlapping, reinforcing, and accelerating one another. Product after product that we extract from the cow will be replaced by superior, cheaper, modern alternatives, triggering a death spiral of increasing prices, decreasing demand, and reversing economies of scale for the industrial cattle farming industry, which will collapse long before we see modern technologies produce the perfect, cellular steak. Chris Smaje who has a blog in the UK called Small Farm Future has published a critique of the Rethinkx report written by a guest writer he called Steve L. and titled FOOD MANUFACTURED IN FACTORIES VS. FOOD GROWN ON FARMS. Steve challenges the ReThinkx claim that - “Our analysis uses sugar (glucose) as the main feedstock, with efficiency trending from 3kgs of feedstock per 1kg of protein produced (a conversion ratio of 3:1) toward a ratio of less than 2:1 by 2030. There is also scope for other carbohydrates to be used for feedstock.” (page 65 - “Rethinking Food and Agriculture 2020-2030”) In Steve L's report he outlines the topic as follows "There are apparently two main approaches to these manufactured foods: biological and chemical. The biological approach includes ‘precision fermentation’ and cell-based meat, and the chemical approach (including ‘power to food’) typically starts with the electrolysis of water to obtain hydrogen which is used to make tryglycerides or other edible compounds." In his report he references a variety of reports and analyses the Rethinkx claims, essentially arguing that they are not supportable by the evidence, and quoted “David Humbird, a UC Berkeley-trained chemical engineer who spent over two years researching the report and found that "the cell-culture process will be plagued by extreme, intractable technical challenges at food scale. In an extensive series of interviews with The Counter, he said it was “hard to find an angle that wasn’t a ludicrous dead end.” Humbird likened the process of researching the report to encountering an impenetrable “Wall of No”—his term for the barriers in thermodynamics, cell metabolism, bioreactor design, ingredient costs, facility construction, and other factors that will need to be overcome before cultivated protein can be produced cheaply enough to displace traditional meat.” If you wish check out Steve L's full report. Below is an extract from another article challenging the claims being made for Precision Fermentation etc. This is a long and thorough analysis of the issues associated with producing lab-grown meat and the very real challenges likely to be faced by those planning to radically scale up production of these products. It is written by Joe Fassler from The Counter website. He quotes Paul Wood, a former pharmaceutical industry executive with extensive experience in precision fermentation processes used to manufacture vaccines and other scientists with experience in the PF field. Wood knows from his experience how extremely technical, resource-intensive, and expensive the processes are and doesn't understand how costly biomanufacturing techniques could ever be used to produce cheap, abundant human food. Joe Fassler says: "But the truth is this: For cultured meat to move the needle on climate, a sequence of as-yet-unforeseen breakthroughs will still be necessary. We’ll need to train cells to behave in ways that no cells have behaved before. We’ll need to engineer bioreactors that defy widely accepted principles of chemistry and physics. We’ll need to build an entirely new nutrient supply chain using sustainable agricultural practices, inventing forms of bulk amino acid production that are cheap, precise, and safe. Investors will need to care less about money. Germs will have to more or less behave. It will be work worthy of many Nobel prizes—certainly for science, possibly for peace. And this expensive, fragile, infinitely complex puzzle will need to come together in the next 10 years. On the other hand, none of that could happen." and “It’s a fable driven by hope, not science, and when the investors finally realize this the market will collapse.” and "But Renninger finds it “frustrating” to see so many resources going into cultured meat. “It is a zero-sum game, to a certain extent,” he said. Money we spend chasing cultured meat is money we can’t use on converting coal plants to biomass, or scaling solar and wind, or modernizing concrete and steel. There’s a reason that the U.S. government employs people like Humbird to do rigorous due diligence on attractive new ideas. When billions are spent on science that doesn’t come together, the biggest losers aren’t really the private companies and trade associations, or the class of professional investors who get rich on speculative tech. Instead, the public loses out—and we lose time we don’t have. As Humbird put it, “If society pays for it and it doesn’t work out, then society’s left holding the bag.” The environmental ravages we face are vast, destabilizing, and encroaching on our real lives right now. The fires, the floods, are already at our door. In all this, it would be so good to know we have a silver bullet. But until solid, publicly accessible science proves otherwise, cultured meat is still a gamble—a final trip to the casino, when our luck long ago ran out. We should ask ourselves if that’s a chance we want to take." Check out the full article from The Counter website. 22) Lab-made milk: getting the creaminess without the climate pollution. Here is an extract from another article where claims are being made that large scale production of lab-grown dairy products are inevitable. For 10,000 years, we’ve done the same thing to produce a drink of milk. Farms have cleared land to grow grass, raised cows, impregnated the animals, taken the calves aside, and milked their herds. Over that time, consumers developed a considerable appetite for cows’ milk, which appears in everything from yoghurt and cheese to biscuits, chocolate and sports shakes. But in the past 50 years, we’ve spotted something going very wrong with the climate, and now we’re left with limited time to avoid catastrophic consequences. And the source of dairy milk – methane-belching cows – is a significant contributor to that problem, particularly in Aotearoa. That knowledge led dairy experts, food scientists and biologists – including a number of Kiwis – to invest in a different way to produce milk. Instead of using a large, sentient mammal to make dairy, Matt Gibson uses microorganisms. The resulting food offers an appealing climate benefit: zero planet-heating methane being belched into the atmosphere. You can check out the full article from Stuff and another article titled "Is precision fermentation the future for food?" offering a counter view in the NZ context. 23) Vertical Farming Has Found Its Fatal Flaw. Europe’s energy crisis is forcing companies to switch strategies or close down. The industry’s future hangs in the balance. Just six months ago, the vibe from Europe’s biggest vertical farm company was unrelentingly optimistic, so what changed? According to Cindy van Rijswick, a strategist at the Dutch research firm RaboResearch, several pressures that have always existed for vertical farms have really come to a head in 2022. For starters, the industry is extremely vulnerable to increases in electricity prices. Powering all of those plant-growing LEDs uses a lot of electricity, and between December 2020 and July 2022 consumer energy prices in the EU went up by nearly 58 percent. Eighteen months ago, European vertical farms might have spent around 25 percent of their operational costs on electricity, but that might have gone up to around 40 percent, estimates van Rijswick. You can check out the full article on wired.com 24) Is There Enough Metal to Replace Oil? This item looks at trying to address some of the big unanswered questions about just what quantities of minerals we have to access to make a transition from a fossil fuelled to a renewable energy world and what economically accessible reserves we currently know about. In the article they say in answer to the question "Is there enough metal to replace oil? - The short answer: No, not even close! Nations of the world are only too aware that fossil fuels need to be phased out for two reasons. First, oil is a finite commodity. It’ll run out in time. Secondly, fossil fuel emissions such as CO2 are destroying the planet’s climate system. However, a recent study puts a damper on the prospects of phasing out fossil fuels in favor of renewables. More to the point, a phase out of fossil fuels by mid century looks to be a nearly impossible Sisyphean task. It’s all about quantities of minerals/metals contained in Mother Earth. There aren’t enough. Simon Michaux, PhD, Geological Survey Finland has done a detailed study of what’s required to phase out fossil fuels in favor of renewables, to wit: “The quantity of metal required to make just one generation of renewable tech units to replace fossil fuels is much larger than first thought. Current mining production of these metals is not even close to meeting demand. Current reported mineral reserves are also not enough in size. Most concerning is copper as one of the flagged shortfalls. Exploration for more at required volumes will be difficult, with this seminar addressing these issues.” (Source: Simon P. Michaux, Associate Research Professor of Geometallurgy Unit Minerals Processing and Materials Research, Geological Survey of Finland, August 18, 2022 – Seminar: What Would It Take To Replace The Existing Fossil Fuel System?) THE PAST – “An industrial ecosystem of unprecedented size and complexity, that took more than a century to build with the support of the highest calorifically dense source of cheap energy the world has ever known (oil) in abundant quantities, with easily available credit, and unlimited mineral resources.” (Michaux) THE PRESENT – “We now seek to build an even more complex system with very expensive energy, a fragile finance system saturated in debt, not enough minerals, with an unprecedented number of human population, embedded in a deteriorating environment.” (Michaux) Current mineral reserves are not adequate to resource metal production to manufacture the generation of renewable energy technology, as current mining is not even close to meeting the expected demand for one generation of renewable technology. The article highlights how easy it is to make big plans and claims for how we could phase out fossil fuels without asking the critical questions about what resources Papatuanuku can actually realistically provide for us. We have to face up to the fact we all live on Spaceship Earth with a finite quantity of resources available to us and somehow learn to live within our means. They provide the following figures. No doubt some new reserves will be discovered and maybe new ways of accessing minerals like lithium will be developed such as extracting it economically from geothermal fluids but it still appears as if there are some major obstacles ahead looking at these figures. The total metals required for one generation of technology to phase out fossil fuels is listed by Required Production followed by Known Reserves for all metals based upon tonnes, as follows: Copper 4,575,523,674 vs. 880,000,000 – a serious shortfall -reserves only cover 20% of requirements. Zinc 35,704,918 vs. 250,000,000 – adequate reserves. Manganese 227,889,504 vs 1,500,000,000 – adequate reserves Nickel 940,578,114 vs. 95,000,000 – huge shortfall – reserves 10% of requirements. Lithium 944,150,293 vs. 95,000,000 = huge shortfall – reserves 10% of requirements. Cobalt 218,396,990 vs. 7,600,000 – huge shortfall – reserves 3.48% of requirements. Graphite 8,973,640,257 vs. 320,000,000 = huge shortfall – 3.57% reserves of requirements. Silicon (metallurgical) 49,571,460 – adequate reserves Silver 145,579 vs. 530,000 – adequate reserves Vanadium 681,865,986 vs. 24,000,000= huge shortfall -3.52% reserves of requirement Zirconium 2,614,126 vs.70, 000,000 – adequate reserves. Check out the full article on the Countercurrents.org website. This website has useful information and a graph showing historic lithium production up to 2021. Here are a couple of other relevant articles well worth a read in my opinion if you're interested in the subject of Limits to Growth. They are from the Australian "Pearls and Irritations" website. The first is headed "Reduce consumption, or face reality of civilisational collapse" by Mark Diesendorf. The second is titled "The dilemma of economic growth" by Jan Bruck. 25) Richard Heinberg - The renewable energy transition is failing. This article provides additional information about challenges we face transitioning from fossil fuels to renewables. “The transition from fossil fuel to renewables faces an uphill battle. Still, this switch is an essential stopgap strategy to keep electricity grids up and running, at least on a minimal scale, as civilization inevitably turns away from a depleting store of oil and gas. The world has become so dependent on grid power for communications, finance, and the preservation of technical, scientific, and cultural knowledge that, if the grids were to go down permanently and soon, it is likely that billions of people would die, and the survivors would be culturally destitute. In essence, we need renewables for a controlled soft landing. But the harsh reality is that, for now, and in the foreseeable future, the energy transition is not going well and has poor overall prospects.We need a realistic plan for energy descent, instead of foolish dreams of eternal consumer abundance by means other than fossil fuels. Currently, politically rooted insistence on continued economic growth is discouraging truth-telling and serious planning for how to live well with less.” They make the interesting statement that - "A French preliminary analysis of the energy transition that assumed maximum possible recycling found that a materials supply crisis could be delayed by up to three centuries. But will the circular economy (itself an enormous undertaking and a distant goal) arrive in time to buy industrial civilization those extra 300 years? Or will we run out of critical materials in just the next few decades in our frantic effort to build as many renewable energy devices as we can in as short a time as possible?" Check out the full article on the resilience.org website. 26) The call to put ‘a price on nature’ can be appealing – but it misunderstands what’s at stake. In this Guardian article Jeff Sparrow says - In a piece for The Conversation, the academic John Henneberry explains how when we price nature: "We apply numbers to those features that we consider important, or that are measurable, or both, and we ignore or exclude other features that don’t meet these criteria. […] As a result of it, nature appears more fragmented because we have to slice it into categories and dice those categories into bits before we can value bits of those bits. The sum of these parts is far short of the whole and does not capture the interconnectedness and holism of nature.” In a context in which we don’t even know how many unique species exist on the planet (estimates range from 5.3 million to 1 trillion, with only 1.6 million of them identified and named), the author Adrienne Buller describes as an extraordinary fantasy the notion that “the biosphere can be readily segmented and ‘unbundled’ into discrete units which can subsequently be individually valued, speculated upon, and exchanged, abstracted entirely from the specifics of time and place.” It’s a point also made in the open letter, which insists: "The monetary values being produced do not represent the value of nature’s ecological functions, not even a proxy. Yet misleading figures are not better than nothing but worse than nothing, as they can lead to wrong policy decisions with irreversible consequences. The monetary valuation of nature’s ecological functions can also give a dangerous and misleading illusion of substitutability between critical ecosystemic functions, where one assumes incorrectly that as long as the total monetary value remains stable, nature is in good shape.” Substitutability is invariably the point of environmental pricing: by transforming the unique components of a biosphere into abstractions as exchangeable as dollars or Euros, it facilitates processes like offsetting, so that destruction in one place can be “compensated” by investment elsewhere. The NZ website "The Conversation" published another good article by John Henneberry on this topic in 2018 titled "How the neoliberal obsession with valuing nature changes our understanding of it". 27) Carbon Brief. I have been getting regular summaries from the organisation Carbon Brief. They provide some excellent up to date material on a wide range of climate and energy related matters. You can subscribe on their website if you're interested. Here is a brief description from their website. - "Carbon Brief is a UK-based website covering the latest developments in climate science, climate policy and energy policy. We specialise in clear, data-driven articles and graphics to help improve the understanding of climate change, both in terms of the science and the policy response. We publish a wide range of content, including science explainers, interviews, analysis and factchecks, as well as daily and weekly email summaries of newspaper and online coverage." 28) 2022 Climate Data summary from Carbon Brief. Carbon Brief recently published its now-customary January deepdive into the key climate data from the previous year. Dr Zeke Hausfather, our climate science contributor, examined and explained all the latest metrics from across the oceans, atmosphere, cryosphere and surface temperature of the planet. His “state of the climate” review showed that 2022 was the warmest year on record for ocean heat content (chart above) and that the past eight years at the planet’s surface have been the warmest since records began in the mid-1800s. Last year also saw a diverse range of extreme weather events across the globe, as CO2, methane and nitrous oxide levels all reached new record highs. Antarctic sea ice also set a record for its lowest extent. Looking ahead, Zeke predicted that global average surface temperatures in 2023 are most likely to be slightly warmer than 2022 – but are unlikely to set a new all-time record given lingering La Niña conditions in the first half of the year. Check out the full article for their complete 2022 "State of the Climate" report. 29) A plan for human survival. Julian Cribb is an Australian science author and author of six books on the human challenge. His latest books on the human future are “Surviving the 21st Century” and “Food or War” and his most recent publication "How to Fix a Broken Planet." If, like me, you believe we have reached the point where we are living on a Broken Planet that is in urgent need of some major repairs and you have reached the end of this newsletter then you may be interested to read the following article from Julian. Here is an extract published recently on the Australian website Pearls and Irritations. "The existential emergency in which all humanity now stands has been building steadily for over half a century. Our capacity to inflict mass harm on ourselves through our own actions has increased exponentially since the end of WWII. We’ve wiped out two thirds of the world’s large animals, we’re losing water, topsoil, fish and forests at appalling rates, we poison everyone and everything on the planet every day; we’re constructing weapons able to obliterate ourselves many times over. We’re shaping a climate that can render the Earth largely uninhabitable within a few generations. We’re building dangerous technologies over which society has no control. We throw away half our food and ruin the planet trying to grow more. We unleash new plagues every few years and spread them worldwide like wildfire. And we lie, constantly and continually, to ourselves about it all. These are not the actions of a wise species. Or even, maybe, an intelligent one. Our governments and corporations seem paralysed, unable to grasp the magnitude of the overwhelming, interlinked risks that are engulfing us. The ten megathreats are: extinction and ecological destruction; resource scarcity; global poisoning; a hothouse Earth; new nuclear arms race; pandemic disease; food insecurity; overpopulation; uncontrolled technologies and a global deluge of misinformation about them. Because they are all connected, none of these threats can be tackled on its own. They must all be tackled together. All of them are consequences of the sheer scale of the human enterprise – overpopulation, overconsumption, overpollution and money are the chief drivers. Mostly, they stem from the 101 billion tonnes of resources we now devour every year to support our ‘lifestyle’ – 12 tonnes each – and the damage this process unleashes on the planet and ourselves. The good news is that solutions to all these threats already exist." Check out the full article on the Pearls and Irritations website. Nga mihi nui, Budyong. 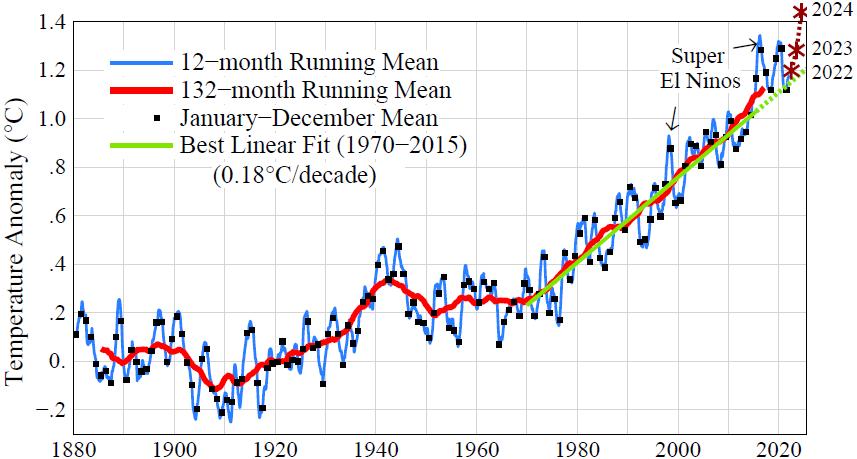 November 2022 CKM Newsletter LOCAL 1) Media articles written by CKM member Tom Powell since the last newsletter. 10/10/2022 - Don't export our electricity - we need it here. 15/10/2022 - To grow or to degrow? That is the question 29/10/2022 - Every one of us will be personally touched by climate change 12/11/2022 - Did the Government get agricultural emissions levy plan right? 2) Three Waters discussion. An extra meeting was organised in August to provide the opportunity for CKM active members to discuss the issues surrounding the 3 Waters debate. As a result a letter of support was put together and sent to the Mayor, Councillors, MDC CEO, Minister David Parker, Minister Nanaia Mahuta and MP Stuart Smith. The summary of the letter stated - "This is a critical time for rebuilding the partnership between central and local government. While central government provides standards and support, we believe it needs to avoid dictating how local and regional communities and institutions apply their different solutions to their own care of New Zealand waters. Cooperation, forbearance and flexibility will be key. In particular, from a local viewpoint, we support the position of the Marlborough District Council as laid out in its submission dated the 20 July, 2022 to the Finance and Expenditure Committee on Water Services Entities Bill. We expect clarity and transparency in public of all governmental decision-making. Finally, we comment that nobody can own water any more than we own the air we breathe; rather, we owe water, air and the land we stand on due care and responsibility. Otherwise, climate, land, sea and the planet altogether will make their own decisions for us and despite us, as we have all been experiencing at home and abroad." The full text of the letter can be read here if you're interested. 3) CKM Submission on Agricultural Emissions Pricing. A submission was written by Tom Powell and Don Quick on this complex subject. Here is the preamble to give you a feel for our thinking on this matter. “In addition to submitting within the framework of the “15 set questions” of the Ministry for the Environment (MfE), we have extracted our answer to question 15 (other priority issues), embedding it within this explanatory supporting preamble statement. Central to CKM’s common concern for our environments, local, national and global, is the belief that all of humanity that relies on industrial technology must seek a new way of thinking about and acting in our relationship with our planet. Although most people acknowledge that we can no longer continue to regard our environment as separate from us, as simply a source of goods from which we can extract what we want without return, the fact is that we continue not only to abuse the environment on which our wellbeing relies but to poison it with our waste. CKM takes the warnings of the environmental sciences with regard to global warming and biodiversity loss as both serious and critically urgent. CKM sees no evidence of new ways of thinking in the document on “pricing agricultural emissions” on which we are submitting. Therefore, we are not willing to relegate our priorities to the last box of what appears to us to be a box-ticking exercise. We have responded to the “set questions”, as requested, worrying that if we don’t answer the questions, our thoughts, and our priorities, will simply be relegated to the box ticked “Other”. “ Check out the full submission on our website if you’re interested. 4) Climate Action Week, February, 2023. Catherine van der Meulen joined us at our October meeting to talk about her plans to organise a Climate Action Week from Monday 13th - Friday 17th February next year. She informed us that the organising group are hosting a "Garden Marlborough" style event where a number of organisations in our community become hosts to open their doors/ gates/ cellars etc to our local business community to come and learn in their environment about the diverse work that they are doing to create a Climate Positive Business and Community. They also plan to have short talks/presentations on a range of topics at the different hosting businesses. We are having ongoing discussions with Catherine about how CKM members may be able to contribute. The Marlborough Express has committed to publishing information about the event in the New Year. 5) Earth Day, 2023. Envirohub Marlborough are organising another annual Earth Day event next year. It is scheduled to for Sunday 30 April, 2023. More information will be available in the New Year. 6) Progress with Proposed Marlborough Environment Plan. (PMEP) An update was presented to the Environment and Planning Committee of the Council on November 24th on progress with the appeals to the PMEP. Since the last report to the Planning, Finance and Community Committee on 8 September 2022, the Environment Court has issued nine consent orders. These consent orders are for the Natural Hazards, Heritage, Energy, Landscape, Transportation, Climate Change, Nuisance and Utilities topics. The completion of this process for the Climate Change chapter is of interest to CKM. There were some minor appeals in the Climate Change chapter, most of which were from the aquaculture industry wanting more explicit acknowledgement of ocean acidification issues within the chapter. For example one Anticipated Environmental Result (AER) stated "The community’s understanding of the effects of climate change and sea level rise improves over time." The wording has been changed to "The community’s understanding of the effects of climate change, sea level rise, and ocean acidification improves over time. The associated "Monitoring Effectiveness" statement for that AER stated "The results of research into the local effects of climate change and sea level rise are reported to the Council. Environmental data, including climate and flooding, is collected and reported to the Council to establish long term trends." The wording has been changed to "The results of research into the local effects of climate change and sea level rise, and ocean acidification are reported to the Council. Environmental data, including climate, flooding and ocean pH, is collected and reported to the Council to establish long term trends." The full, final Climate Change chapter, Chapter 19, can be downloaded on the Council website here along with other chapters for anyone interested. 7) Update on Wairau Aquifer discussions with Council staff. Budyong, Don and Dave recently met with Council staff members, Pere Hawes and Hans Versteegh for a discussion about the Wairau Aquifer and the issues arising from the identified declining recharge. This is part of our ongoing communications with Council staff about this matter and follows on from our report on this topic in the August newsletter related to the Gravel Bed Rivers research and water allocation from the aquifer. We have documented our discussions in a report to the CKM meeting. This report plus further correspondence on this matter can be found on our website if you’re interested in this topic. NATIONAL 8) Ocean acidity rising in New Zealand coastal waters. The Stats NZ report, based on NIWA data, showed acidity has increased 8.6 percent between 1998 and 2020. It's caused by the ocean absorbing carbon dioxide from the air, which can dissolve the shells of pāua, mussels and other kaimoana. NIWA principal marine biogeochemist Dr Cliff Law said the increase is "alarming", but the trend has been observed for some time. Ocean acidity has increased by 30 percent over the last 250 years, and will increase by up to 150 percent by the end of the century, Law said. Check out the full article. 9) Green CO2 for Horticulture - A Kiwi innovation. Hot Lime Labs was founded in 2017 using technology originally developed at Callaghan Innovation. Dr Vlatko Materic, founder and CEO of Hot Lime Labs, had been researching and working on CO2 capture systems for large scale thermal power plants for over a decade at the former government research institute, Industrial Research Limited – now Callaghan Innovation. It was during this time he developed the Hot Lime capture technology. The technology showed great promise for this application, however, the economic drivers did not exist for power plant operators to justify the additional costs of installing and operating CO2 capture system using the technology. Fast forward 10 years and Vlatko discovered the vast unmet demand for clean CO2 in the greenhouse industry and quickly found that both technology and commercial drivers were well aligned. The Hot Lime Labs CO2 capture system converts wood waste biomass into clean CO2 for commercial greenhouses, increasing crop productivity and growth. The system currently converts a range of wood waste into CO2 through our novel process. In future, the system will broaden to be able to convert other waste biomass such as crop waste, waste oils and anaerobic digester gases. We can also potentially help you out if you have large quantities of problematic biomass to deal with. Check out the website for more info. 10) Zero Jet – Another Kiwi innovation. The world’s lightest electric jet tender. The innovative ZeroJet system is safe, easy to use, compact and quiet but most importantly, environmentally friendly, and emission-free. ZeroJet is the first jet propulsion system to be designed specifically for an electric motor, delivering the perfect balance of performance and runtime. Alongside the material and technical development journey of ZeroJet, some powerful comparisons have been made to the automotive industry, to gauge the impact of traditional petrol-powered outboard motors on the marine environment. In short, taking one 20hp four-stroke outboard off the water is the equivalent of taking 150 cars off the road - and that’s something we’re striving to have a hand in. Our plans include partnering with more boat builders, expanding internationally, and developing systems for larger 5m and 6m tenders, all working towards our ultimate audacious goal of eliminating the need for combustion engines on small watercraft. Check out their website. 11) NZ expresses active interest in joining German ‘climate club’. This is an interesting development and might be a sign of how trading between nations may change in the years ahead. The issue I see is that I'm don’t think NZ can be categorised as "steaming ahead" or in the "vanguard" yet! The issue of emissions from animal farming in particular is still unresolved, and we seem to be over reliant on planting trees and buying overseas credits to meet our Paris obligations. Hardly the sort of actions I would describe as revolutionary. I guess we have to live in hope that the legal framework that is now in place in NZ will bring about the necessary changes in behaviour etc that we need to actually reduce emissions. New Zealand has expressed interest in joining a German climate initiative to collaborate on decarbonising industry and harmonise carbon prices across borders, according to Climate Change Minister James Shaw. The climate club would aim to rectify the unfair situation by creating a trading bloc of ambitious countries who could freely exchange goods without concerns about emissions leakage. Meanwhile, non-members would face carbon tariffs when trying to trade in emissions-intensive goods with any members of the bloc. As James says "After a while, the countries that are steaming ahead are going to look sideways at the countries that are dragging the chain and say, why are we doing all the heavy-lifting here?" he said. "I think that you will start to see trade advantage accrue to those countries that are in the vanguard." Check out the full article. 12) Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment letter to PM. I was interested to read that the office of the Parliamentary Commissioner for the Environment, headed by Simon Upton sent a letter to the government after the Prime Minister made a statement to Parliament on Feb 8th this year where she said – “NZ is uniquely placed to become a world leader in hydrogen production using renewable energy, creating new export opportunities, high wage jobs and regional industries.” Green hydrogen production may well be part of the mix in the future for powering heavy transport vehicles, ships etc but the Commissioner raises some very pertinent questions as to whether we should be considering large scale green hydrogen production here in NZ. In the letter the PCE made the following points – There was a presumption that green hydrogen was a good idea without first doing an energy system analysis.
If you are interested for more info check out the full letter. 13) The Dry Year Myth and a Critique on Lake Onslow concept. EnergyWatch publishes issues once or twice a year with a range of very interesting and well researched articles. The July issue from this year has an analysis of the Lake Onslow proposal and whether it is the best solution for meeting renewable electricity production targets in dry years. It suggests that the multi-million dollar “New Zealand Battery” study is using a sledgehammer to crack a nut. They say that study appears founded on the premise that the Lake Onslow scheme is the only way to future-proof electricity supply in NZ, a premise they wish to challenge. Summary
The EnergyWatch report is comprehensive and unequivocal in it’s opposition to the Lake Onslow project. If you are interested in the details you can download the full report. Forest and Bird also published an article on this subject in September. In the article they conclude -
Check out the full article. 14) Electricity Privatisation Delivers “Excess Dividends” At Cost Of People And Planet. It’s great to see a growing awareness in NZ of the dysfunctional nature of our electricity sector. This new report “Generating Scarcity; How the gentailers hike electricity prices and halt decarbonisation” co-authored by FIRST Union, the NZCTU and 350 AotearoaNZ argues that since the partial-privatisation of our electricity companies, the four big gentailers have delivered billions in excess dividends to shareholders and thereby are starving the market of investments in renewables. “We’re trapped in a toxic cycle whereby gentailers have a perverse incentive to keep fossil fuels in the grid which hikes power prices, enables them to make record profits, and distribute excess dividends which again prevents new generation from being built. We will not see an end to this unless the Government sets the right levers and uses its power as a majority shareholder in the electricity generation market.”, said Feldmeier. The Executive Director of the climate justice organisation said, “There is large interest among communities in Aotearoa to contribute in meaningful ways to climate change mitigation. 350 Aotearoa calls for expanding public participation in the renewable energy transition and the broader functioning of the energy sector.” Check out the full article. 15) Cellular Agriculture information in the NZ context. The Office of the Prime Minister’s Chief Science Advisor has a section on their website with information about Cellular Agriculture and a “Cellular Agriculture Resource Portal”. It is put together by Dr Olivia Ogilvie who is the granddaughter of dear friends of ours from when we lived on the Kapiti Coast in the 2000’s. If you are interested in this topic you can check out the website. INTERNATIONAL 16) Climate crisis: past eight years were the eight hottest ever, says UN. I’m making a real effort in this newsletter to limit the number of items highlighting how serious the Climate Crisis has become. We all know the situation is worsening each year so I’ve only chosen two that report on recent concerning research. Both of them were released before the COP 27 talks in Egypt and reading them will serve to accentuate the issues facing life on Planet Earth, now that we know how little was achieved at the talks. It really does seem that the COP conferences are too cumbersome and too easily influenced by fossil fuel lobbyists with bottomless pockets for us to have any hope that the big decisions necessary for ensuring real emissions reductions, can be made in a timely manner. Here is a quote from the first article - Prof Mike Meredith, at the British Antarctic Survey, said: “The messages in this report could barely be bleaker – all over our planet, records are being shattered as different parts of the climate system begin to break down. The loss of ice is especially alarming as the impacts on people, societies and economies are huge. If this doesn’t focus the minds of the global leaders at COP27, I don’t know what will.” Check out the full article. 17) NASA Studies Find Previously Unknown Loss of Antarctic Ice. New research on Antarctica, including the first map of iceberg calving, doubles the previous estimates of loss from ice shelves and details how the continent is changing. The greatest uncertainty in forecasting global sea level rise is how Antarctica’s ice loss will accelerate as the climate warms. Two studies published Aug. 10 and led by researchers at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California reveal unexpected new data about how the Antarctic Ice Sheet has been losing mass in recent decades. One study, published in the journal Nature, maps how iceberg calving – the breaking off of ice from a glacier front – has changed the Antarctic coastline over the last 25 years. The researchers found that the edge of the ice sheet has been shedding icebergs faster than the ice can be replaced. This surprise finding doubles previous estimates of ice loss from Antarctic’s floating ice shelves since 1997, from 6 trillion to 12 trillion metric tons. Ice loss from calving has weakened the ice shelves and allowed Antarctic glaciers to flow more rapidly to the ocean, accelerating the rate of global sea level rise. The other study, published in Earth System Science Data, shows in unprecedented detail how the thinning of Antarctic ice as ocean water melts it has spread from the continent’s outward edges into its interior, almost doubling in the western parts of the ice sheet over the past decade. Combined, the complementary reports give the most complete view yet of how the frozen continent is changing. Check out the full article. 18) Vanuatu, one of the most climate-vulnerable countries, launches ambitious climate plan. The Pacific country of Vanuatu has launched one of the world’s most ambitious climate policies, committing to 100% renewable energy in electricity generation by 2030 and ambitious targets on loss and damage. The announcement signals yet another instance of the small island state making its mark in international climate efforts. At last year’s UN climate summit in Glasgow, all countries were urged to “revisit and strengthen” their nationally determined contributions (NDCs) on climate action by the end of 2022. Vanuatu is one of just 12 countries to have done so, and its ambitious targets have been praised by regional experts. Check out the full article. 19) Vanuatu formally launches push for Fossil Fuel Non-proliferation Treaty Vanuatu is calling on other nations to join it in establishing a fossil fuel non-proliferation treaty. This has been proposed as an international mechanism to address the source of 86 percent of the CO2 emissions that cause climate change. The President of Vanuatu Nikenike Vurobaravu, made the historic call in September at the United Nations General Assembly. Check out the full article. If you haven’t already done so you may wish to endorse the Fossil Fuel Non-Proliferation Treaty. On the website they say -
20) Energy charter treaty makes climate action nearly illegal in 52 countries. This recent development in Europe is very interesting. It is unbelievable to me that there is an international agreement that gives fossil fuel companies the right to sue governments for profits lost as a result of policy changes. Why did anyone ever sign such an agreement. Anyway it’s good to see momentum growing within Europe to withdraw from the Treaty. Here is an extract from one of the articles about this issue. The three coalition parties forming the German government on Friday agreed the country should leave the Energy Charter Treaty, making it the biggest economy to announce it's quitting the embattled deal. "We are consistently aligning our trade policy with climate protection and are withdrawing accordingly from the Energy Charter Treaty," Franziska Brantner, a parliamentary state secretary in the economy and climate ministry, said in a press release. The pact, designed in the 1990s, allows international investors in energy projects to sue governments for profits lost as a result of policy changes. It’s now viewed as a major threat to national climate plans to shut down coal plants or limit production of oil and gas. The decision follows announcements from France, Spain, the Netherlands, Slovenia and Poland that they will withdraw from the pact. It is a major blow to the deal and also to the European Commission, which has urged countries to back reforms to the treaty. The Commission completed a negotiation with other treaty members this summer that would give the EU an exemption to phase out protections for fossil fuel projects in the EU over the next 10 years. Check out the full article and this article from The Conversation and this article about France’s withdrawal from the Treaty. 21) Where now with climate in Australia? The government is proceeding with its $20 billion “powering the nation” plan. This will strengthen the electricity grid so it can handle much larger amounts of power from renewable sources. It will open the way to more grid investment at the state level and large investment by private enterprise in wind and solar power and energy storage. As part of this, an initiative set up in principle by the Coalition but not followed through should lead to big private investment in offshore wind power. Bruce Mountain, a leading energy economist at Victoria University, says that to achieve Labor’s 43 percent emissions reduction largely through the electricity system, Australia needs to add 45 gigawatts of wind and solar generation and 15 GW of storage by the end of this decade. These are serious numbers with a serious cost: around $115 billion. For perspective, since 2010 we have installed 32 GW of renewable generators and just one GW of storage. Check out the full article. 22) Twelve angry children: young jurors call adults to account for climate crisis in The Trials. I thought this play called “The Trials” that was staged in London in August was a great way to highlight the issues facing young people in our dysfunctional world. Dawn King’s new play at the Donmar imagines a reckoning for environmental chaos, presided over by the kids who inherit the mess. We join the writer and cast, including stars of Heartstopper, in rehearsal. The play imagines a world a few decades into the future where a group of people are on trial, Nuremberg-style, for their culpability in the climate crisis. How many flights did they take? Did they eat meat? Sure, they recycled, but so what? The penalties for exceeding personal carbon allowances are severe; the jurors are played by teenagers who have inherited the mess. The defendants are clearly stand-ins for the rest of us, who have fiddled while Rome (and many other places) burned. Check out the full article. 23) Give legal rights to animals, trees and rivers, say experts. We must make major and essential changes if we are to return the Earth and all its amazing ecosystems to a healthy state. To do this we have to find new ways of living on our planet that prioritise the needs of nature. This will not only benefit us and our descendants but all other life forms, the life giving air we breathe and water, the elixir of life. The next four items look at different ways of running our economy and interacting with Nature. A report released in October and titled “Law in the Emerging Bio Age” looks at how we can use the legal framework to help achieve this aim. Granting legal rights and protections to non-human entities such as animals, trees and rivers is essential if countries are to tackle climate breakdown and biodiversity loss, experts have said. The authors of a report titled Law in the Emerging Bio Age say legal frameworks have a key part to play in governing human interactions with the environment and biotechnology. Ecuador and Bolivia have already enshrined rights for the natural world, while there is a campaign to make ecocide a prosecutable offence at the international criminal court. The report for the Law Society, the professional body for solicitors in England and Wales, explores how the relationship between humans and mother earth might be recalibrated in the future. Dr Wendy Schultz, a futurist and report co-author, said: “There is a growing understanding that something very different has to be done if our children are going to have a planet to live on that is in any way pleasant, much less survivable, so this is an expanding trend. Is it happening as fast as any of us would want? Possibly not, which is why it’s important to get the word out.” Check out the full article. If you’re interested you can download the full report and a three page summary. 24) It's time to give up on growth - why degrowth is the key to our future. An Opinion piece published on the Stuff website recently was written by Deidre Kent who is a lifelong NZ environmental activist. Deidre gives a very clear explanation of why we need to change our planetary operating system. Degrowth is a planned and democratic reduction of unnecessary production in rich countries designed to bring the economy back into balance with the living world in a safe and equitable way. Check out the full article. 25) ‘A new way of life’: the Marxist, post-capitalist, green manifesto captivating Japan. I found this article well worth a read. It addresses the growing belief that our whole economic system requires a major overhaul if we seriously want to halt the Climate and Biodiversity Crisis. Here is an extract. The climate crisis will spiral out of control unless the world applies “emergency brakes” to capitalism and devises a “new way of living”, according to a Japanese academic whose book on Marxism and the environment has become a surprise bestseller. The message from Kohei Saito, an associate professor at Tokyo University, is simple: capitalism’s demand for unlimited profits is destroying the planet and only “degrowth” can repair the damage by slowing down social production and sharing wealth. In practical terms, that means an end to mass production and the mass consumption of wasteful goods such as fast fashion. In Capital in the Anthropocene, Saito also advocates decarbonisation through shorter working hours and prioritising essential “labour-intensive” work such as caregiving. “We face a very difficult situation: the pandemic, poverty, climate change, the war in Ukraine, inflation … it is impossible to imagine a future in which we can grow the economy and at the same time live in a sustainable manner without fundamentally changing anything about our way of life. “If economic policies have been failing for 30 years, then why don’t we invent a new way of life? The desire for that is suddenly there.” Check out the full article. 26) The Global Carbon Reward policy. Here is another policy that is being promoted as an effective way of rewarding those who reduce carbon emissions. The important aspect of this policy in my opinion is that the carbon currency cannot function as a carbon offset credit. Emitters must reduce actual emissions to receive the reward rather than offsetting their emissions by paying someone else to sequester carbon. Offsetting, especially on the international market, is too difficult to monitor to ensure there is no corruption and double dipping. In the Wikipedia entry about this policy they state - “The global carbon reward is not a carbon offset credit. A carbon offset is a recorded reduction in CO2 or other greenhouse gas emissions that is used to compensate for emissions made elsewhere. The reward is issued as a currency that does not convey ownership of the mitigated carbon. All of the mitigated carbon that is awarded will be immediately retired from carbon markets and will be held by the authority for the policy, called the carbon exchange authority. They go on to say - “The global carbon reward is a proposed international policy for establishing and funding a new global carbon market for decarbonising all sectors of the world economy, and for establishing and funding a new economic sector dedicated to carbon dioxide removal (CDR). The policy is market-based, and it will offer proportional financial rewards in exchange for verifiable climate mitigation services and co-benefits. The policy approach was first presented in 2017 by Delton Chen, Joël van der Beek, and Jonathan Cloud to address the 2015 Paris Agreement, and it has since been refined. The policy employs a carbon currency to establish a global reward price for mitigated carbon. The carbon currency will not convey ownership of mitigated carbon, and consequently the carbon currency cannot function as a carbon offset credit. The carbon currency will function as a financial asset and incentive. A supranational authority is needed to implement the policy and to manage the supply and demand of the carbon currency. This authority is referred to as the carbon exchange authority. One of the authority's key functions is to coordinate the operations of major central banks in order to give the carbon currency a guaranteed floor price. A predictable rising floor price will attract private investment demand for the currency, and it will transfer a significant portion of the mitigation cost into currency markets. The policy will not result in any direct costs for governments, businesses or citizens. Consequently, the policy has scope to create a new socioeconomic pathway to achieve the goals of the Paris Agreement.” Check out the full Wikipedia entry. 27) An African initiative to reduce transport emissions. BasiGo is an e-mobility start-up looking to revolutionize the transportation sector by providing public transport to bus owners with a cost-effective, electric alternative to diesel. BasiGo’s K6 electric bus is the first of its kind in Kenya. The 25-seat K6 electric bus allows operators in Kenya the freedom from diesel, improved reliability, comprehensive monitoring, and an improved experience for passengers. The company has been piloting the K6 electric bus with a few partners and more recently, has collaborated with Kenya's largest commercial bank to finance buses for public transport operators. In just a few months, BasiGo’s K6 bus has driven over 100,000 km and transported more than 130,000 passengers, all with less than one day of downtime. And the company has already received over 100 reservations for electric buses from owners. Through their pay-as-you-drive program, BasiGo is making EVs as accessible and affordable as traditional diesel buses by financing the value of the battery separate from the value of the bus. Owners purchase the electric bus and then lease the battery from BasiGo through a subscription fee based on kilometers driven. The subscription service also includes nightly charging of the battery, all service and maintenance expenses for the bus, customer care, and roadside assistance, as well as free battery replacements in the event of an issue. BasiGo’s simplified business model gives owners peace of mind and accelerates the transition for Kenya’s transportation system by making the upfront price of the electric bus equal to a diesel bus. Check out their website for more information. 28) James Hansen's August Temperature update. Here is the sobering prediction for global temperatures over the next couple of years, from James Hansen and his team published in September this year. The past three months were remarkably warm on global average – remarkable because this is a La Nina year, when the cool phase of the El Nino Southern Oscillation keeps the low latitude Pacific Ocean relatively cool. These three months – Northern Hemisphere summer – were each at or near records for the month, despite the La Nina. Every month this year has been warmer than the same month last year, even though the present La Nina is as deep as last year. Our interpretation is that the current warmth is spurred by the record Earth energy imbalance, which in turn is spurred by rapid growth of greenhouse gases, reduction of human-caused aerosols, and the rising phase of the solar irradiance cycle. NOAA and the relevant scientific community predict that the La Nina will continue at least through this coming winter, for a third consecutive year. El Nino/La Nina are the largest cause of global temperature variability on the time scale of a few years and they are notoriously difficult to predict more than a few months ahead. Nevertheless, we have some inside information, which encourages us to hazard a prediction for the next three annual mean global temperatures – we might then learn something from comparison with future reality. Prediction of the annual 2022 global temperature is child’s play at this point: the final four months this year should average higher than the same months last year, so the 12-month running mean at the end of this year will have ticked up to about the level in 2017. That will put 2022 in approximately a dead heat with 2017 for 4th warmest year in the record. The next year, 2023, will be warmer because of the present strong planetary energy imbalance, which is driven by the factors noted above – mainly increasing greenhouse gases. Perhaps an El Nino will begin in the second half of the year, but the El Nino effect on global temperature lags by 3-4 months. So, the 2023 temperature should be higher than in 2022, rivalling the warmest years. Finally, we suggest that 2024 is likely to be off the chart as the warmest year on record. Without inside information, that would be a dangerous prediction, but we proffer it because it is unlikely that the current La Nina will continue a fourth year. Even a little futz of an El Nino – like the tropical warming in 2018-19, which barely qualified as an El Nino – should be sufficient for record global temperature. A classical, strong El Nino in 2023-24 could push global temperature to about +1.5°C relative to the 1880-1920 mean, which is our estimate of preindustrial temperature. 29) Countries’ climate pledges built on flawed data, Washington Post investigation finds. I’ve included this article as it underlines one of the big issues I believe we all face with dealing with the Climate Crisis. It is an example of something becoming well known now – GREENWASHING. It is very understandable that countries and businesses easily succumb to the temptation to use creative accounting and selective data selection to paint a rosy picture but unfortunately unless GHG emissions stop rising and start falling very soon we will all have to face the consequences. Malaysia’s latest catalogue of its greenhouse gas emissions to the United Nations reads like a report from a parallel universe. The 285-page document suggests that Malaysia’s trees are absorbing carbon four times faster than similar forests in neighbouring Indonesia. The surprising claim has allowed the country to subtract over 243 million tons of carbon dioxide from its 2016 inventory — slashing 73 percent of emissions from its bottom line. The plan to save the world from the worst of climate change is built on data. But the data the world is relying on is inaccurate. “If we don’t know the state of emissions today, we don’t know whether we’re cutting emissions meaningfully and substantially,” said Rob Jackson, a professor at Stanford University and chair of the Global Carbon Project, a collaboration of hundreds of researchers. “The atmosphere ultimately is the truth. The atmosphere is what we care about. The concentration of methane and other greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is what’s affecting climate.” “In the end, everything becomes a bit of a fantasy,” said Philippe Ciais, a scientist with France’s Laboratory of Climate and Environmental Sciences who tracks emissions based on satellite data. “Because between the world of reporting and the real world of emissions, you start to have large discrepancies.” The emissions reports are so unwieldy that the United Nations does not have a complete database to track country emissions. Some 45 countries have not reported any new greenhouse gas numbers since 2009. Ultimately, it’s not the politics, the accounting or the pledges that will determine how much the planet warms but the hard numbers of atmospheric science: the parts per million of greenhouse gases in the air. Check out the full article 30) Global carbon inequality over 1990–2019 This research paper takes a close look at the different contributions that individuals make towards global carbon emissions and proposes some progressive ways of making high emitters pay their fair share. In the paper the author Lucas Chance says - All humans contribute to climate change but not equally. Here I estimate the global inequality of individual greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions between 1990 and 2019 using a newly assembled dataset of income and wealth inequality, environmental input-output tables and a framework differentiating emissions from consumption and investments. In my benchmark estimates, I find that the bottom 50% of the world population emitted 12% of global emissions in 2019, whereas the top 10% emitted 48% of the total. Since 1990, the bottom 50% of the world population has been responsible for only 16% of all emissions, whereas the top 1% has been responsible for 23% of the total. While per-capita emissions of the global top 1% increased since 1990, emissions from low- and middle-income groups within rich countries declined. Contrary to the situation in 1990, 63% of the global inequality in individual emissions is now due to a gap between low and high emitters within countries rather than between countries. Finally, the bulk of total emissions from the global top 1% of the world population comes from their investments rather than from their consumption. These findings have implications for contemporary debates on fair climate policies and stress the need for governments to develop better data on individual emissions to monitor progress towards sustainable lifestyles. If you’re interested you can check out and download the full research paper. 31) Australia climate inaction violated Torres Strait Islanders' rights, U.N. says. A United Nations committee found on Friday that Australia had violated the human rights of a group of islanders off its north coast by failing to adequately protect them from the impacts of climate change, such as by cutting greenhouse gas emissions. The complaint, filed over three years ago by eight Torres Strait Islanders and their children, is one of a growing body of climate cases being brought around the world on human rights grounds, and the ruling is expected to embolden others. Rising sea levels have already damaged food sources and ancestral burial sites, scattering human remains, the islanders argued, saying their homes are at risk of being submerged. Check out the full article. 32) Seawater-splitting system could scale-up renewable hydrogen production. Here is an extract from an article with encouraging information about a new technology for producing hydrogen gas from sea water rather than relying on fresh water resources. Saltwater could be used to produce green hydrogen using a system that combines electrochemical water splitting with forward osmosis. The approach could allow up-scaling of hydrogen fuel production using the planet’s predominantly salty natural water sources without pre-treatment or purification. Using solar energy to electrochemically split water into oxygen and hydrogen, akin to how plants photosynthesise, shows much promise for renewable energy. The hydrogen that’s liberated can then be mixed with carbon dioxide to make hydrogen fuels. ‘The beauty of the work is that there are no moving parts or extra energy inputs required here, just an inexpensive semipermeable membrane,’ comments Mark Symes, who investigates electrocatalysis at the University of Glasgow. ‘It’s definitely one of those papers that makes you wonder, “How come no one thought of that before?” I would not be surprised to see rapid development of this idea into a large-scale system for electrolysis in untreated water.’ Check out the full article. 33) First Solid Form Hydrogen Propulsion Vessel Ordered for Amsterdam. The construction contract has been awarded for a hydrogen demonstration vessel that will use a new solid form hydrogen for propulsion that researchers believe will pave the way for a safer and broader application of hydrogen to fuel vessels. Known as Neo Orbis, the demonstration vessel is expected to start trials in June 2023 as the next phase in the multi-year European H2Ships program. The construction contract for the Neo Orbis was awarded to Next Generation Shipyards in the Netherlands. The tender process for the vessel’s construction began in March 2022. The vessel will be approximately 65 feet long similar to the tour boats that have operated in Amsterdam for years transporting passengers and offering sightseeing excursions. It is designed to operate both in Amsterdam’s canals as well as the seaport area between Amsterdam and Ijmuiden. According to the project organizers, it will become the first ship in the world sailing on electricity, propelled with hydrogen in a solid form as the energy carrier. The fuel is made by mixing sodium borohydride powder with a stabilizer and ultrapure water into an aqueous non-combustible liquid fuel. The dissolved sodium borohydride reacts with a catalyst, producing hydrogen while the spent fuel is converted back to sodium borohydride. In the long term, the project envisions creating a closed system, by turning the residual materials into new sodium borohydride fuel. Check out the full article. 34) New System Retrofits Diesel Engines to Run on 90 Per Cent Hydrogen. A Team from UNSW Engine Research Laboratory have developed a new Hydrogen-Diesel Direct Injection Dual-Fuel System that significantly cuts carbon emissions. They have successfully converted a diesel engine to run as a hydrogen-diesel hybrid engine – reducing CO2 emissions by more than 85 per cent in the process. They say the most immediate potential use for the new technology is in industrial locations where permanent hydrogen fuel supply lines are already in place. That includes mining sites, where studies have shown that about 30 per cent of greenhouse-gas emissions are caused by the use of diesel engines, largely in mining vehicles and power generators. Check out the full article. 35) What does water want? Most humans seem to have forgotten. If you’ve got to the end of this newsletter congratulations. My eldest sister in Perth, WA recently sent me this article which I wanted to share. Here is an extract - “Most modern humans have forgotten that fresh water’s true nature is to flex with the rhythms of the earth, expanding and retreating in an eternal dance upon the land. It’s hard to feel these rhythms when rivers and streams are buried and hurried away via concrete pipes or canals. In fact, water is inclined to linger to a degree that would shock most of us because our conventional infrastructure has erased so many of its slow phases: floodplains, wetlands, mountain meadows and forests. The climate crisis can seem overwhelming, but Slow Water empowers people to make their own communities more resilient. Such projects can simultaneously buffer us from flooding and drought, slow climate change via natural carbon sinks, and support other forms of life, which in turn helps water systems maintain themselves. At the scale of home, town and watershed, we can bring back into our human habitats small, connected pieces of wildness where water can freely interact with land once again. These more natural places can also cultivate more peaceful spaces within us, and greater personal adaptability. Slowing ourselves to observe the nuances of our environment – the ebb and flow of water, the growth and decay of plants, the behaviours of other animals – is meditative and joyful. These are invitations to get curious; to ask: ‘What does water want?” Check out the full article. Cheers, Budyong. Here is another selection of items from Marlborough, NZ and worldwide for your interest. I would like to start with a thought provoking quote from the Surplus Energy Economics website. "No amount of financial stimulus, and no rise in price, can produce resources which do not exist in nature. We can lend and print money into existence, but we cannot similarly create the low-cost energy without which the economy cannot function. The reality is that prosperity is a material concept, understandable only in terms of resources in general, and of the “master resource” of energy in particular. As a recent reappraisal by Gaya Herrington confirms, the authors of The Limits to Growth (LtG) were right when, back in 1972, they modelled the Earth as an inter-connected system, and found definite material limitations to expansion. In the narrower fields of economics and finance, it’s becoming ever clearer that we have been living through a quarter-century precursor zone during which the potential for further growth has been exhausted. What we are experiencing now is the disruption which attends the ending of this transitional phase, and the onset of involuntary economic contraction." LOCAL 1) Gravel Bed Rivers (GBR) research on Wairau River and Aquifer. A presentation was made to the MDC Environment Committee on June 15th providing them with the latest information arising from the GBR research program which started in 2019. The purpose of this latest report was "To provide an update to the Committee on research results from the national Gravel Bed Rivers project investigating the hydraulic connection between braided gravel rivers and alluvial aquifers." In their Executive Summary they state - "The prime reasons for the ongoing decline in Wairau Aquifer well levels is less Wairau River water available for recharge and a reduction in the capacity of the natural pathways to move water from the river into the aquifer. This is compounded by demand in some drier seasons." This is not really an unexpected conclusion when we know the river has been modified severely from it's original natural course and is now contained within stopbanks. It is interesting to note that the research team think that water extraction from the river and aquifer is not a major contributor to the ongoing decline trend and that it is the reduced recharge that is of the greatest significance. The research team have proposed - "Having established a conceptual model of how the river-groundwater system work, the river-groundwater system will be modelled more accurately than previously. A model will be used to test the sensitivity of the river-groundwater water balance to riverbed elevation, scouring, and floodway width. The results will be used as a basis for a cost-benefit analysis to see how changes to current river management would impact the local economy." If effective solutions can not be found to stop the decline in the aquifer the consequences for those growing and processing grapes and others who rely on this water for their operations and livelihoods will, in time, be considerable. Add to this the prediction that we are likely to experience hotter and drier summers due to global warming and it is not hard to imagine serious impacts for Marlborough in the decades ahead. I recommend reading the full Executive Summary if you wish to understand more clearly the dynamics of the reduced aquifer recharge process proposed by the research team. It is of further concern to read that "The decline in Wairau Aquifer levels is consistent with widespread deepening of wells over the past 35 years at least. Deepening wells improves individuals access to groundwater but will not prevent aquifer fed springs from drying up as they rely on shallow groundwater breaking the surface for their existence." At the same meeting MDC Groundwater Scientist Peter Davidson also presented the annual Groundwater Quantity State of Environment report. One bit of information from the report (page 12) stood out for me. Peter believes that "based on an extrapolation of the current rate of flow recession, Spring Creek will recede to State Highway 1 by about the year 2100 and by association all of the springs including in Blenheim." I see this as concerning information. One thing our communications with MDC staff have highlighted is that there is not enough evidence of the actual volumes of water being drawn out of the aquifer by water users to ascertain yet how much this water use is impacting the declining trend in the aquifer, as actual water use has only been metered for the last 5 years or so. The lower Wairau aquifer has 3 Freshwater Management Units (FMU's). Levels are set, that if reached, will trigger restrictions for water users in those areas. For anyone interested you can view the Graphs showing the cut-off levels for the Northern (Wratts Rd), Central (Mills and Ford Rd) and Urban (Murphy's Rd) springs FMU's. You can also access the graphs showing long term data from the monitoring wells on the council website here. I have analysed some data supplied by MDC and it is interesting to note that in the dry years of 2015, 2019 and 2020 the aquifer level in the Northern (Wratts Rd) monitoring bore was only 50 - 60mm above the restriction level. This is the bore closest to the Spring Creek headwaters and therefore the best indicator of likely impacts on the springs. In communication with council staff we have learned that there are restrictions on all Wairau Aquifer Sectors except for the Lower Wairau and what they call the Recharge Sector of the main aquifer, which is a large proportion of the total aquifer. The reason the Recharge Sector has no restrictions currently is that MDC weren’t confident at the time of writing the MEP (Marlborough Environment Plan) that they had sufficient understanding of whether reducing cumulative abstraction would result in any benefits on downstream groundwater fed spring flows. They also say the pMEP restrictions are currently 100 % reliable but due to the declining trend in Wairau Aquifer levels restrictions are likely to become permanent at some point in the future, which is why MDC is focusing on what they call “alternative approaches to managing seasonal and boundary effects.” We are not clear what that actually means so will need to do some more research to learn more. It seems that any actions arising from the GBR research, to try and reduce or stop the declining trend in the aquifer are likely to be very expensive and to take decades to prove their worth. Suffice it to say it seems clear that this issue will be ongoing and not easy to resolve. The pMEP restriction regime is currently subject to appeals which should be heard some time in 2023. Maia Hart has also done a good article on the GBR report in Stuff where she says - "New research suggests historic work to narrow the Wairau River could be contributing to declining levels in the recharge aquifer – one of Marlborough’s main water sources. The Wairau aquifer is the main groundwater system underlying the Wairau Plain and a source of irrigation, drinking and stock water. Water seeping from the Wairau River into the aquifer is the main ways it is recharged. Its levels have dropped since 1973, at rates unable to be explained by irrigation." 2) Wairau Aquifer no longer over allocated. MDC put out a media release on June 1st announcing "The Wairau Aquifer Freshwater Management Unit (FMU) allocation status has recently changed from over allocated to having allocation available. This change in allocation is a result of recent water take permit expiries and the application of reasonable use calculations through the provisions of the Proposed Marlborough Environment Plan (PMEP)." CKM have had some communications with council and staff about the wisdom of allocating any extra water that becomes available from the aquifer. We wondered if it would be prudent to apply the precautionary principle and have a moratorium on new water allocations until the GBR research is completed, and recommendations and decisions are made about the amount of water reasonably available without seriously impacting the springs and whether the current restrictions levels set in the aquifer may need altering. Unfortunately we have been informed that if water becomes available under current settings they have a legal obligation to make it available. 3) Communications with new F&B Top of the South manager, Scott Burnett and Environment Minister David Parker. I recently wrote a letter to David Parker asking him if there was any allowance in the Resource Management legislation for a moratorium on water allocation for the Wairau Aquifer.. Here is an extract from his reply - "As the Minister for the Environment, I am responsible at a high level for freshwater, however any regulations are the responsibility of councils who determine what consents to issue in accordance with their current regional plan rules. The Marlborough District Council is progressing with the requirement to give effect to the NPS-FM (National Policy Statement - Freshwater Management) in their plan by December 2024, and when they notify their updated plan ahead of that date, I encourage you to make a submission as that is the best mechanism to formally have your say." CKM will want to look at putting a submission in to the council when the time arises. I also met with Scott Burnett who has recently been appointed to replace Debs Martin as the Top of the South manager for Forest & Bird. It was good to meet and establish a connection and we've agreed to work together and network when appropriate. Scott is keen to connect us with the F&B national Freshwater advocate Tom Kay. When the time comes to submit to council on the NPS-FM it would be good for us to combine knowledge and resources. Tom is currently working on a "Room for the River" campaign for F&B and the Wairau would be a perfect example of the detrimental consequences that can result from river containment. I have also received an email from a CKM member, James Wilson, with a link from the Newsroom website to a long and interesting article on this topic, titled "NZ on the cusp of a rivers revolution". You may be interested to see it and read James' contribution in the "comments" section at the bottom. 4) CKM presentation on The Treaty of Waitangi and the 1835 Declaration of Independence. CKM member Don Quick gave a very informative and well received presentation at a recent monthly meeting. For anyone interested you can access the recording here - The password is: PH2!^$ex 5) Top of the South Organic Waste Mapping Study. Have you heard about "insect conversion technology"? Here is some info about an initiative for the Top or the South region to better utilise our food waste. They say one man’s trash is another man’s treasure. Organic waste management is currently a significant cost to the Top of the South community and could be reduced by embracing a multi-sector collaborative upcycling strategy across the region, according to a recent study. An organic waste mapping study jointly funded by Marlborough Research Centre (MRC) and Agricultural and Marketing Research and Development Trust (AGMARDT) found that total volumes in the Top of the South are in excess of 700,000 tons per year. “We now have a comprehensive inventory of the available bio-resources (waste streams) which is a valuable starting point from which to develop regional strategies and multi-sector business opportunities to reduce and upcycle waste,” says MRC’s Chief executive Gerald Hope. The study was led by Plant & Food Research. “The study covered the Marlborough, Nelson and Tasman regions and its purpose was to identify what organic material the Top of the South has to offer for bioconversion technologies and the key stakeholders,” says Project Leader Dr Damian Martin, Science Group Leader -Viticulture & Oenology, Plant & Food Research, who is based at MRC’s Budge Street campus. “The conclusions of the report are promising with respect to the opportunity for an insect bioconversion project in the Top of the South.” Key figures -
6) Sea level rise: we have less time to act than we thought, by Tim Naish. The Nelson Tasman Climate Forum "Climate Action Week" grew out of a response to the Emissions Reduction Plan released earlier this year. One of the guest speakers they organised was Tim Naish who is Professor in Earth Sciences, at the Antarctic Research Centre at Victoria University. He has leadership roles on the world climate research programme, the scientific committee on Antarctic research and the Antarctic science platform. He has extensively researched sea level rise resulting from global warming of oceans and ice melting, including melting of the Antarctic ice sheets. Tim co-leads the NZ Sea Rise Research Programme working with 30 experts to provide specific estimates of expected sea level rise. This work connects vertical land movement data with climate-driven sea level rise data to forecast locally relevant sea level changes. It includes site specific forecasts for Nelson and Tasman. (I had an item on this in the last newsletter). In this webinar Tim clearly explains the implications for Nelson and Tasman of sea level rise and land movement. Though he did not focus on Marlborough the information is still very interesting for better understanding some of the impacts expected in Te Tauihu. 7) Wireless electricity for the masses could become a reality thanks to Kiwi startup. "Wireless electricity may sound like science fiction - but the founder of a Kiwi startup says one day it may be as common as receiving a text. The technology could allow remote areas like Stewart Island to receive electricity from the mainland, or a homeowner in Germany to buy New Zealand electricity. About 15 minutes from New Plymouth, Auckland-based startup Emrod, with the support of NZ’s future energy centre, Ara Ake, and Powerco, has begun construction on its first outdoor demonstration site for wireless power-beaming technology. Electricity will be converted into an electromagnetic beam between two antennas a few hundred metres apart at the site which is expected to be running by the end of June." This is an interesting technology though I do wonder what the outcome for innocent birds flying through the energy beam would be and whether there might be other unforeseen consequences? They say in the Stuff article - "...the technology has layers of safety, including being placed up high to avoid people crossing through the beam, and having a ‘safety curtain’ that will switch the beam off if anything crosses it." NATIONAL 8) National Climate Adaptation Plan released. Long-term adaptation goals.
A summary is available on the MfE website and the full Plan can also be downloaded there. MBIE have also published information on their website where they say - We need to change how we do things so we can thrive in a different climate to the one we've had in the past. Some areas in New Zealand won't be suitable for building and decisions need to be made about how to limit damage to existing buildings. This will require some changes to the way the building and construction sector operates.Over the next six years, the Building for Climate Change programme will lead the following actions in the National Adaptation Plan:
9) Co-creating a pathway to survival. The Pathway to Survival website has some interesting info and webinars available. It has been set up by a group of people from within Extinction Rebellion (XR) groups in Aotearoa who want the government to take urgent decisive action on the intersecting crises of ecosystem collapse, climate and social injustice and colonisation. 10) Hospital Retires Coal Boilers for Health. DETA Consulting were recently commissioned to assess the best option for converting the Timaru Hospital from burning coal for their process heat requirements to a low emissions alternative. Below are are some extracts from their report on the DETA Consulting website about this project. This is a good example of how a mix of technologies can be used to replace coal burning for process heat. Even before the New Zealand Government mandated carbon neutrality (under the Carbon Neutral Government Programme) – the Facilities team at Timaru Hospital were committed to replacing the 1970’s vintage coal boilers with a low carbon alternative. All the hospital’s process heat requirements were supplied by the boilers, needing more than 2,000 tonnes of coal per year, leading to carbon emissions of more than 4,500 tCO2-e. Starting with an Options Study, DETA quickly identified that:
11) Why are we still burning coal? NZ Geographic recently published a comprehensive article providing an excellent analysis for those interested in this topic. It looks at the issues driving continued coal use and hindering conversion to alternative fuel sources for large industrial coal users. They say - The crux of the issue is that “Anything that relies on power from the current New Zealand electricity market is going to be substantially more expensive than coal”. According to Fonterra, which burns coal at nine of its 29 dairy plants, the fossil fuel is 3.25 times cheaper than electricity as a source of process heat. The dairy giant says converting to electricity at scale would cripple its bottom line. A 2021 report for the Ministry for the Environment investigated four coal-intensive industries and found that all beneficiary companies were receiving more free carbon units than their actual climate liability—some by three times as much. In 2020, New Zealand Steel was handed 2,030,166 free New Zealand Units (NZUs) worth $30 million more than it actually needed to cover its emissions. New Zealand Aluminium Smelters Limited (Rio Tinto) got 1,558,268 NZUs, yet emitted just 637,000 tonnes in the year to June 2021—effectively a subsidy of almost $60 million. Turners & Growers Fresh Limited received more than 19,000 NZUs to grow tomatoes. When you recall that a tonne of coal releases twice that amount of CO2-e, what at first seems merely a loophole quickly reveals itself to be a gushing rupture. Critics say that industrial allocations are practically a subsidy to wreck the climate—and the government isn’t denying it. In July 2021, it released a discussion document seeking views on how to put a stop to this ill-conceived largesse. Check out the full article for more information. 12) Carbon Sequestration by Native Forest - Setting the Record Straight. Well-managed planted indigenous forest is better at sequestering carbon and faster growing than commonly considered. The Pure Advantage group have published research on this topic. This research is a first for planted native forest using methodology comparable to that used for planted radiata pine forest in New Zealand, and is now presented in an informative free e-book which can be viewed free online. 13) How not to solve the climate change problem. This article from "The Conversation" written by Kevin Trenberth at Auckland University is a straightforward and easy to understand analysis of the problem and the major constraints associated with some proposed solutions. When politicians talk about reaching “net zero” emissions, they’re often counting on trees or technology that can pull carbon dioxide out of the air. What they don’t mention is just how much these proposals or geoengineering would cost to allow the world to continue burning fossil fuels. There are many proposals for removing carbon dioxide, but most make differences only at the edges, and carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere have continued to increase relentlessly, even through the pandemic. 14) Wishing for fairy dust – why the NZ Biofuels Obligation is the worst kind of magical thinking. Below is an extract from an excellent analysis, produced by Jake Roos and published on the Low Carbon Kapiti website, of the unintended negative consequences of introducing a biofuels mandate in NZ. He says - Wouldn’t it be great if wishes came true, and all your problems just went away? If all you needed to do is ask for something and it materialised out of thin air before you? Of course it would, but the world doesn’t work like that. But it seems the NZ Government is in the thrall of such magical thinking when it comes to ‘sustainable’ biofuels. To summarise:
GLOBAL 15) Young people go to European court to stop treaty that aids fossil fuel investors. Five people, aged between 17 and 31, who have experienced devastating floods, forest fires and hurricanes are bringing a case to the European court of human rights, where they will argue that their governments’ membership of the little-known energy charter treaty (ECT) is a dangerous obstacle to action on the climate crisis. It is the first time that the Strasbourg court will be asked to consider the treaty, a secretive investor court system that enables fossil fuel companies to sue governments for lost profits. Check out the full article here. 16) The world's first operational 'sand battery' can store energy for months. The Interesting Engineering website had an article last month about research looking at the viability of using a sand battery to store energy as heat. In their report they say - "A team of researchers from Finland has set up the world's first commercial-scale 'sand battery' that can be used to store power generated from renewable sources for months at a time to solve the problem of year-round supply, BBC reported. The push for renewable power has meant that researchers are looking for new ways to store energy over the long term. While batteries made using lithium and other earth minerals can be purposed to work as energy farms, the solution becomes unsustainable if the whole world shift to renewables. Recently, we reported how Switzerland spent 14 years repurposing its natural reservoirs as giant water batteries. While this uses the centuries-old concept to tap into the potential energy of water stored at a higher level, the construction of such facilities can cost millions of dollars. The Finnish solution could be a much cheaper alternative." 17) The exponential rise of CO2 in our planet's atmosphere. In 1949, it took 20 years for atmospheric Co2 to rise by 20 ppm, in midlife 1980, it took 15 years to rise 20 ppm, now, it has taken 10 years to rise 20 ppm......... 18) We cannot adapt our way out of climate crisis, warns leading scientist. I have a lot of respect for climate scientist Katharine Hayhoe and was encouraged to see this Guardian article highlighting the importance of keeping our focus on emissions reduction, and that this must be our priority if we wish to maintain a liveable planet Earth. What she says is hard hitting and confronting but I believe has to be said. Here is an extract from the article - The world cannot adapt its way out of the climate crisis, and counting on adaptation to limit damage is no substitute for urgently cutting greenhouse gases, a leading climate scientist has warned. Katharine Hayhoe, chief scientist for the Nature Conservancy in the US and professor at Texas Tech University, said the world was heading for dangers unseen in the 10,000 years of human civilisation, and efforts to make the world more resilient were needed but by themselves could not soften the impact enough. “People do not understand the magnitude of what is going on,” she said. “This will be greater than anything we have ever seen in the past. This will be unprecedented. Every living thing will be affected.” Hayhoe said the IPCC findings had not been broadly understood by many people. “This is an unprecedented experiment with the climate,” she said. “The reality is that we will not have anything left that we value, if we do not address the climate crisis.” 19) Have you heard of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (Ipbes)? As readers of this newsletter will be aware CKM members are just as concerned about threats to biodiversity as they are about global warming. The existential crisis facing life on our planet is multi-faceted and cannot be addressed in a piecemeal fashion. To quote from the Dasgupta Review from two years ago - “Nature’s value must be at the heart of economics”. The major report recently released by Ipbes is equally as important as the IPCC reports on Climate Change. The Ipbes report provides compelling evidence that humans are overexploiting wild species and habitats. Harmful activities, including habitat destruction, poor farming practices and pollution, have altered ecosystems significantly, driving many species past the point of recovery. It's amazing that a report by this organisation, which is critical to helping us understand the biodiversity crisis facing Mother Nature, is so little known about. If you're interested check out the full article where you can also access the report. 20) Tipping Point risks for critical climate systems. The Breakthrough National Centre for Climate Restoration in Australia has published a new report written by David Spratt and Ian Dunlop with a foreward by Professor Sir David King FRS. "Climate Dominoes: Tipping point risks for critical climate systems, outlines the scientific evidence that critical climate tipping points face grave risks in Antarctica, the Arctic, Greenland Ice Sheet, Amazon rainforest and for coral reefs. It concludes that as a result of climate denial and inaction, the Great Barrier Reef, along with coral reefs worldwide, is in a death spiral even at today’s 1.2oC average global temperature increase." This article outlines the focus of the report. It says - "The recent Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Sixth Assessment Reports (AR6) are the most important analyses of humanity’s future on Earth to date. As Professor Sir David King FRS says in his foreword to “Climate Dominoes”: “Never before have we had so much scientific evidence demonstrating that we are in the midst of a global climate emergency.” AR6 provides a stark warning that humanity’s chances of outrunning the devastating impacts of climate change are uncomfortably low. The fact that these reports have been ignored by our political leaders is an abrogation of their primary responsibility to ensure the security of the Australian people. Unfortunately there is a blind spot in the AR6 analysis, in that the severity of human impact on our planetary ecosystems is leading us toward a range of irreversible tipping points. These are the greatest risks of climate change, for the process does not necessarily progress in a linear manner correlated with increasing atmospheric carbon concentrations. Instead, at certain points, it may “tip” abruptly from one relatively stable state to another far less conducive to human prosperity or survival. The “Climate Dominoes” report has reviewed the latest science and concludes that tipping point risks are greater than previously thought:
21) The ultra-polluting Scarborough-Pluto gas project in West Australia. An article written by Bill Hare of Murdoch University in West Australia claims this one project alone could blow through the new Australian Labor government's climate target – and it just got the green light."The Albanese government has this week thrown its support behind what’ll be one of Australia’s most polluting developments: the Scarborough-Pluto gas project in Western Australia. Our analysis last year found the full Scarborough-Pluto project will emit almost 1.4 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases over its lifetime. That’s over three times Australia’s current annual emissions, and around 14 times WA’s annual emissions. We calculate that the emissions from this project and all of its related activities will add about 41 megatonnes per year to Australia’s national emissions by 2030. That is a materially relevant number – it’s nearly 7% of our emissions in 2005, which is the year we use as a baseline for emissions targets. To put it another way, it’s nearly twice as much as the emissions avoided by all the rooftop solar panels in Australia each year." 22) Former Australian chief scientist to head review of carbon credit scheme after whistleblower revelations. The former Australian chief scientist and senior academic, Prof Ian Chubb, has been appointed to head a thorough review of Australia’s carbon credit scheme as experts escalate calls for a complete overhaul of the system. Chris Bowen, the climate change minister, announced on Friday that Chubb, a neuroscientist and former vice-chancellor of the Australian National University, would lead the six-month review of the scheme, after a respected whistleblower described it as a fraud and waste of taxpayer money. Carbon credits are bought by governments and businesses as an alternative to cutting carbon dioxide emissions. While their use to help meet emissions targets has significant support – particularly among polluting companies promising to offset their impact on the planet – critics have raised concern about whether credits issued in Australia represent real emissions cuts beyond what would have happened anyway. This article outlines major deficiencies in the Australian carbon credit scheme. Why are we not surprised? 23) A huge Atlantic ocean current is slowing down. If it collapses, La Niña could become the norm for our part of the world. This article from the Conversation highlights the latest research looking at the slowing down of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation and the likely impacts for Australia. NZ will of course be similarly impacted and Marlborough just experiencing it's wettest month on record is an example of what they are predicting. "Climate change is slowing down the conveyor belt of ocean currents that brings warm water from the tropics up to the North Atlantic. Our research, published today in Nature Climate Change, looks at the profound consequences to global climate if this Atlantic conveyor collapses entirely. We found the collapse of this system – called the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation – would shift the Earth’s climate to a more La Niña-like state. This would mean more flooding rains over eastern Australia and worse droughts and bushfire seasons over southwest United States. East-coast Australians know what unrelenting La Niña feels like. Climate change has loaded our atmosphere with moister air, while two summers of La Niña warmed the ocean north of Australia. Both contributed to some of the wettest conditions ever experienced, with record-breaking floods in New South Wales and Queensland. Meanwhile, over the southwest of North America, a record drought and severe bushfires have put a huge strain on emergency services and agriculture, with the 2021 fires alone estimated to have cost at least US$70 billion. The oceans are the flywheel of Earth’s climate, slowing the pace of change by absorbing heat and carbon in vast quantities. But there is payback, with sea level rise, ice melt, and a significant slowdown of the Atlantic overturning circulation projected for this century. Now we know this slowdown will not just affect the North Atlantic region, but as far away as Australia and Antarctica. We can prevent these changes from happening by growing a new low-carbon economy. Doing so will change, for the second time in less than a century, the course of Earth’s climate history – this time for the better." 24) State of the Global Climate 2021 Report. The recent release of the World Meteorological Organisation's State of the Global Climate 2021 report is available. The summary below is an extract from an article on the Australian website "Pearls and Irritations". Every year the World Meteorological Organization issues ‘State of the Global Climate’, an authoritative report covering the latest global climate indicators, the year’s high impact events (heatwaves, floods, droughts and the like) and assessments of risks and impacts (e.g. food security, population displacement, effects on ecosystems). The 2021 edition confirms current problems and future risks:
The WMO has produced an excellent interactive online ‘storymap’ that summarises the results, and contains lots of pictures, graphs, 1-2 minute explanatory videos of various phenomena and quiz questions. This is a valuable resource for anyone needing access to an up to date and thorough summary of the state of the global climate. 25) Methane much more sensitive to global heating than previously thought. I found a recent study discussed in this article very interesting. It highlights an undesirable impact on global methane levels arising from increased wildfires worldwide. A link is available in the article to download the full study. About 40% of methane emissions come from natural sources such as wetlands, while 60% come from anthropogenic sources such as cattle farming, fossil fuel extraction and landfill sites. Possible explanations for the rise in methane emissions range from expanding exploration of oil and natural gas, rising emissions from agriculture and landfill, and rising natural emissions as tropical wetlands warm and Arctic tundra melts. The predominant way in which methane is “mopped up” is via reaction with hydroxyl radicals (OH) in the atmosphere. “The hydroxyl radical has been termed the ‘detergent’ of the atmosphere because it works to cleanse the atmosphere of harmful trace gases,” said Redfern. But hydroxyl radicals also react with carbon monoxide, and an increase in wildfires may have pumped more carbon monoxide into the atmosphere and altered the chemical balance. “On average, a carbon monoxide molecule remains in the atmosphere for about three months before it’s attacked by a hydroxyl radical, while methane persists for about a decade. So wildfires have a swift impact on using up the hydroxyl ‘detergent’ and reduce the methane removal,” said Redfern. 26) A Case Study of Fossil-Fuel Depletion. This is a long but very relevant case study by Blair Fix, a political economist, using the Alberta, Canada oil and gas industry as the study area. Here are some extracts - If you had to choose one word that describes human history since the industrial revolution, what would it be? I’d vote for ‘exponential’. Over the last two centuries, so many things have grown exponentially that it’s hard to keep track. Less discussed is the corollary of exponential growth, which is exponential depletion. The two dynamics go hand in hand. When one thing grows exponentially, another thing must deplete exponentially. This fact follows from simple conservation laws. If you want your stock of A to grow, you must deplete your stock of B. There is no alternative. Since the industrial revolution began, humans have been expanding our stock of technology by depleting the Earth’s stock of fossil fuels (among other resources). Energy return on investment is not the only way to measure the easy-to-getness of a resource. Another option is to look at the size of the reserve being exploited. Let’s use water to illustrate the principle. Consider the difference between the following scenarios:
The same principle applies to the extraction of oil and gas. The low-hanging fruit consists of the enormous reserves that can be tapped with a single well. The hard-to-get fruit(s) are the tiny reserves that are numerous yet diffuse. According to the low-hanging fruit principle, we ought to tap the biggest reserves first. Nga mihi nui, Budyong. Kia ora Hope you are all well out there. Here is another selection of items for your perusal. Treat it like a smorgasbord and just take what interests you. LOCAL 1) MDC Emissions Inventory Report released - Marlborough District Council has released its first reports detailing the carbon footprint from its operations, finding just over 75 per cent of measurable emissions come from its landfill. The reports, for the years ending 2019 and 2020, were prepared by independent consultants CarbonEES to serve as a baseline that the Council can benchmark against for future years. An initial benchmark was the first task in the Climate Change Action Plan, which was approved in March 2020, just as Covid-19 began to surface. After the 2020 report had been prepared, Council undertook a second report for 2019 in order to understand its pre-Covid emissions. The Report states - The objectives of this carbon foot-printing project are to:
Scope 2 are indirect emissions associated with the generation of electricity purchased by MDC. Scope 3 are other indirect emissions that are a consequence of MDC's activities but from sources they do not own or directly control. (construction/infrastructure projects, bus services, etc) The first point to note is that the report only includes emissions from council owned AND operated sources. The organisational boundary follows an operational control approach. As such, the emissions inventory includes all sources associated with activities Marlborough District Council had operational control (authority to introduce and implement operating policies) over... (which excludes Port Marlborough, Marlborough Airport, Marlborough Regional Forestry, Marlborough Sustainable Housing Trust and Marlborough Stadium Trust.) The Report writers also recommended to Council "that council work with the airport, the port, and any other entities which the council owns but does not operate to calculate these emissions. If these emissions were known to council they could be included as a Scope 3 emissions source under category 15, Investments." In conclusion they recommend:
The Council also released a useful media statement for those who haven’t seen it. 2) Marlborough Landfill Gas Utilisation – The Contract for the beneficial use of landfill gas has been awarded to LMS Energy Limited. The first phase of the Contract is for LMS to carry out an investigation of the existing landfill gas collection and destruction system. LMS will then provide staff with a report on the efficiency of the current system and where any improvements in landfill gas capture could be made. Improvements could include extending the gas capture system by constructing additional gas boreholes. Any improvements will be tied to existing budgets. Thereafter, the gas field will then be monitored over a minimum 6-month period to ensure the quality and quantity of the gas is consistent. Stage 2 of the assessment would then see the design of a suitable biogas plant that would utilise the available landfill gas as a fuel to drive a turbine for electricity production. FYI - LMS Energy is Australia’s largest and most experienced landfill biogas company. The recovery of landfill biogas reduces carbon emissions and provides a reliable source of renewable energy. Each year, LMS’ projects reduce over 4 million tonnes of carbon from being emitted into the atmosphere, making LMS Australia’s largest emissions reducer. LMS has successfully delivered more landfill biogas projects than any other Australian company and are highly recognised as innovators in this industry. 3) Repurposing of Unwanted Goods Project - Here is an opportunity to redirect unwanted goods from going to landfill, by finding new homes for them. This helps to maximise the benefit to our community from the production of those goods. Reuse of goods is one of the most efficient things we can all do to reduce our carbon footprint. The Collection and Repurposing of Unwanted Goods Project is funded through existing budgets and a grant from the waste minimisation fund. The project began in March 2021 and is scheduled for completion by 30 June 2022. The project reporting is split across two milestones. Milestone 1 has now been completed and the relevant reporting information submitted to the waste minimisation funds team at the Ministry for the Environment. The objectives of milestone 1 were: 1. Establish a system for the collection and redistribution of unwanted reusable items by project completion. 2. Establish a redistribution system for unwanted goods based on the following criteria a) No transport and b) Self-identified immediate need. 3. Report on incidences of general illegal dumping across the project period compared to the 12-month period prior to the project. More info on the project and associated booking system can be found here: NATIONAL 4) What would a National government do on climate change? For anyone who missed seeing Tom Powell's article recently it is worth having a look at it and reading the detailed response from Scott Simpson, the National Party Climate Change spokesperson, that was published in the article. In writing the article we appreciated the input and feedback we received from CKM member Toby Stevenson and Tim Jones from Coal Action Network. Max Rashbrooke also wrote a good article focusing on the weaknesses of the NZ ETS, and showing support of the concerns expressed in Tom's opinion piece. 5) Emissions Reduction Plan (ERP) release - Aotearoa New Zealand's first emissions reduction plan was recently released, titled "Te hau mārohi ki anamata - Towards a productive, sustainable and inclusive economy." The plan states that it "contains strategies, policies and actions for achieving our first emissions budget and contributing to global efforts to limit global temperature rise to 1.5˚C above pre-industrial levels." The Ministry of Environment website has a summary of the plan and you can also download the full document there if you wish. If like me you struggle to get your head around the question of whether this Plan is going to really bring about the deep seated changes we require to help keep our planet liveable then here are a few options for gauging responses from people better informed than me. This Scoop article canvasses opinions from 13 different scientists focusing on areas such as Transport, Agriculture, Energy, Waste and Building & Construction and provides an opportunity to build some understanding of the Plan. There are also some very useful contributions taking an Overview of the Plan. There are positive statements recognising the progress that has been made but from my reading I get the feeling that politics (an election next year) have again got in the way of making the big and critical changes required. Here are a couple of quotes - "Well, the emission reduction plan is yet another step forward in meeting targets, but I don’t detect any urgency." and "While its objectives focus on the socio-cultural well-being of New Zealanders, the actions presented in this plan are mostly technocratic. Technology will not save us from climate change, as climate change is a political problem more than a technical one. This report considers no limits to growth and no attempts for de-growth, only an attempt to have a “de-carbonized growth” through technology and policy." I've also read other comments elsewhere such as "the ERP was even less ambitious and showed less urgency than the discussion document." One significant development in the ERP is the changed focus to 50% renewable energy across the energy sector, away from the government's previously stated 100% renewable electricity target, though the question this raises is - How serious are the supporting actions to deliver the new target? The ERP refers to the issues of energy security and cost concerns and this has prompted caution over phasing out natural gas. The plan states - “Phasing out fossil gas presents short-term and long-term challenges, including balancing capital investment with declining fossil gas use, fossil gas affordability and the risk of stranded network assets. The government is working to address these challenges and set out a pathway for the fossil gas sector.” This quote from an article on the pay walled Business Desk website states - "This will be done through a gas transition plan that will feed into a wider energy strategy that will focus on increasing renewables across the entire sector and not just electricity generation. This will include work led by the GIC (The Gas Industry Company (GIC) regulates the sector), to consider whether any mechanisms are needed to ensure fossil gas is available to industrial users in times of unexpectedly tight supply”. Some believe the signalling around the loosening of the 100% renewable electricity target and the gas transition plan will be interpreted by the energy sector as a win and a reason to believe that gas will continue to have a role. The Climate Change Commission advised the government to set a date from when no new gas connections should be allowed but their concerns about energy security and affordability are among the reasons the government has gone against the advice on the phasing out of gas. This Stuff article looks at the Government's aim to boost the renewable energy target across the whole energy sector from the current 28% share to 50% by 2035 and addresses the question of gas transition. It states - "The head of the independent Climate Change Commission is urging caution by anyone planning to connect a home to the natural (fossil-fueled) gas network, despite the Government balking at setting an end date for new gas hook-ups." So the ERP is explicit about a gas transition plan but there appears to be silence on coal for electricity generation. Coal is mentioned frequently in respect of coal boilers but there is nothing in the Plan that restrains the use of coal for generation. Some parts of the (ERP) stand out as good moves for the transport sector. In particular, it sets this target: “Reduce total kilometres travelled [VKT] by the light fleet by 20 per cent by 2035 through improved urban form and providing better travel options, particularly in our largest cities.” This target plus the higher standard of justification required for new roading could lead to substantial emissions reduction in urban transport. The Greater Auckland website has a guest post by sustainable transport and accessibility advocate Tim Adriaansen that I found to be a useful summary on the ERP. 6) The NZ SeaRise Project - Te Tai Pari O Aotearoa programme has released location specific sea level rise projections out to the year 2300 for every 2 km of the coast of Aotearoa New Zealand. These projections can be accessed through a new online tool developed by Takiwā, a data management and analytics platform. For the first time, New Zealanders will be able to see how much and how fast sea level will rise along ‘their own’ stretch of coast and in their neighbourhood. The tool allows users to click on a particular location on the coast and see how much sea level is expected to rise, and by when, under different climate change scenarios. Climate change and warming temperatures are causing sea level to rise, on average, by 3.5 mm per year. This sea level rise is caused by thermal expansion of the ocean, by melting glaciers, and by melting of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets. However, local sea level rise around the coast of Aotearoa is also affected by up and down movements of our land. We are very aware when these vertical land movements occur in large jumps during earthquakes, but less obvious to us are the smaller shifts that occur continuously in between large seismic events. These small but continuous changes add up, and in areas that are going down (subsiding) the annual rate of sea level rise can double. We have connected this vertical land movement data with climate driven sea level rise to provide locally-relevant sea level projections. 7) Draft national adaptation plan - We’re consulting on a draft national plan to help Aotearoa New Zealand adapt to and minimise the harmful impacts of climate change. New Zealand’s first national adaptation plan will build the foundation for adaptation action so that all sectors and communities are able to live and thrive in a changing climate. The consultation also outlines proposals for flood insurance and managed retreat policies. Consultation will close at 11:59pm on 3 June 2022. To learn more check out the full consultation document. 8) New Zealand’s Process Heat Fuel Future. Part 1: South Island - In 2020 DETA Consulting published the whitepaper, Carbon Roadmap to 2050. In the foreword of this new report, NZ's Process Heat Fuel Future, they say they want to bring - "...the conversation around specifically to industrial process heat. It is time to look forward and think of the big picture - how feasible is it to use alternatives such as wood (biomass) and electricity, and what are some of the long-term implications in making the switch?" The report helps industries to understand what biomass levels could be available when they transition away from coal. They go on to say in the Executive Summary - "Coal remains a low-cost option for process heat users. However, it is also a very significant contributor to climate change. As Aotearoa New Zealand moves towards a low carbon future, organisations that rely heavily on coal and other fossil fuels for process heat need to adapt or be left behind – a rising Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS) will make coal substantially more expensive than it is today, and the New Zealand Government has implemented a ban on all new low to medium temperature coal boilers as of March 2022, with plans to phase out existing coal boilers by 2037. Across the South Island, there is 1.46 GW of non- renewable heat capacity, or 24.3 Petajoule (PJ) of annual heat production from fossil fuels, primarily from coal. In other words, the equivalent of 65% of electricity consumed annually by the South Island, is being produced from non-renewable fossil fuels. Industries know they need to move away from fossil fuels and are primarily considering biomass and electric alternatives." Here are a couple of examples from the report that highlights some of the challenges that will need to be dealt with as fossil fuel fired boilers (primarily coal) for industrial process heat are phased out by 2037 as required by government regulation - "Canterbury’s wood fibre availability is severely diminished due to massive forest clearing efforts in the late 1990s to early 2000s. By 2031 the Canterbury region will need 7.6 PJ or 55% of its heat energy from electric boilers or other non- biomass technologies. That’s equivalent to 35% of Canterbury’s current yearly electricity consumption." AND "‘We found that fossil fuel boilers produce about 24.3 PJ of heat. That’s equivalent to 65% of the electricity consumption of the entire South Island’. However, fossil fuel boilers typically operate around 75-85% efficiency, so to produce 24.3 PJ of heat requires approximately 31.5 PJ of fuel energy." 9) Save BOARD - Low Carbon Building Materials made from Upcycled packaging - Here's a new development for NZ. I hope they succeed and grow. Made in New Zealand; healthy, affordable, high performance, low carbon building materials that make a circular economy an everyday reality. We take everyday packaging waste and upcycle it into high performing building materials - durable, inherently moisture and mould resistant. Our board products are also 100% recyclable as all recovered offcuts and end of life products can be remanufactured into new boards providing a circular solution.
10) Making climate a boardroom priority. Chapter Zero New Zealand is part of a global network of board directors committed to taking action on climate change. It is hosted in Aotearoa by the Institute of Directors. Here is a brief summary from their website - Climate change is shaping a new reality, creating risks and opportunities for business in a diverse number of ways. Investors, regulators and other stakeholders are now challenging companies to take responsibility by adopting an integrated, strategic approach to addressing the climate emergency. The urgent need to address the climate emergency requires governments and business to accelerate the transition to a new economic model, which seeks to limit global average temperature increases to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, consistent with the 2018 recommendations of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). To fulfil their fiduciary duties in the long-term service of their organisations, directors need to be fully aware of the implications of climate change, have the skills, tools, processes and information to act, and commit to steward their companies through the challenges climate change entails to embed it within their companies’ strategic planning. 11) Many of New Zealand’s glaciers could disappear in a decade, scientists warn. New Zealand’s glaciers are becoming “smaller and more skeletal” due to the effects of climate change and scientists predict many could disappear within a decade. An annual end-of-summer survey that records the snowline of more than 50 South Island glaciers has revealed continued loss of snow and ice. Every year, the National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (Niwa), the Victoria University of Wellington and the conservation department gather thousands of aerial photographs of the glaciers to measure the altitude of the snowline and see how much of the previous winter’s snow has remained covering each glacier. That snowline, also known as the equilibrium line altitude (ELA), allows scientists to evaluate the glacier’s health. If the glacier size has decreased, then the line will be higher, because less winter snow remains. “We were expecting the snowlines to be high because of the warm weather we’ve had and sadly, our instincts were confirmed,” said Dr Andrew Lorrey, a principal scientist at Niwa. New Zealand’s glaciers had lost mass most years over the past decade, said Dr Lauren Vargo from Victoria University. “But what was more striking to me is how much smaller and more skeletal so many of the glaciers are becoming.” Check out the full article. INTERNATIONAL 12) Iceland: cross-party demand for ecocide law goes to parliament - It is encouraging to see progress being made in another country towards getting Ecocide law legislated. It would be great if NZ got on board with this initiative. “Auður Önnu Magnúsdóttir, general manager of the Icelandic Environment Association, a Member of Parliament for the Pirate Party, announced that: “It's time for us to hold people accountable if nature is harmed in such a way that it threatens world peace, security and well-being. That is why I was submitting a parliamentary resolution proposing that ecocide be recognized as an international crime. It is especially good to see broad support for the issue - we are 12 MPs from four parties who are responsible for it - and hopefully Iceland can take a leading position in this fight for the rights of Mother Earth, which is in full swing all over the world." Check out the full text of the press release. 13) Revealed: the ‘carbon bombs’ set to trigger catastrophic climate breakdown - This Guardian article highlights details of major oil and gas projects currently planned by the major fossil fuel companies. The world’s biggest fossil fuel firms are quietly planning scores of “carbon bomb” oil and gas projects that would drive the climate past internationally agreed temperature limits with catastrophic global impacts, a Guardian investigation shows. The exclusive data shows these firms are in effect placing multibillion-dollar bets against humanity halting global heating. Their huge investments in new fossil fuel production could pay off only if countries fail to rapidly slash carbon emissions, which scientists say is vital. The lure of colossal payouts in the years to come appears to be irresistible to the oil companies, despite the world’s climate scientists stating in February that further delay in cutting fossil fuel use would mean missing our last chance “to secure a liveable and sustainable future for all”. As the UN secretary general, António Guterres, warned world leaders in April: “Our addiction to fossil fuels is killing us.” Details of the projects being planned are not easily accessible but an investigation published in the Guardian shows: The fossil fuel industry’s short-term expansion plans involve the start of oil and gas projects that will produce greenhouse gases equivalent to a decade of CO2 emissions from China, the world’s biggest polluter. These plans include 195 carbon bombs, gigantic oil and gas projects that would each result in at least a billion tonnes of CO2 emissions over their lifetimes, in total equivalent to about 18 years of current global CO2 emissions. About 60% of these have already started pumping. The dozen biggest oil companies are on track to spend $103m a day for the rest of the decade exploiting new fields of oil and gas that cannot be burned if global heating is to be limited to well under 2C. The Middle East and Russia often attract the most attention in relation to future oil and gas production but the US, Canada and Australia are among the countries with the biggest expansion plans and the highest number of carbon bombs. The US, Canada and Australia also give some of the world’s biggest subsidies for fossil fuels per capita. In a similar vein this article highlights a study that proposes the shut down of fossil fuel production sites early to avoid climate chaos. It says - "Nearly half of existing fossil fuel production sites need to be shut down early if global heating is to be limited to 1.5C, the internationally agreed goal for avoiding climate catastrophe, according to a new scientific study. The assessment goes beyond the call by the International Energy Agency in 2021 to stop all new fossil fuel development to avoid the worst impacts of global heating, a statement seen as radical at the time. The new research reaches its starker conclusion by not assuming that new technologies will be able to suck huge amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere to compensate for the burning of coal, oil and gas. Experts said relying on such technologies was a risky gamble." 14) A couple of developments in the field of Hydrogen - A new method for rapid, efficient hydrogen generation from water. Aluminum is a highly reactive metal that can strip oxygen from water molecules to generate hydrogen gas. Now, researchers at UC Santa Cruz have developed a new cost-effective and effective way to use aluminum’s reactivity to generate clean hydrogen fuel. In a new study, a team of researchers shows that an easily produced composite of gallium and aluminum creates aluminum nanoparticles that react rapidly with water at room temperature to yield large amounts of hydrogen. According to researchers, the gallium was easily recovered for reuse after the reaction, which yields 90% of the hydrogen that could theoretically be produced from the reaction of all the aluminum in the composite. While gallium is not abundant and is relatively expensive, it can be recovered and reused multiple times without losing effectiveness. However, it remains to be seen if this process can be scaled up to be practical for commercial hydrogen production. Natural hydrogen exploration ‘boom’ snaps up one third of South Australia. 15) Compressed Air Technology. Here is another interesting way of utilising renewable electricity for transport and as a way to store energy. A NZ company called Air Future is promoting this technology here. COMPRESSED AIR TECHNOLOGY is one of the best possible solutions because its carbon footprint is optimal, its reservoir is chemically inert and its very reasonable cost makes it possible to optimise energy production resulting from sustainable development. With the vision to make ecology accessable to all, Motor Development International (MDI) has developed a disruptive clean high technology of engines running on compressed air, which caters for a wide variety of applications operable to Sustain Mobility and Energy Storage Solutions. The MDI high-tech engines using only compressed air are totally clean. Global energy challenges dictate the choice of new production paradigms and energy storage means. To accumulate and store energy from a primary source and then use it with a very high conversion efficiency is the challenge that the MDI concept of compressed air engines meets and achieves. The MDI reversible high-tech engines compress ambient air in approved tanks of various capacities at a pressure of 248 bars. The expansion of this stored energy in the form of movement allows you to replace all heat engines and cover any type of application: to move vehicles or to store and re-use electric energy. 16) Solar energy can now be stored for up to 18 years, say scientists - Solar-powered electronics are one step closer to becoming an everyday part of our lives thanks to a “radical” new scientific breakthrough. In 2017, scientists at a Swedish university created an energy system that makes it possible to capture and store solar energy for up to 18 years, releasing it as heat when needed. Now the researchers have succeeded in getting the system to produce electricity by connecting it to a thermoelectric generator. Though still in its early stages, the concept developed at Chalmers University of Technology in Gothenberg could pave the way for self-charging electronics that use stored solar energy on demand. “This is a radically new way of generating electricity from solar energy. It means that we can use solar energy to produce electricity regardless of weather, time of day, season, or geographical location,” explains research leader Kasper Moth-Poulsen, Professor at the Department of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering at Chalmers. Check out the full article. 17) Corn-Based Ethanol May Be Worse For the Climate Than Gasoline, a New Study Finds. Ethanol made from corn grown across millions of acres of American farmland has become the country’s premier renewable fuel, touted as a low-carbon alternative to traditional gasoline and a key component of the country’s efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. But a new study, published this week, finds that corn-based ethanol may actually be worse for the climate than fossil-based gasoline, and has other environmental downsides. “We thought and hoped it would be a climate solution and reduce and replace our reliance on gasoline,” said Tyler Lark, a researcher with the Nelson Institute for Environmental Studies at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, and lead author of the study. “It turns out to be no better for the climate than the gasoline it aims to replace and comes with all kinds of other impacts.” Check out the full article for more info. 18) Modernity is incompatible with planetary limits: Developing a PLAN for the future. This scientific research paper asks some serious questions and is refreshing in that it does not dodge the difficult issues. This age of modernity is characterized by consistent growth in energy use, economic activity, and resource consumption, and a generally increasing standard of living—albeit inequitably distributed. All currently living humans, and most academic disciplines, have developed in this age, which appears normal and indefinite to us. But modernity has been enabled by the rapid and accelerating expenditure of our one-time inheritance of fossil fuels, and by drawing down the resources and ecosystems of our finite Earth—none of which can be sustained as we transition from a resource-rich frontier to a human-dominated planet. Climate change is often singled out as modernity’s existential crisis, but it is only one of a series of interlocking challenges constituting an unprecedented predicament that must be understood and mitigated in order to live within planetary limits. While energetic and technological challenges attract significant attention, arguably the greatest challenges are conceptual or even cultural. In particular, as we review in this Perspective, today’s political economy has been designed to value short-term financial wealth over the real treasure of Earth’s functioning ecosystems, to discount the future at the expense of the present, and to demand infinite exponential growth…which is simply impossible on a finite planet. Given all this, humanity should view its present overshoot-prone trajectory with tremendous suspicion, humility, and concern. We call for the establishment of a transdisciplinary network of scholars from across the entire academic landscape to develop a global understanding of planetary limits and how humanity can adapt to the associated realities. We present a set of foundational principles to serve as a starting point to anchor this network and drive a new area of focused inquiry to develop a shared vision of viable future paths. What would a lower-fossil-energy future look like? Can an energy regime transformation take place as broadly and quickly as needed to offset declining net energy? Is it as unlikely as preliminary studies suggest that renewable energy technology/innovation might save the modern human project from the challenges of a resource-constrained future? Will the future look more like the distant past than the present? When does the downward portion of the fossil fuel age begin? What can be done to minimize the chances of colossal failure or sub-systemic breakdown, which in the worst case could threaten preservation of science and human knowledge? Certainly, failure to acknowledge dire possibilities invites huge risk. Much is at stake, and humanity must be very cautious about the temptation for denial, dismissal, or idolatrous hope for some technological breakthrough—especially in light of credible causes for concern. 19) The future of food and energy with Mike Joy. The quote below on the opening screen of the webinar, gives a feel for the focus of the talk. The talk was organised by Nelson Tasman Climate Forum. Mike provided some very useful topical information in his talk. "Rather than trying to comfort politicians in their utopias, scientists should instead help them to get out of the denial of reality." Gerhard Bonhomme, Professor Emeritus, University Lorraine. Chairman Energy/Environment Commission of the French Physical Society. 20) In-depth Q&A: The IPCC’s sixth assessment on how climate change impacts the world. The Carbon Brief website have posted a very good overview of the IPCC’s AR6 Sixth Assessment report that was released in August last year. Most readers of this newsletter will be aware of the AR6 report and also possibly aware of how daunting it is at more than 3000 pages long. For anybody wanting to understand a bit more than just the headlines that we get in the media this in-depth Q&A is a very good resource. 21) NFT scams, toxic ‘mines’ and lost life savings: the cryptocurrency dream is fading fast - Cryptocurrencies, according to their most ardent supporters, are supposed to supplant nations’ existing currencies and end central banks’ control over the money supply. Instead, individuals will be able to trade with each other in a decentralised, digital financial ecosystem. This is a good thing, they promise, because unlike states and their central banks, technology is incorruptible. Crypto-evangelists imagine technology as a replacement for social and political institutions.But technology never replaces social and political behaviour; it merely alters the rules and norms we follow. To see this in action, one need only look at the plummeting value of Terra Luna, a crypto token that crashed by 98% in a day, causing some investors to lose their life savings; the plunging value of Bitcoin and Ethereum; or the countless scam victims whose non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have been stolen. Check out the full article. 22) PV Magazine - This website has a wide range of interesting items on developments in photovoltaics, battery storage, hydrogen technology, etc 23) Algae-Powered Computing -Scientists used a widespread species of blue-green algae to power a microprocessor continuously for a year — and counting — using nothing but ambient light and water. Their system has the potential as a reliable and renewable way to power small electronic devices. The system, comparable in size to an AA battery, contains a type of non-toxic algae called Synechocystis that harvests energy naturally from the sun through photosynthesis. The tiny electrical current this generates then interacts with an aluminum electrode and is used to power a microprocessor. “Our photosynthetic device doesn’t run down the way a battery does because it’s continually using light as the energy source.” The system is made of ordinary, inexpensive, and mostly recyclable materials. This means it could easily be replicated hundreds of thousands of times to power large numbers of small devices as part of the Internet of Things. The researchers say it is likely to be most useful in off-grid situations or remote locations, where small amounts of electrical power can be very beneficial. The researchers say that powering trillions of Internet of Things devices using lithium-ion batteries would be impractical: it would need three times more lithium than is produced across the world annually. And traditional photovoltaic devices are made using hazardous materials that have adverse environmental effects. Check out the full article. 24) The secret world beneath our feet is mind-blowing – and the key to our planet’s future - I would like to finish this time with two articles by George Monbiot focusing on food and soil. As you are no doubt aware by now I'm very interested in keeping a focus on the big picture issues impacting the future our amazing planet and it's ability to support life. These articles highlight another critical area we need to learn more about. I highly recommend them. Don’t dismiss soil: its unknowable wonders could ensure the survival of our species. Beneath our feet is an ecosystem so astonishing that it tests the limits of our imagination. It’s as diverse as a rainforest or a coral reef. We depend on it for 99% of our food, yet we scarcely know it. Soil. But even more arresting than soil’s diversity and abundance is the question of what it actually is. Most people see it as a dull mass of ground-up rock and dead plants. But it turns out to be a biological structure, built by living creatures to secure their survival, like a wasps’ nest or a beaver dam. Microbes make cements out of carbon, with which they stick mineral particles together, creating pores and passages through which water, oxygen and nutrients pass. The tiny clumps they build become the blocks the animals in the soil use to construct bigger labyrinths. While there are international treaties on telecommunication, civil aviation, investment guarantees, intellectual property, psychotropic substances and doping in sport, there is no global treaty on soil. The notion that this complex and scarcely understood system can withstand all we throw at it and continue to support us could be the most dangerous of all our beliefs. While no solution is a panacea, I believe that some of the components of a new global food system – one that is more resilient, more distributed, more diverse and more sustainable – are falling into place. If it happens, it will be built on our new knowledge of the most neglected of major ecosystems: the soil. It could resolve the greatest of all dilemmas: how to feed ourselves without destroying the living systems on which we depend. The future is underground. Check out the full article. The banks collapsed in 2008 – and our food system is about to do the same - "For the past few years, scientists have been frantically sounding an alarm that governments refuse to hear: the global food system is beginning to look like the global financial system in the run-up to 2008. A paper in Nature Sustainability reports that in the food system, “shock frequency has increased through time on land and sea at a global scale”. In researching my book Regenesis, I came to realise that it’s this escalating series of contagious shocks, exacerbated by financial speculation, that has been driving global hunger. Now the global food system must survive not only its internal frailties, but also environmental and political disruptions that might interact with each other. To give a current example, in mid-April, the Indian government suggested that it could make up the shortfall in global food exports caused by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. Just a month later, it banned exports of wheat, after crops shrivelled in a devastating heatwave. We urgently need to diversify global food production, both geographically and in terms of crops and farming techniques. We need to break the grip of massive corporations and financial speculators. We need to create backup systems, producing food by entirely different means. We need to introduce spare capacity into a system threatened by its own efficiencies. If so many can go hungry at a time of unprecedented bounty, the consequences of the major crop failure that environmental breakdown could cause defy imagination. The system has to change." Check out the full article. Nga mihi, Budyong.  Kia ora Welcome all to a new year. What will 2022 have in store for us? My feeling is that the one thing we can be certain of is that there will be further unexpected surprises that will continue to challenge our communities, society as a whole and each one of us as individuals. Hope you can find some things of interest to you from the following selection. I've started this newsletter with a range of info looking at the discussion around the pros and cons of using wood biomass and/or electricity for process heat. 1) Talleys receive "Government Investment in Decarbonising Industry Fund" (GIDI) grant - Successful applicants for the second round of the GIDI Fund were announced by Minister for Energy and Resources Dr Megan Woods on September 30 last year. Twenty-three projects will receive government co-investment from Round Two of the $69m GIDI Fund. The recipients will receive $28.7 million and will match this with $54.5m of their own funding. The local Talleys factory received a one million dollar grant. The project will replace three diesel and two coal boilers with a new 6MW wood pellet fired boiler. The steam reticulation system will also be improved with a new steam distribution header that will improve energy efficiency. It is interesting to note they have chosen wood pellets as their new energy source. Research done by Tom and myself last year came to the conclusion that users of process heat who decide to use biomass would be be best placed to install boilers that could burn a range of wet and dry biomass fuels rather than limiting themselves to a single dry product such as wood pellets. In many instances there is also a good case for using electricity directly. Our research resulted in us concluding that New Zealand needs to plan the whole biomass supply and demand process very carefully, otherwise we could easily find ourselves having expectations of biomass that can't be met or result in undesirable consequences. You can read all about it in our article printed by Stuff. 2) Biomass clear favourite for decarbonising SI process heat. Biomass is the clear favourite for industrial process heat users in the South Island looking to decarbonise their operations, according to the Energy Efficiency and Conservation Authority. Initial EECA data indicates that 90 per cent of high-temperature boiler operators in Canterbury and Southland prefer biomass to electrification because of cost considerations. Electrode boilers have much higher capital costs than thermal boilers and expose users to changes in wholesale electricity prices. It is much cheaper and easier to convert existing boilers to run on biomass while retaining coal as a backstop. DETA Consulting is leading the primary data collection for EECA’s regional heat demand database project. DETA managing director Jonathan Pooch told an EECA decarbonisation workshop on Friday that this “clear, dominant bias” towards biomass for the southern process heat sector is understandable. Electrification is expensive, and natural gas and geothermal options aren’t available in the South Island. The upshot is dramatically increasing demand for woody-biomass fuels in a part of the country where the bioenergy manufacturing and supply-chain is less developed than in the North Island. “There is a broader conversation that needs to be had, probably as part of a broader energy strategy, about forestry and biomass,” he says. “It’s not an insurmountable challenge, but it is a challenge.” This presents many challenges – particularly when coal remains the cheapest option overall even as prices rise through the Emissions Trading Scheme. “The brutal reality is that the ETS still needs to do some heavy lifting to price coal. It’s going in the right direction – but coal is still the lowest-cost option available.” Pooch estimates large-scale conversion to biomass would require about 13 per cent of the South Island’s annual forest harvest. He thinks there are enough raw materials in the South Island to meet this demand, but the question remains whether the market can tolerate the high prices that diverting those volumes of fibre from existing uses would have. Existing supply is also dominated by waste product and there is comparatively little in the way of higher-energy products like wood pellets. Increased competition for raw materials would require more planting, including short-rotation crops. “We’ve got to see a rapid evolution of this biomass market into something that’s perceived as low risk compared to the baseline of coal and the supply chain that’s been around for 100 years or more.” Check out the full article on the DETA website. 3) NZ replacing coal boilers with wood pellets but some say it slows carbon neutral progress.This article and this interview from RNZ provide some good extra information on this topic and support careful analysis when deciding where the use of wood or electricity is the best option for process heat. Here's an extract from the article - Professor Andrew Blakers from Australian National University said a problem with wood pellets was they depended on the felling of pine trees every 20 to 30 years. A much larger amount of carbon would be soaked up if that same land was instead planted in natives and left alone. "Wood pellets are a very bad way to allegedly reduce your carbon footprint. If the forests are being used for wood pellets, you're better off to convert that area of land to native forests, let it soak up carbon for the next 200 years and get up to 250 tons per hectare of carbon." This was up to five times as much carbon as that soaked up by a pine plantation harvested every two decades, he said. However Massey University's professor emeritus Ralph Sims, who was a regular contributor to the International Panel on Climate Change, said wood pellets did have a role, especially at filling the gap between now and when cheap renewable energy became available. "High temperature heat can be produced by electro thermal technologies, but they tend to be a bit expensive at the moment, but that's an alternative. But if we've got a waste product, like our forest residues lying on the ground as an energy source which is storable, then why not collect it and use it." However Ralph Sims said wood pellets were only a good idea if they were made from wood waste, not, as was happening in North America, whole trees, which were turned in to pellets and exported to Europe. "The worst thing possible is deforestation of any forest whether it's in New Zealand, North Carolina, or the Amazon or Indonesia. We don't want to touch those forests. We want to encourage their survival and enhance their growth if that's possible, as well." 4) Anne Salmond: NZ’s climate planting asking for trouble. New Zealand’s strategy for responding to climate change is fundamentally flawed. Much of the nation’s carbon debt is to be addressed by ‘off-setting’ – planting trees to sequester carbon, either at home or abroad. On one hand, the government proposes to spend billions of dollars on international carbon credits – in other words, paying people in other countries to plant trees to sequester the carbon emitted in New Zealand. On the other hand, the Emissions Trading Scheme has been designed as a ‘market’ for the owners of trees in New Zealand to sell the carbon they sequester to buyers who want to offset the carbon they generate. Since most of the plantations in New Zealand are owned offshore, we’re paying even more to people in other countries to sequester the carbon we’re emitting. The ETS is a spreadsheet designed in a silo, and an ecologist’s nightmare. It privileges the planting of monocultures of exotic conifers in New Zealand, while failing to assess their social, cultural, ecological and economic impacts on local communities and landscapes. Check out the full Newsroom article. 5) The Biomass Industry Expands Across the South, Thanks in Part to UK Subsidies. Critics Say it’s Not ‘Carbon Neutral’. Hundreds of scientists around the world have been arguing that biofuels policies and practices are often far from climate friendly, and that European subsidies propping up the industry are, in fact, dangerous. While the industry generally maintains that it only uses wood waste or low-value trees to make pellets, critics have issued reports with photographs that they say show destructive logging practices and the conversion of entire trees to wood pellets. The argument centers on how quickly new tree growth can absorb the carbon dioxide that’s emitted from power plants that burn wood pellets, given an increasing sense of urgency over the speed with which global greenhouse gas emissions must be reduced to avoid the worst effects of global warming. “Burning wood puts more carbon dioxide in the air right now, today, with certainty, than the fossil fuels you were burning,” John Sterman, a professor of management and engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, told Inside Climate News. Bluntly, the scientists including Peter Raven, director emeritus of the Missouri Botanical Society and former President of the American Association for Advancement of Science, wrote: “Trees are more valuable alive than dead both for climate and for biodiversity. To meet future net zero emission goals, your governments should work to preserve and restore forests and not to burn them.” The scientists maintain that subsidies have escalated tree harvesting for energy production at a rate that is creating a “carbon debt” that eventually might be paid back by regrowth—but not nearly fast enough. “Regrowth takes time the world does not have,” the scientists argued in their recent letter. Numerous studies, they pointed out, have shown that “this burning of wood will increase warming for decades to centuries. That is true even when the wood replaces coal, oil or natural gas.” Check out the full article for more detail. 6) Summary of Biofuel vs Biomass. This article gives a good summary of the difference between biofuel and biomass.
7) Te Uru Rākau Publishes the State of Knowledge Report on Transitioning Plantations to Native Forest. The Ministry of Primary Industries commissioned a review of (1) the state of knowledge on the topic of transitioning exotic plantations to native forest and (2) of the existing data and research approaches for addressing knowledge gaps for forest carbon aspects of transitioning plantations. If you're interested check out the abstract and full research paper. 8) Local Marlborough company Carbonscape update - Chemical engineer Ivan Williams believes the worldwide ‘megatrend’ of electrification could mean big business for CarbonScape, the company he runs which is headquartered in Blenheim and which aims to supply a key ingredient in lithium-ion batteries: graphite. He says “We hold the key to a tech which can make batteries greener, cheaper. Our mission in a sense is decarbonisation through renewable battery material. We’re nearing the end of validation with a major player and that will be the end of a small Marlborough story and the beginning of a global success story for sustainable battery technology.” The full article is available in the online magazine, NZ Entrepreneur. 9) MDC Waste Calculator info. MDC have made a "Waste Calculator" available on their website. The calculator will work out costs associated with fees paid, time involved and distance travelled in relation to both your recycling and refuse. Once you have completed the questionnaire you will be sent the results of the calculation by email. The results are based on how you answered the questions. You might be surprised at the amount of money you are paying each year. Generally, people don’t take into account their own time or the distance travelled but these should be included if we want an accurate estimate of what you are spending. The calculator will also provide an indication of the distance you travel and the amount of emissions you produce. 10) What can NZ learn from the EU? In this article "Our Climate Declaration" member Pat Baskett looks to the EU's Green Deal for inspiration on how NZ should be addressing climate change. The Green Deal sets up an Energy Efficiency Directive to reduce overall energy use, cut emissions and tackle energy poverty. Its ambitious binding annual target for reducing energy use at EU level aims to almost double the annual energy saving obligation for member states. 11) Climate Action Tracker on NZ’s inadequate climate response. New Zealand is at a turning point, which provides an opportunity to set ambitious policies to decarbonise all sectors. The country’s newly-established Climate Change Commission has reviewed the government’s climate policies, and published recommendations on a carbon budget. New Zealand is one of the few countries to have a net zero emissions by 2050 goal enshrined in law, its Zero Carbon Act, but short-term policies cannot yet keep up with that ambition. New Zealand is increasingly relying on the mitigation potential of the land use and forestry sector to meet its target rather than focusing efforts on reducing emissions from high emitting sectors. Although included in the Act, methane from agriculture and waste (over 40% of New Zealand's emissions) is exempt from the net zero emissions goal, and has a separate target (at least 24-47% reduction below 2017 levels by 2050), not yet covered by significant policies. Overall, Climate Action Tracker rates New Zealand’s current climate targets, policies and finance as “Highly insufficient”. 12) Documents reveal scale of change needed to cut emissions - The massive scale of the nationwide changes needed quickly to cut climate gas emissions was laid bare in government documents released last November. The Ministry for the Environment succinctly pulled together advice the Climate Change Commission gave the government. It said the commission's pathway to slash emissions shows the "clear departure from business as usual", and indicates the "scale and pace of change" required from key sources of emissions. The full article is available here - NOTE - New Zealand’s first three emissions budgets were planned to be set by 31 December 2021 but this has now been extended to May this year. 13) Emissions Reduction Plan discussion document joint response from Sustainable Business Council and the Climate Leaders Coalition. You can download their full Emissions Reduction Plan discussion document response titled "Transitioning to a low-emissions and climate-resilient future". In the foreword they state - "This first Emissions Reduction Plan is our opportunity to truly put our climate ambitions into action and ensure New Zealand gets on track to be a low-emissions country by 2050. The time is now for a bold plan that sets out that pathway, and crucially, mobilises all New Zealanders – government, business, NGOs and civil society alike – to meet the challenge of our times. The document provides recommendations for key policies the Government should pursue in the Emissions Reduction Plan. Critically, it also identifies the need for genuine partnership between government and business if we are to bend the emissions curve in the short amount of time we have left." 14) Report from the future: Aotearoa New Zealand is looking good in 2040 – here’s how we did it. This article printed recently in The Conversation imagines Aotearoa NZ in 2040 and what we might have done to secure our survival and avoid catastrophe. It provides some good food for thought and begs some questions.
15) The NZ Footprint Project. Dr Ella Susanne Lawton was the primary researcher for the New Zealand Footprint Project in 2013. The project looked at how different lifestyles and urban forms consumed differently and the types of changes needed to live within each person’s fair earth share. The project team was also interested in understanding the role that policy could play in the development of urban forms that support individuals and communities to reduce their individual and collective footprint. Ella is a generalist specialist with a passion for connecting people to their natural environment. She believes that science is failing to give people an honest insight into the resource constrained future we are headed for. 16) ‘ACC – Accelerating Climate Change’ report launched by 350 Aotearoa. 350 Aotearoa recently relaunched their ACC Go Fossil Free campaign in December 2021. Here is the full report. "ACC – Accelerating Climate Change" exposes the relationship between the fossil fuel industry and our public fund that is investing against the public good. Find out more about ACC’s investments in the major players, the greenhouse gas giants, and the companies whose activities have most directly affected the people of Aotearoa, Pacific Islanders, and frontline communities across the world. 17) Para Kore. I came across this initiative working towards living in a world without waste recently and wanted to share it with you. On their website they say - Our vision is for a thriving natural environment that nurtures our communities, marae, and whānau, who in turn contribute to the collective wellbeing of Papatūānuku and Ranginui. Through indigenous knowledge and values, Para Kore encourages re-normalisation of zero-waste, closed loop living practices and philosophies across Aotearoa. Our values of manaakitanga, whakapapa, kaitiakitanga, māramatanga and rangatiratanga guide our activities and our work with others. Our mission at Para Kore is to educate and advocate from a Māori worldview for a world without waste. 18) Pest-free NZ islands suck more carbon - international study. Many pest-free islands are sucking noticeably more carbon since introduced predators were removed, according to a study that looked at 130 New Zealand islands. Researchers used remote satellite sensing and artificial intelligence to track whether removing invasive pests from islands had boosted tree cover and density on 460 islands globally, including Little Barrier, Motiti, Raoul, Great Mercury and Campbell islands. Check out the full Stuff article. 19) Fortescue Future Industries to investigate repurposing parts of New Zealand oil refinery. Fortescue Future Industries (FFI) and Refining NZ (RNZ) have agreed to investigate repurposing facilities at the RNZ Marsden Point oil refinery to produce green hydrogen and green hydrogen products. FFI and RNZ have signed a Memorandum of Understanding to study the commercial and technical feasibility of producing, storing, distributing, and exporting industrial-scale green hydrogen and green hydrogen products from the decommissioned RNZ site as it transitions to an import-only fuel terminal. “Green hydrogen production at Marsden Point will potentially deliver energy security, good local jobs, and the decarbonisation of local heavy industry – all while reducing emissions for New Zealand,” Dr Forrest said. Check out the full statement on their website. Here's an extract from another statement about developments by FFI, this time at their facility in WA.There are several dominoes that have to stack up to make green hydrogen work. One is cheap energy and the other is cheap electrolysers. Australia has abundant sunshine to provide the energy. Now, Fortescue Future Industries (FFI) is working on the next piece of the puzzle, electrolysers, making hydrogen using an electrolyser designed and built by the FFI team. They succeeded in this 10 days ago, producing industrial-grade hydrogen for the first time in their Western Australia facility. For those interested in more information about the hydrogen revolution that some see as an essential component of reducing our fossil fuel use quickly this article and this one are both worth a read. 20) New Zealand company that could revolutionise carbon capture gets $1m funding. A company spun out of the University of Canterbury has raised $1 million from private investors to progress methods that could sequester vast amounts of carbon dioxide. The process starts with a common mineral called olivine. Capturing all the Earth’s carbon emissions for 2021 would require 16 per cent of the olivine deposit located in Red Hills, near Nelson. An olivine deposit in Oman is large enough to sequester all man-made carbon emissions for the next 1000 years, according to Dr Allan Scott, an associate professor of civil engineering at the university. Olivine can be processed into magnesium hydroxide, which has long been recognised as an efficient carbon capture material. This means that carbon dioxide, an important greenhouse gas, is converted into a different substance and does not become CO2 again. The method would most suit industrial-level carbon emissions, Scott said. In this future scenario, a powdery form of magnesium hydroxide would be transported to a factory and combined with its CO2 emissions to produce a “safe carbonate substance which can be repurposed for a variety of uses from masonry construction blocks to cement additives,” he said. “Our method is capable of significantly reducing CO2 emissions that is not only environmentally friendly, but is also scalable and profitable,” said Scott. “We’ve not found any other method out there right now that comes close. Yet olivine has been overlooked in the rush to explore ways of tackling climate change, van Dongen said. "It absorbs CO2 very easily," van Dongen told Dezeen. "One tonne of olivine sand can take in up to one tonne of CO2, depending on the conditions. You just have to spread it out and nature will do its job." European climate initiative Climate-KIC estimates that olivine could capture 850,000 tonnes of CO2 if it was used in small-scale projects in Rotterdam alone. Potential uses include fertiliser and a replacement for sand and gravel in landscaping projects. Van Dongen said that the potential of natural materials such as olivine is being ignored as researchers and startups rush to develop more complex ways of reducing atmospheric carbon. "One problem is the fact that research institutes that have or receive funding for CO2 absorption can’t patent the spreading of a mineral," she said. "We are so stuck in thought patterns of industrialisation and capitalism that naturally occurring reactions can't win against the tech solutions." You can see more info in this Stuff article, this article and the Project Vesta website, which looks at the potential of "Coastal Carbon Capture". Their "process aims to accelerate the natural chemical weathering of the mineral olivine by spreading large amounts of ground olivine-containing rock onto coastlines where it can dissolve in seawater, thereby increasing the rate of CO2 absorption by the ocean (Bach et al. 2019). When olivine dissolves in water, it drives the below reaction to the right, thus increasing CO2 uptake, increasing pH, and generating alkalinity. As a result, this process has the potential co-benefit of counteracting ocean acidification." I haven't gone into the detail of the Project Vesta in depth but do wonder about what the net gain in CO2 sequestered by the process would be, after allowing for what I presume would be considerable use of fossil fuels to mine, grind and then transport the Olivine rock to suitable coastlines to be deposited. I couldn't see any analysis of this but the science of using Olivine rock to sequester CO2 is certainly interesting. 21) World total energy supply by source. I found it quite sobering looking at the graphs on the International Energy Agency (IEA) website showing the relative energy use from different sources over the last 40 years and the proportions of that energy which comes from renewable sources, fossil fuels and nuclear. If you're interested too you can check it out on their website. 22) An interesting graphic showing the steady rise in reported disasters over the last few decades. 23) Scientists watch giant ‘doomsday’ glacier in Antarctica with concern. Twenty years ago, an area of ice thought to weigh almost 500bn tonnes dramatically broke off the Antarctic continent and shattered into thousands of icebergs into the Weddell Sea. The 1,255-sq-mile (3,250-sq-km) Larsen B ice shelf was known to be melting fast but no one had predicted that it would take just one month for the 200-metre-thick behemoth to completely disintegrate. Glaciologists were shocked as much by the speed as by the scale of the collapse. “This is staggering. It’s just broken apart. It fell over like a wall and has broken as if into hundreds of thousands of bricks”, said one. This week, ice scientists meeting in New Orleans warned that something even more alarming was brewing on the West Antarctic ice sheet – a vast basin of ice on the Antarctic peninsula. Years of research by teams of British and American researchers showed that great cracks and fissures had opened up both on top of and underneath the Thwaites glacier, one of the biggest in the world, and it was feared that parts of it, too, may fracture and collapse possibly within five years or less. For more detail check out the full Guardian article. 24) Poorer countries spend five times more on debt than climate crisis. “Heidi Chow, executive director of Jubilee Debt Campaign, said lower income countries will be raising the impact of debt on their ability to tackle climate change at Cop26 meeting in Glasgow this weekend. Lower income countries are handing over billions of dollars in debt repayments to rich countries, banks and international financial institutions at a time when resources are desperately needed to fight the climate crisis,” she said. "In Glasgow, wealthy polluting nations need to stop shirking their responsibilities and provide climate finance through grants, as well as cancel debts.” Check out the full article. 25) World's most powerful tidal turbine - This short 12 minute video is about a Scottish system to harvest tidal power first trialed last year. It seems quite innovative and simple. The world's oceans hold almost unimaginable amounts of energy, but harnessing that energy in a way that can provide a predictable and reliable source of electrical power has proven to be very difficult. Now a jumbo jet sized floating platform supporting two large turbines has been launched off the coast of Scotland, providing new hope for a potentially influential industry. The producer of the video has a YouTube channel focussed on climate and sustainable energy called "Just Have a Think". He has a wide selection of videos on new battery and energy technologies that are relatively short with good graphics for anyone interested. 26) Gelion Energy. Australia-based Gelion, whose non-flow zinc-bromide battery technology was spun out of the University of Sydney, has signed a deal that could see it supply hundreds of megawatt-hours of battery systems for power projects in Papua New Guinea, starting next year. Gelion’s battery technology uses an electrolytic gel that is inherently fire retardant. In a recent test by the company’s tech team, the battery did not catch fire, and even continued to operate, while being heated on a barbeque plate at about 700 degrees for half an hour. On a practical level, this means the Endure battery systems can operate at temperatures up to 50°C without the need for air-conditioning systems. Other advantages include that the batteries can be discharged to zero volts without impacting performance, are more energy dense and last longer than traditional lead-acid batteries, and offer a safe and recyclable alternative to lithium-ion batteries for stationary storage. “Gelion’s robust and scalable zinc-bromide Endure batteries, coupled with large-scale solar energy could provide remote PNG communities with an affordable, renewable and robust solution for their energy needs,” said Mayur managing director Paul Mulder. Check out the full article. 27) News Corp’s climate pivot perpetrates a new fraud and draws us closer to climate catastrophe. Dr Bronwyn Kelly is the Founder of Australian Community Futures Planning (ACFP) . She is the author of "By 2050: Planning a better future for our children in 21st century democratic Australia". Here is an extract from a recent article she wrote. Not only does News Corp’s new climate change campaign come after years of spreading climate misinformation, it is also simply replacing its last fraud with another. For the past decade, stalwarts of Rupert Murdoch’s News Corp have claimed that climate change is a hoax and a fraud perpetrated on the Australian people. News Corp has orchestrated a campaign of climate misinformation so successful that it has resulted in some of the most harmful policy decisions imaginable for a 21st century developed country. That the misinformation was deliberate is obvious from the fact that it was stubbornly sustained as an editorial direction running contrary, year after year, to the vast majority of scientific findings. Hypocrisy and lies were even proudly admitted to by some commentators. 28) You can’t beat climate change without tackling disinformation. Over more than a century, PR firms built and fine-tuned a machine to deceive the public, writes Amy Westervelt for The Nation. In the past month or so, climate disinformation has been making its way into the news more than usual. There was the House Oversight Committee’s climate disinformation hearing in October, and then, just days later, leaked documents from Facebook revealed its role in spreading climate denial. The Oversight Committee’s investigation continues, as does the work to fully understand social media’s role in disinformation, about climate and otherwise. But for all we know about disinformation and how dangerously effective it can be, tackling the problem rarely makes its way into conversations focused on climate solutions. This raises the question: How are you going to implement new green technology or policies without eliminating the obstacle that’s helped block both for decades? We don’t necessarily have a solution to climate disinformation yet. But it’s clear it will not be dismantled by a company policy here and a congressional investigation there. A problem this large and complex requires concerted effort to solve—and we can’t even start until a critical mass of people realise that doing so is critical to the success of any climate solution. Check out the full Newsroom article. 29) Airlines flying near-empty ‘ghost flights’ to retain EU airport slots. This article highlights the ultimate in human stupidity and ignorance of the crisis we are facing. European airlines forced to fly empty planes so they can retain their landing rights at different airports! 30) WA State Government to unlock land for renewable energy and economic diversification. Exciting new large-scale carbon farming opportunities on Crown and pastoral land.
Lands Minister Tony Buti today announced proposed changes to Western Australia's Land Administration Act to introduce a new, more flexible form of land tenure for unallocated Crown land and pastoral land. The changes mean WA will be better placed to leverage opportunities in the rapidly-growing renewable energy sector which requires large areas of land for operations like carbon farming, wind farms, solar energy and hydrogen production. Check out the full media statement. 31) The role of energy demand reduction in achieving net-zero in the UK. This study was undertaken by the Centre for Research into Energy Demand Solutions (CREDS), and provides the most comprehensive assessment to date of the role of reducing energy demand to meet the UK’s net-zero climate target. This report highlights the critical importance of developed countries reducing their energy demand if we are to have any chance collectively of meeting a 2050 net zero target. In the report they state - Without energy demand reduction we will not achieve the UK’s Sixth Carbon Budget target in 2035 of 78% below 1990 levels, or our 2050 net-zero target. None of our Low Energy Demand (LED) scenarios compromise our quality of life. Instead, they seek to enhance it with numerous co-benefits associated with healthier diets, active living, clean air, safe communities, warm homes, rebalancing work and driving down inequality. All this is possible while halving the UK’s energy demand. There are clear advantages associated with energy demand reduction in achieving our path to net-zero compared to other options. Lowering energy demand has five important effects:
Check out the full report on the CREDS website. 32) Belgian parliament votes to recognise international crime of ecocide. There is ongoing steady progress towards the crime of ecocide being adopted internationally thanks largely to the efforts of the Stop Ecocide group. The Belgian parliament has adopted, by a strong majority, a resolution by the Ecolo-Groen parties aimed at recognising an international crime of ecocide. By adopting this resolution, the parliament is making three demands of the Belgian government. It asks: 1. to "initiate a new international treaty of the most proactive countries (a 'coalition of the willing') to prosecute and prevent ecocide at the international level"; 2. to "propose an amendment to the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court of The Hague to include the new crime of ecocide" (in the same way as crimes against humanity); and 3. "to report to parliament on the upcoming expert opinion on the inclusion of the crime of 'ecocide’ in the Belgian penal code ". 33) Half world’s fossil fuel assets could become worthless by 2036 in net zero transition. $11tn fossil fuel asset crash could cause 2008-style financial crisis, warns new study. About half of the world’s fossil fuel assets will be worthless by 2036 under a net zero transition, according to research. Countries that are slow to decarbonise will suffer but early movers will profit; the study finds that renewables and freed-up investment will more than make up for the losses to the global economy. It highlights the risk of producing far more oil and gas than required for future demand, which is estimated to leave $11tn-$14tn (£8.1tn-£10.3tn) in so-called stranded assets – infrastructure, property and investments where the value has fallen so steeply they must be written off. Check out the full article. 34) Why The "War" on Climate Change is Bipolar. For those who are reading this newsletter and have reached this far I want to finish with some further items relevant to the information in our last newsletter looking at "Limits to Growth" and "Overshoot". This first item is a blogpost from Erik Michaels printed just before COP26. Here is an extract. "...reductionist thinking (focusing on climate change instead of ecological overshoot, the cause of climate change) has led a broad portion of society to focus on emissions. Emissions are caused by energy use — the more building, manufacturing, and transportation that takes place, the more energy use occurs. The more consumption that occurs, the more energy use occurs. The entire economy operates courtesy of energy use, so the more jobs there are, the more energy use occurs. So, building new infrastructure and creating new jobs is an excellent way to RAISE emissions, not lower them. This is because increasing energy use also increases ecological overshoot. Some people claim that in order to reduce emissions, we must invest in new technology and raise efficiency of the technology we use. Unfortunately, this actually produces MORE emissions through the process of Jevons Paradox (aka the “rebound effect”). In reality, there is only one way to reduce emissions — and that is to reduce energy use. LESS technology, not more, is the answer. Of course, nobody wants to hear that or think about it. One thing which has become more and more clear as time has moved forward is that the messaging on climate change is bipolar (contradictory; incongruent; hypocritical) in its assessment. More and more articles talk about how we need this and how we need that in order to "fight" climate change DESPITE the facts that climate change is caused by ecological overshoot and building more products (especially building materials) only increases ecological overshoot. Some articles discuss ideas which have already been proven by science to be impossible. 35) The Enigma of Climate Inaction: On the Human Nature of Policy Failure. I highly recommend this talk by Professor Bill Rees. It is one of the best I've listened to recently. He is a bio-ecologist, ecological economist and former Director and Professor Emeritus of the University of British Columbia’s School of Community and Regional Planning. His early research focused on environmental assessment but gradually extended to the biophysical requirements for sustainability and the implications of global ecological trends. Along the way, he developed a special interest in modern cities as ‘dissipative structures’ and therefore as particularly vulnerable components of the total human ecosystem. You can learn more about him on his "Post Carbon Institute" website. His talk is a very insightful analysis of how human behaviours have resulted in the predicament we find ourselves in. He says the modern human mind has a limited capacity to cope with complexity pointing out that climate change is only one of many symptoms of ecological overshoot and that the human enterprise is using resources and generating wastes in excess of the regenerative and assimilative capacities of the ecosphere. 36) Do the Math - Using physics and estimation to assess energy, growth, options – by Tom Murphy. Tom Murphy is a professor of physics at the University of California, San Diego. Following his natural instincts to educate, Murphy is eager to get people thinking about the quantitatively convincing case that our pursuit of an ever-bigger scale of life faces gigantic challenges and carries significant risks. ….ignoring physical limits is unwise when suddenly 8 billion people are scooping out the inheritance of Earth’s finite one-time resources as fast as humanly possible. We have not seen the full consequences yet, and can no longer take the foundation for granted, as we have already used up a shocking fraction of Earth’s offerings in the blink of an eye on timescales of evolution or even of civilization. We are chewing on the power cord to our life support machine, as if it’s just another fun choice on the menu. It’s the worst choice we could make, as exciting as Amazon deliveries might be. If you want to see more check out Tom's full blogpost. 37) The real state of the economy. "Surplus Energy Economics" is another interesting blogsite with regular contributions from Dr Tim Morgan. Here is an extract from a recent blog to give you a feel for the content. It highlights a recurring theme for those of us who are concerned about overshoot and it's implications. We must face up to the inescapable fact that there are limits to what resources the planet can continue to provide us. We understand two central realities that are neither known to, nor accepted by, the orthodox approach to economics. First, we are aware of the critical distinction between the ‘real’ economy of goods and services and the ‘financial’ economy of money and credit. Second, we recognize that the real or material economy is an energy system, in which prosperity is a function of the availability, value and cost of energy. This understanding enables us to define the current economic predicament. The financial economy has grown rapidly, driven by unprecedentedly expansive credit and monetary policies. The real economy, meanwhile, has decelerated towards de-growth, because the energy equation has become progressively more unfavourable. This has opened up a gap between the ‘two economies’ of energy and money. The wider this gap becomes, the greater are the forces trending towards a restoration of equilibrium. The take-off in inflation is a logical sign of the return of equilibrium, because prices are the point of intersection between the real economy and its financial proxy. In terms of anticipating the future, the forced restoration of equilibrium between the financial and the material economies is critical. The energy economy, shaped by physical realities, cannot be made to align itself with its financial counterpart. Therefore, the return of equilibrium must involve shrinking the financial system back into proportion with the underlying economy. 38) Understanding Collapse - Exploring some of the key ideas surrounding collapse. Here is a short description of the FAN Initiative group from their website - The FAN Initiative is a set of colleagues deeply concerned about what we see as breakdowns in bio-physical and societal systems. Science can and should guide our response to this predicament. Others with their hands on the levers of governance, education, economy, and worldview shaping belief systems should at least have the scientific information readily available. We collect and contribute information to this site. This site is our contribution. The FAN helps us navigate the threat of catastrophic collapse even as deep fissures and fractures become evident. Here is an extract from a recent posting on their site titled "Understanding Collapse". To the best of our knowledge, humanity faces an unprecedented global crisis within a timescale that calls for a different approach than simply addressing it as a potentially soluble set of isolated problems. Our civilization is an extraordinary thing. Compared to other civilizations in the past (say, the Maya or the Roman Empire), ours is vastly, vastly more colossal and intricate than any of these. We should be mindful that whatever the anxieties of the moment, our human system – our civilization – is not yet broken. It is highly organized and coherent, being remarkably efficient at solving problems. We have transportation, food supply chains, raw materials and manufacturing, public security, the financial system, sanitation, health and welfare, energy generation, power grids and many other things that are intact and functioning incredibly well. The fact that we can buy food in the supermarket tomorrow or plan a meeting at the other end of the planet and reasonably expect to be there half a year from now, implies a casual acceptance of the stability of highly complex conditions. We have this tighter and tighter, more efficient machine running under the hubcap of our normal lives. It has brought us many benefits. We don’t notice it, because it works. But it is building a vulnerability within itself. As civilization evolves, it is increasing in complexity, interdependence, the speed of processes and delocalization of the systems we have come to depend upon. 39) Beware: Gaia may destroy humans before we destroy the Earth. Here is an extract from an article written by James Lovelock and printed in the Guardian late last year. James is now 102 years old and still contributing. Good on him! I don’t know if it is too late for humanity to avert a climate catastrophe, but I am sure there is no chance if we continue to treat global heating and the destruction of nature as separate problems. That is the wrongheaded approach of the United Nations, which is about to stage one big global conference for the climate in Glasgow, having just finished a different big global conference for biodiversity in Kunming. This division is as much of a mistake as the error made by universities when they teach chemistry in a different class from biology and physics. It is impossible to understand these subjects in isolation because they are interconnected. The same is true of living organisms that greatly influence the global environment. The composition of the Earth’s atmosphere and the temperature of the surface is actively maintained and regulated by the biosphere, by life, by what the ancient Greeks used to call Gaia. I am not hopeful of a positive outcome at Cop26, knowing who is participating. I was not invited to Glasgow, though that is hardly a surprise. As well as being 102 years old, I am an independent scientist, and the university academics have never been comfortable with that. But my fellow humans must learn to live in partnership with the Earth, otherwise the rest of creation will, as part of Gaia, unconsciously move the Earth to a new state in which humans may no longer be welcome. The virus, Covid-19, may well have been one negative feedback. Gaia will try harder next time with something even nastier. Nga mihi, Budyong. |
AuthorThese newsletters are put together by Budyong Hill in an attempt to help keep Marlborough people informed of issues both global and local. The aim is help raise awareness of the myriad challenges facing the essential life support systems that our amazing planet provides for us every day. Archives
May 2024
Categories |
Climate Karanga Marlborough

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed